Health care delivery system in India - community Health Nursing
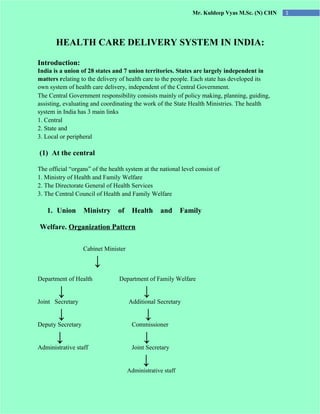
- 1. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 1 HEALTH CARE DELIVERY SYSTEM IN INDIA: Introduction: India is a union of 28 states and 7 union territories. States are largely independent in matters relating to the delivery of health care to the people. Each state has developed its own system of health care delivery, independent of the Central Government. The Central Government responsibility consists mainly of policy making, planning, guiding, assisting, evaluating and coordinating the work of the State Health Ministries. The health system in India has 3 main links 1. Central 2. State and 3. Local or peripheral (1) At the central The official “organs” of the health system at the national level consist of 1. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare 2. The Directorate General of Health Services 3. The Central Council of Health and Family Welfare 1. Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. Organization Pattern Cabinet Minister ↓ Department of Health Department of Family Welfare ↓ ↓ Joint Secretary Additional Secretary ↓ ↓ Deputy Secretary Commissioner ↓ ↓ Administrative staff Joint Secretary ↓ Administrative staff
- 2. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 2 Functions: (1) Union list 1. International health relations and administration of port quarantine 2. Administration of Central Institutes such as All India Institute of Hygiene and Public Health, Kolkata. 3. Promotion of research through research centers 4. Regulation and development of medical, pharmaceutical, dental and nursing Professions 5. Establishment and maintenance of drug standards 6. Census and collection and publication of other statistical data 7. Immigration and emigration 8. Regulation of labor in the working of mines and oil fields 9. Coordination with states and with other ministries for promotion of health (2) Concurrent list The functions listed under the concurrent list are the responsibility of both the union and state governments. 1. Prevention and extension of communicable diseases 2. Prevention of adulteration of food stuffs 3. Control of drugs and poisons 4. Vital statistics 5. Labor welfare 6. Ports other than major 7. Economic and social planning 8. Population control and Family Planning 9. Preparation of health education material for creating health awareness through Central Health Education Bureau. 10. Collection, compilation, analysis, evaluation and dissemination of information Through the Central Bureau of Health Intelligence 11. National Medical Library
- 3. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 3 2. Directorate General of Health Services Organization Pattern Directorate General of health services ↓ Director General of health services ↓ Additional Director General of health service ↓ Deputy Directorate General of health services ↓ Administrative staff Functions: 1. International health relations and quarantine of all major ports in country and International airport 2. Control of drug standards 3. Maintain medical store depots 4. Administration of post graduate training programmes 5. Administration of certain medical colleges in India 6. Conducting medical research through Indian Council of Medical Research 7. Central Government Health Schemes. 8. Implementation of national health programmes 9. Preparation of health education material for creating health awareness through Central Health Education Bureau. 10. Collection, compilation, analysis, evaluation and dissemination of information through the Central Bureau of Health Intelligence 11. National Medical Library
- 4. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 4 3. Central Council of Health Organization Pattern Chairman (Union health Minister) ↓ Members (State health Minister) Functions 1. To consider and recommend broad outlines of policy regard to matters Concerning health like environment hygiene, nutrition and health education. 2. To make proposals for legislation relating to medical and public health matters. 3. To make recommendations to the Central Government regarding distribution of Grants-in-aid II. At the State level The health subjects are divided into three groups: federal, concurrent and state. The state list is the responsibility of the state, including provision of medical care, preventive health services and pilgrimage within the state. State health administration At present there are 28 states in India, each state having its own health administration Organization Pattern (1) State Ministry of Health & family welfare ↓ Deputy Minister of Health and Family Welfare ↓ Health Secretary ↓ Deputy Secretaries ↓ Administrative staff
- 5. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 5 (2) State Director of health ↓ Director of Medical Education Director of Health Services ↓ ↓ Dean of medical college Additional Director of Health Services ↓ ↓ State nursing superintendent Deputy Director of Health Services ↓ ↓ Hospital Education Regional Functional ↓ ↓ ↓ Nsg Superintendent Nsg Officer MCH, TB, Leprosy, Immunization ↓ ↓ Ward Incharge Senior tutor ↓ ↓ Nsg Staff Junior tutor Functions of state health Director: (1) Studies in depth the health problem and needs in the state and plans scheme to Solve them (2) Providing curative &preventive services (3) Provision for control of milk and food sanitation (4) Prevention of any outbreak of communicable diseases (5) Promotion of health education (6) Promotion of health programmes such as school health, family planning, Occupational health (7) Supervision of PHC (8) Establishing training courses for health personnel (9)Co-ordination of all health services with other minister of state such as minister of education, central health minister &voluntary agency
- 6. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 6 III. At the district level T here are 593 ( year 2001 ) districts in India. Within each district, there are 6 types of administrative areas. 1. Sub –division 2. Tehsils( Taluks ) 3. Community Development Blocks 4. Municipalities and Corporations 5. Villages and 6. Panchayats Most district in India are divided into two or more subdivision, each incharge of an Assistant Collector or Sub Collector Each division is again divided into taluks, incharge of a Thasildhar. A taluk usually comprises between 200 to 600 villages The community development block comprises approximately 100 villages and about 80000 to 1,20,000 population, in charge of a Block Development Officer. Finally, there are the village panchayats, which are institutions of rural local self-government. The urban areas of the district are organized into Town Area Committees (in areas with population ranging between 5,000 to 10,000 Municipal Boards (in areas with population rangingbetween 10,000 and 2,00,000) Corporations (with population above 2,00,000) The Town Area Committees are like panchayats.They provide sanitary services. The Municipal Boards are headed by Chairmen /President, elected by members. The functions of Municipal Board: Construction and maintenance of roads Sanitation and drainage Street lighting Water supply Maintenance of hospitals and dispensaries Education and Registration of births and deaths etc The Corporations are headed by Mayors, elected by councillors, who are elected from different wards of the city. The executive agency includes the
- 7. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 7 commissioner, the secretary, the engineer and the health officer. The activities are similar to those of municipalities, on a much wider scale. Panchayat Raj - The panchayat raj is a 3-tier structure of rural local self-government in India linking the village to the district.It includes Panchayat (at the village level) Panchayat Samiti( at the block level) Zila Parishad(at the district level) (1) Panchayat (at the village level): The Panchayat Raj at the village level consists of The Gram Sabha The Gram Panchayat The Gram Sabha: It is the assembly of all the adults of the village, which meets at least twice a year.The gram sabha considers proposals for taxation,and elect members of The Gram Panchayat. The Gram Panchayat It is the executive organ of the gram sabha and an agency for planning and development at the village level. The population covered varies from 5000 to 15000 or more.The members of panchayat hold offices for a period of 3to4 years. Every panchayat has an elected president (Sarpanch or Sabhapati or Mukhia), a vice president and panchayat secretary. It covers the civic administration including sanitation and public health and work for the social and economic development of the village (2) Panchayat Samiti (at the block level): The block consists of about 100 villages and a population of about 80,000 to 1,20,000. The panchayat samiti consists of Sarpanch, MLAs, MPs residing in block area, representative of women, SC, ST and cooperative socities. The primary function of The Panchayat Samiti is the execute the community development programme in the block. The Block development Officer and his staff give technical assistance and guidance in development work. (3) Zila Parishad (at the district level):
- 8. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 8 The Zila Parishad is the agency of rural local self governmen at the district level . The members of Zila parishad include all heads of panchayat samiti in the district,MPs, MLAs, representative of SC, ST and women and 2 persons of experience in administration,public life or rural development. Its functions and powers vary from state to state. Health care system: (1) At village level (2) At sub center level (3) At PHC level (4) At CHC level (1) At village level: At the village level, elementary services are rendered by (a) Village health guides (b) Local dais (c) Anganwadi workers (d) ASHA (a) Village health guides: Village health guide is a person with an aptitude for social service and is not full time govt. functionary. Village health guides scheme was introduced on 2 nd oct. 1977. Guidelines for their selection: (1) They should be permanent resident of the local community, preferably women (2) They should be able to read and write, having minimum formal education at least up to the VI std. (3) They should be acceptable to all sections of community (4) They should be able spare at least 2 to 3 hours every day for community health work. After selection the health guide undergo a short training in primary health care. The training is arranged in the nearest PHC, subcenter or other suitable place for the duration of 200 hours, spread over a period of 3 months. During the training period they receive a stipend of Rs. 200 per month. Functions of Village health guides: (1) Provide treatment for common minor ailments (2) First aid during accidents and emergency (3) MCH care (4) Family planning (5) Health education
- 9. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 9 (2) Local dais: Most deliveries in rural areas are handled by untrained dais. Th e training for dais given for 30 working days. Each dai is paid stipend of Rs. 300 during the training period.The training is given at PHC,subcenters or MCH center for 2 days in a week and on the remaining four days of the week they accompany the health worker(female) to the village. During her training each dai is required to conduct at least 2 deliveries under the supervision and guidance of health worker (female), ANM,health assistant (female). Functions of dais: (1) MCH care (2) Family planning (3) Immunization (4) Education about health (5) Referral services (6) Safe water and basic sanitation (7) Nutrition (3) Anganwadi worker: Under the ICDS scheme there is an anganwadi worker for a population of 1000.There are about 100 such workers in each ICDS project. The anganwadi worker is selected from the community and she undergoes training in various aspect of health, nutrition and child development for 4 months. She is a part time worker and paid an honorarium of Rs.200-250 per month for the services. Functions of anganwadi worker: (1) MCH care (2) Family planning (3) Immunization (4) Education about health (5) Referral services (6) Safe water and basic sanitation (7) Supplementary nutrition (8) Nonformal education of children Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) One of the key components of the National Rural Health Mission is to provide every village in the country with a trained female community health activist – ‘ASHA’ or Accredited Social Health Activist. Selected from the village itself and accountable to it, the ASHA will be trained to
- 10. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 10 work as an interface between the community and the public health system. Following are the key components of ASHA: SELECTION OF ASHA The general norm will be ‘One ASHA per 1000 population’. In tribal, hilly, desert areas the norm could be relaxed to one ASHA per habitation, dependant on workload etc. The States will also need to work out the district and block-wise coverage/phasing for selection of ASHAs. It is envisaged that the selection and training process of ASHA will be given due attention by the concerned State to ensure that at least 40 percent of the ASHAs in the State are selected and given induction training in the first year as per the norms given in the guidelines. Rest of the ASHAs can subsequently be selected and trained during second and third year. Criteria for Selection ASHA must be primarily a woman resident of the village ‘Married/Widow/Divorced’ and preferably in the age group of 25 to 45 yrs. ASHA should have effective communication skills, leadership qualities and be able to reach out to the community. She should be a literate woman with formal education up to Eighth Class. This may be relaxed only if no suitable person with this qualification is available. Adequate representation from disadvantaged population groups should be ensured to serve such groups better. Roles and responsibilities of ASHA: ASHA will take steps to create awareness and provide information to the community on determinants of health such as nutrition, basic sanitation & hygienic practices, healthy living and working conditions, information on existing health services and the need for timely utilization of health & family welfare services. She will counsel women on birth preparedness, importance of safe delivery, breast- feeding and complementary feeding, immunization, contraception and prevention of common infections including Reproductive Tract Infection/Sexually Transmitted Infection (RTIs/STIs) and care of the young child. ASHA will mobilize the community and facilitate them in accessing health and health related services available at the village/sub-center/primary health centers, such as Immunization, Ante Natal Check-up (ANC), Post Natal Check-up (PNC), ICDS, sanitation and other services being provided by the government.
- 11. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 11 She will work with the Village Health & Sanitation Committee of the Gram Panchayat to develop a comprehensive village health plan. She will arrange escort/accompany pregnant women & children requiring treatment/ admission to the nearest pre-identified health facility i.e. Primary Health Centre/ Community Health Centre/ First Referral Unit (PHC/CHC /FRU). ASHA will provide primary medical care for minor ailments such as diarrhea, fevers, and first aid for minor injuries. She will be a provider of Directly Observed Treatment Short-course (DOTS) under Revised National Tuberculosis Control Programmed. She will also act as a depot holder for essential provisions being made available to every habitation like Oral Rehydration Therapy (ORS), Iron Folic Acid Tablet (IFA), chloroquine, Disposable Delivery Kits (DDK), Oral Pills & Condoms, etc. A Drug Kit will be provided to each ASHA. Contents of the kit will be based on the recommendations of the expert/technical advisory group set up by the Government of India. Her role as a provider can be enhanced subsequently. States can explore the possibility of graded training to her for providing newborn care and management of a range of common ailments particularly childhood illnesses. She will inform about the births and deaths in her village and any unusual health problems/disease outbreaks in the community to the Sub-Centers/Primary Health Centre. She will promote construction of household toilets under Total Sanitation Campaign. Fulfillment of all these roles by ASHA is envisaged through continuous training and up-gradation of her skills, spread over two years or more Comparison of health care delivery system in Rajasthan and Maharashtra: (1) Subcenter: Topics Maharashtra Rajasthan (1) Population covered 5000 in general 3600 in general 3000 in tribal & hilly areas 2800 in tribal & hilly areas (2) Functions (1) MCH care (1) MCH care (2) Family planning (2) Family planning (3) Immunization (3) Immunization (4) Education about health (4) Education about health (5) Referral services (5) Safe water and basic sanitation (6) Prevention and control of locally endemic diseases
- 12. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 12 Designation Maharashtra Rajasthan (3) Staffing pattern Health worker female 1 Health worker female 1 Health worker male 1 Health worker male 1 Voluntary worker 1 ANM 1 (paid Rs 100 per month as Honorarium (2) Primary health center: Designation Maharashtra Rajasthan (1) Population covered 30,000 rural population in plains 48000 population in plains 20,000 population in hilly, tribal 30000 population in tribal and hilly (2) Functions (1) MCH care (1) MCH care (2) Family planning (2) Family planning (3) Immunization (3) Immunization (4) Education about health (4) Education about health (5) Referral services (5) Referral services (6) Safe water and basic (6) Safe water and basic sanitation sanitation (7) Prevention and control of (7) Prevention and control of locally endemic diseases locally endemic diseases (8) Collection and reporting of vital (8) Collection and report in statistics Of vital statistics (9) National health programmes (9) National health (10) Training of health guides, health programmes workers, local dais and health (10) Training of health guides, assistant health workers, local (11) Basic laboratory services dais and health assistant (11) Basic laboratory services (3) Staffing pattern 2 Medical officer 1 Medical officer Pharmacist 1 Pharmacist 1 Nurse midwife 1 Nurse midwife 1 Health worker female 1 Health worker female 1 Health worker male 1Block extension educator 1 Block extension educator 1 Health assistant (female) 1 Health assistant (female) 1 Health assistant male 1 Health assistant male 1 U.D.C 1 U.D.C 1
- 13. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 13 L.D.C 1 L.D.C 1 Driver 1 Driver 1 ClassIV 4 ClassIV 2 (3) Community health center: Designation Maharashtra Rajasthan (1) Population covered 80,000 to 1.20 lakhs 74,000 to 1.5 lakhs (2) Bed capacity 30 Beds 24 Beds (3) Specialty Surgery, medicine, obstetrics and Surgery, medicine, gynecologist and pediatrics with X-ray and obstetrics and lab facilities. gynecologist and pediatrics with X-ray and (3) Functions lab facilities. Care of routine and emergency (1) MCH care (2) Family planningcases in surgery (3) ImmunizationCare of routine and emergency (4) Education aboutcases in medicine health24 hours delivery services (5) Referral servicesincluding normal and assisted (6) Safe water and basicdeliveries sanitation Essential and emergency obstetric (7) Prevention and care including caesarean sections control of locally and other Medical interventions. endemic diseases Full range of family planning (8) Collection and services including laparoscopic report in of vital services statistics Safe abortion service (9) 24 hours delivery Newborn care services including Routine and emergency care of normal and assisted children deliveries Other management including
- 14. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 14 Nasal packing,tracheostomy,foreign body removal (10) All national health programmes delivered through CHC Other services (a) Blood storage facility (b) Essential lab. Services (c ) Referral (transport) services Existing clinical manpower (4) Staffing pattern General surgeon 1 Physician 1 Obstetrics/ gynecologist 1 Pediatrician 1 Proposed clinical man power Anesthetics 1 Eye surgeon 1 Public health programme 1 manager Existing support manpower Nurse midwife 9 Dresser 1 Pharmacist 1 Lab. Technician 1 Radiographer 1 Ophthalmic 1 Ward boy 2 Sweeper 3 Chowkidar 1 OPD attendant 1 Statistical assistant 1 OT attendant 1 Registration clerk 1 (10) Essential and emergency obstetric care including caesarean sections and other Medical interventions. (11) Full range of family planning services including laparoscopic services (12) Safe abortion service (13) Newborn care (14) Routine and emergency care of children’s. (15) ) All national health programmes delivered through CHC Existing clinical manpower General surgeon 1 Physician 1 Obstetrics/ gynecologist 1 Pediatrician 1 Proposed clinical man power Anesthetic 1 Public health programme 1 manager Existing support manpower Nurse midwife 12 Dresser 1 Pharmacist 2 Lab. Technician 1 Radiographer 1 Ophthalmic 1 Ward boy 2 Sweeper 3 Chowkidar 2 OPD attendant 1 Statistical assistant 1 OT attendant 1 Registration clerk 2
- 15. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 15 Job description of the members of the health team: (1) Medical officer: He is the captain of the health team at the primary health center. He devotes the morning hours attending to patients in the out-door,in the afternoon and supervises the field work. He visits each subcenter regularly on fixed days and hours and provides guidance, supervision and leadership to the health team. He spends one day in each month organizing staff meetings at PHC to discuss the problems and review the progress of health activities. He ensures that national health programmes are being implemented in in his area properly The success of PHC depends largely on the team leadership which the medical officer is able to provide. The medical officer must be a planner, the promoter, the director, the supervisior, the coordinator as well as the evaluator. (2) Health worker male and female: Under the multipurpose worker scheme, one health worker female and one male are posted to each sub-centers and are expected to cover 5000 of population (3000 in tribal and hilly areas) health worker female limits her activities among 350-500 families. Health worker female: She will register pregnant women from three months of pregnancies onwards. Maintain maternity record, register of antenatal cases, eligible couple register, children register up to date. She will provide care to pregnant women especially registered mother throughout the period of pregnancy; Give advice on nutrition to expectant and nursing mothers about storage, preparation and distribution of food. Immunize pregnant mothers with tetanus toxoid. Conduct about 50% of total deliveries at home. Supervise deliveries conducted by Dais and whenever call in. Spread the message of family planning to the couples; motivate them for family planning individually and in groups. Distribute conventional contraceptives to the couples. Assess the growth and development of the infant and take necessary action. Records and reports births and deaths in her area.
- 16. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 16 Test urine for albumin and sugar and do Hb during her home visit. Arrange and help M.O and health assistant in conducting MCH and family planning clinics at subcenters. Maintain the cleanliness of subcenter. Attend staff meetings at PHC, CD block or both. Health worker male: He will survey all the families in his area and collect all the information about each village/ locality in his area. Identify the cases of communicable diseases and notify the health assistant male and M.O PHC immediately. Educate the community about importance of control and preventive measures against communicable diseases. Assist the village health guide in undertaking the activities under TB programme properly. Educate community on the method of liquid and solid waste, home sanitation, advantage and use of sanitary latrines. Assist the health assistant male in the school health programme. Utilize the information from the eligible couple and child register for the family planning programme. Spread the message of family planning to the couples; motivate them for family planning individually and in groups. Distribute conventional contraceptives to the couples. Provide follow-up services to male family planning acceptors. Health assistant male and female: Health assistant male and female will supervise 4 health workers each of the corresponding category. Health assistant female: Supervise and guide the health workers in the delivery of health care services to the community. Carry out supervisory home visiting. Guide the health workers (female) in Distribution of conventional contraceptives to the couples. Visit each of the 4 subcenters at least once in a week on fixed days.
- 17. Mr. Kuldeep Vyas M.Sc. (N) CHN 17 Respond to urgent calls from the health workers and trained dais and render necessary help. Organize and utilize the mahila mandal, teachers etc., in the family welfare programme. Provide information on the availability of services for MTPs and refer suitable cases to the approved institution. Supervise the immunization of all pregnant women and children (0-5 years) Collect and compile the the weekly reports of births and deaths occurring in his area. Educate the community regarding the need of registration of vital events. . Health assistant male: Supervise the work of Health worker male during concurrent visit. Check minimum 10% of houses in village. Supervise the spraying of insecticides during local spraying along with the health worker (male). Conduct immunization of all school going children with the help of health worker (male). Supervise the immunization of all children’s (0-5 years). Assist M.O.PHC in organization of family planning camps and drives. . Provide information on the availability of services for MTPs and refer suitable cases to the approved institution. Ensures follow-up of all cases of vasectomy, tubectomy IUD and other family planning acceptors. Ensure that all the cases of malnutrition infants and young childrens (0-5years) are given the necessary treatment and advice and refer serious cases to PHC. Ensure that Iron and folic acid and Vitamin A are distributed to the beneficiaries. Conduct MCH and family planning clinics and carry out educational activities. Organize and conduct training for dais women leaders with the help of health workers Collect and compile the the weekly reports of births and deaths occurring in his area. Educate the community regarding the need of registration of vital events. REFERENCES (1) k. Park, Text book of preventive and social medicine, Bhanot publication, 18 th edition, Page no.674-699. (2) B.T.Basvanthappa, Community health nursing, Jaypee, Publication, 6 th edition, Page no.584-605. (3) K.K. Gulani, Community health nursing, Kumar Publication, 3 rd edition, Page no.591-593. (4) Dr. Sr. Mary Lucita, Public health and Community Health, Nursing, B.I. publication, 1 st edition, Page no.25-34. (5) John M. Cookfair, Nursing care in the community, Mosby, Publication, 2 nd edition, Page no. 65-81. (6) www.google. com.
