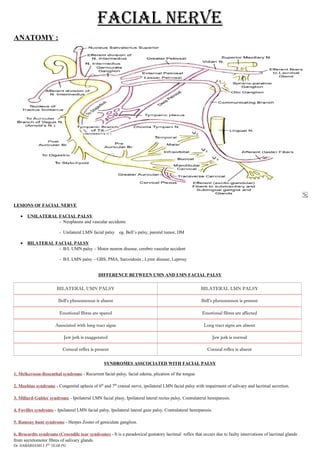
Facial nerve
- 1. FACIAL NERVE ANATOMY : LESIONS OF FACIAL NERVE • UNILATERAL FACIAL PALSY - Neoplasms and vascular accidents - Unilateral LMN facial palsy eg. Bell’s palsy, parotid tumor, DM • BILATERAL FACIAL PALSY - B/L UMN palsy – Motor neuron disease, cerebro vascular accident - B/L LMN palsy – GBS, PMA, Sarcoidosis , Lyme disease, Leprosy DIFFERENCE BETWEEN UMN AND LMN FACIAL PALSY BILATERAL UMN PALSY BILATERAL LMN PALSY Bell’s phenomenon is absent Bell’s phenomenon is present Emotional fibres are spared Emotional fibres are affected Associated with long tract signs Long tract signs are absent Jaw jerk is exaggerated Jaw jerk is normal Corneal reflex is present Corneal reflex is absent SYNDROMES ASSCOCIATED WITH FACIAL PALSY 1. Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome - Recurrent facial palsy, facial edema, plication of the tongue 2. Moebius syndrome - Congenital aplasia of 6th and 7th cranial nerve, ipsilateral LMN facial palsy with impairment of salivary and lacrimal secretion. 3. Millard-Gubler syndrome - Ipsilateral LMN facial plasy, Ipsilateral lateral rectus palsy, Contralateral hemiparesis. 4. Fovilles syndrome - Ipsilateral LMN facial palsy, Ipsilateral lateral gaze palsy, Contralateral hemiparesis 5. Ramsay hunt syndrome - Herpes Zoster of geniculate ganglion. 6. Brocardts syndrome (Crocodile tear syndrome) - It is a paradoxical gustatory lacrimal reflex that occurs due to faulty innervations of lacrimal glands from secretomotor fibres of salivary glands. Dr. SABAREESH J 3RD YEAR PG
