Learning theorymatrix[1]
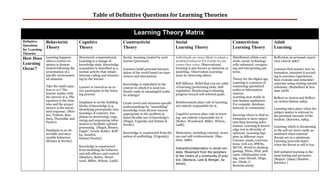
- 1. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Learning Theory Matrix Definitive Behaviorist Cognitive Constructivist Social Connectivism Adult Questions for Learning Theory Theory Theory Learning Theory Learning Theory Learning Theories How Does Learning happens Structured, computational. Social, meaning created by each Individuals are more likely to adopt a Distributed within a net- Reflection on personal experi- when a correct re- Learning is a change of learner (personal). modeled behavior if it results in out- work, social, technologi- ence (Jarvis 1987) Learning sponse is demon- knowledge state. Knowledge comes they value. Observational cally enhanced, recogniz- Occur? strated following the acquisition is described as a Learners build personal interpre- learning is also known as imitation or ing and interpreting pat- Learners first acquire new in- presentation of a mental activity that entails tation of the world based on expe- modeling. Observation Learning: terns. formation, interpret it accord- specific environmen- internal coding and structur- riences and interactions learn by observing others. ing to previous experiences, tal stimulus. ing by the learner. Theory for the digital age. then evaluate and remember Self-Efficacy: Belief that you are cable Learning is a process of concepts using existing mental Knowledge is embedded in the Take the math equa- Learner is viewed as an ac- of learning/performing tasks. Self- connecting specialized schemata. (Rumelhart & Nor- context in which it is used (au- tion 2+2=? The tive participant in the learn- regulation: Monitoring/evaluating nodes or information man 1978) thentic tasks in meaningful realis- learner replies with ing process. progress toward self-selected goals. sources. tic settings) the answer of 4. The Learning may reside in Reflect-in-Action and Reflect- equation is the stim- non-human appliances. on-Action (Schon 1983). Emphasis is on the building Create novel and situation-specific Reinforcement plays role in learning, ulus and the proper For example, database, blocks of knowledge (e.g. understandings by "assembling" not entirely responsible for it. answer is the associ- network or community. Learning takes place when the identifying prerequisite rela- knowledge from diverse sources ated response. (Skin- subject matter is relevant to tionships of content). Em- appropriate to the problem at Cognitive process plays role in learn- ner, Tolman, Ban- Knowing where to find in- the personal interests of the phasis on structuring, orga- hand (flexible use of knowledge). ing, not entirely responsible for it. dura, Thorndike and formation is more impor- student. (Knowles, 1984). nizing and sequencing infor- (Piaget, Vygotsky and Ertmer & (Rotter, Woodward, Miller, Wilson, Pavlov). tant than knowing infor- mation to facilitate optimal Newby) Ladd). mation. Learning & knowl- Learning which is threatening processing. (Piaget, Bruner, Emphasis is on ob- edge rest in diversity of to the self are more easily as- Gagne’, Lewin, Kohler, Koff- servable and mea- Knowledge is constructed from the Motivation, including external, vicari- opinions. Learning hap- similated when external ka, Ausubel, surable behaviors notion of scaffolding. (Vygotsky) ous and self-reinforcement. (Ban- pens in different ways. threats are at a minimum. Ertmer/Newby). (Ertmer & Newby). dura, 1986). Courses, email, conversa- Learning proceeds faster tions, web 2.0, MWDs, when the threat to self is low. Knowledge is constructed MUVE, World to desktop, Interaction/observation in social con- from modeling the behavior gaming, PDAs, iPod, pod- and self-efficacy and control. texts. Movement from the periphery Self-initiated learning is the to the Centre of a community of prac- casts, collaborative writ- most lasting and pervasive. (Bandura, Rotter, Wood- ing, voice thread, blogs, tice. (Bandura, Lave & Wenger, Sa- (Rogers, (1994) (Maslow, ward, Miller, Wilson, Ladd). etc. (Dede, C. lomon). Knowles ) Siemens,2005)
- 2. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Definitive Behaviorist Cognitive Constructivist Social Connectivism Adult Questions Theory Theory Theory Learning Theory Learning Theory Learning for Learning Theories What fac- Nature of reward, Existing schema previous Engagement, participation, so- Albert Bandura argued that ag- Diversity of network, Motivation affects the tors influ- punishment, and experiences. (Piaget, cial cultural. (Piaget & Vygot- gression in children is influenced strength of ties, context of learning strategies and oth- ence stimuli. Bruner, Gagne’ and sky) by the reinforcement of family occurrence. Balance er cognitive processes an Ausubel). Learner and environmental fac- members, the media, and the en- among experiential learn- individual brings to bear on learning? ing, guided mentoring and Environmental tors are the specific interaction vironment"(Bandura, 1976). a task (Dweck & Elliott, collective reflection. Ex- conditions receive Emphasis is placed on the between them. (Ertmer & New- 1983; Eccles & Wigfield, pression through nonlin- the greatest role of practice with cor- by). Environmental influence. Engage- ear association webs of 1985) emphasis. rective feedback. (Ertmer ment, participation and social cul- representations. Co-design & Newby) Constructivists argue that be- tural. Response consequences of learning experiences Assimilation and accom- havior is situational deter- (such as rewards or punishments) personalized to individual modation (Piaget 1966) Nature of reward, mined (Jonnassen 1991a). (Bandura 1976). needs and preferences. (Siemens , Cultural, political, physical punishment, stim- Downes, 2005) Learning new vocabulary words and social dynamics (Tara uli. (Thorndike, Existing schema previous is enhanced by exposure and Fenwick and Mark Tennant Pavlov, Watson, subsequent interaction with Behavior is stiuationally Guthrie, Hull, Tol- experiences. (Koffka, 1999). those words in context (as op- determined (Jonassen, man, Skinner, Kohler, Lewin, Piaget, posed to learning their mean- 1991a). Ladd) Social interaction and the Ausubel, Bruner, Gagne) ings from a dictionary). (Ert- environment (Vygotsky mer & Newby). Actions is viewed as “an interpretation of the cur- 1978) rent situation based on an Situations actually co-produce entire history of previous Level of Intellectual Devel- knowledge (along with cogni- interactions” (Clancey, tion) through activity (Brown, opment. Educational Objec- 1986) Collins, and Duguid 1989). tives. Situations actually coo-pro- Every action is viewed as “an duce knowledge (along with interpretation of the current cognition) through activity. situation based on an entire Brown, Collins, and Duguid history of previous interac- 1989). tions.” (Clancey, 1986).
- 3. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Definitive Cognitive Constructivist Connectivism Questions Theory Theory Social Learning for Behaviorist Learning Theory Adult Theory Learning Theory Learning Theories What is Memory is Encoding, storage, trans- Prior knowledge remixed to Gain attention to overcome com- Adaptive patterns, rep- Rehearsal –involves active the role of hardwiring of repeated form, rehearse and re- trieval. current context. peting stimuli. resentative of current state, existing in net- processing—Chunking (Newell, A, 1990). memory? experiences – The goal of instruction is not to Promote retention by using im- works. where reward and Learning results when in- ensure that individuals know agery and metaphors. (Siemens & Downes Experience is a factor in punishment are formation is stored in particular facts but rather those 2005) one’s ability to create, re- most influential. memory in an organized, they elaborate on and interpret Use exercises that reproduces be- tain and transfer knowl- meaningful manner. information. havior for try out and practice “Understanding is de- edge (Reagans 2003). Forgetting is veloped through contin- attributed to the Designers use techniques The emphasis is not on retriev- Provide reinforcement for motiva- ued, situated use and Holds changing concept of “nonuse” of a such as advance organiz- ing intact knowledge struc- tion (Bandura, 1986). does not crystallize into self. (Moslow & Rogers) response over ers, analogies, hierarchi- tures, but on providing learners categorical definition” time. cal relationships, and ma- with the means to create novel (Brown et al, 1989, trices to help learners re- and situation-specific under- pf33). The use of periodic late new information to standings by “assembling” prior practice or review prior knowledge. knowledge from diverse The emphasis is not on serves to maintain sources appropriate to the retrieving intact knowl- a learner’s Forgetting is the inability to problem at hand. For example, edge structures, but on readiness to retrieve information from the knowledge of “design” ac- providing learners with response (Schunk, memory because of interfer- tivities has to be used by a prac- the means to create nov- 1991) ence, memory loss, or miss- titioner in too many different el and situation-specific ing or inadequate cues need- ways for them all to be antici- understandings by “as- Gaining attention ed to access information pated in advance. sembling” prior knowl- (reception), (Ertmer & Newby). edge from diverse Informing learners sources appropriate to of the objective the problem at hand. (expectancy). (Spiro, Feltovick, Jacob- son, and Coulson, 1991).
- 4. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Connectivism Adult Definitive Cognitive Constructivist Social Learning Learning Questions Theory Learning Theory Theory Theory for Learn- ing Theo- Behaviorist ries Theory How does Stimuli and Re- Transfer of learning oc- Facilitation, openness (Moslow and Connecting to adding Critical reflection transfer oc- sponses curs due to previous en- Socialization (Piaget, Vygotsky). Rogers) nodes, growing the net- Reflection/think time. cur? (Thorndike, countered situations. Build personal interpretations of work. Social/conceptual (Garvin 1993). Pavlov, Watson, (Thorndike 1928). the world based on individual ex- Behavior reproduction supported and biological. Guthrie, Hull, Tol- periences and interactions (con- by self-efficacy and regulation. (Siemens, Downes) Development – the ability man, Skinner). Ac- Communicate or transfer stantly open to change cannot (Bandura, 1986). to think critically. (Merriam cording to Tolman, knowledge in the most ef- achieve a predetermined, "correct" meaning, knowledge emerges in and Caffarella 1999) a new stimulus ficient, effective manner relevant contexts). (the sign) becomes (mind-independent, can associated with al- be mapped onto learners) Learning is an active process of ready meaningful constructing rather than acquiring stimuli (the signifi- Focus of instruction is to knowledge. cate) through a se- create learning or change ries of pairings. by encouraging the learn- Instruction is a process of support- er to use appropriate ing knowledge construction rather Result of learning strategies than communicating knowledge. generalization. Situations Learning results when infor- Do not structure learning for the mation is stored in memory task, but engage learner in the ac- involving identical in an organized, meaningful tual use of the tools in real world or similar features way. Teachers/designers are situations. (Lave & Wenger, Pi- allow behaviors to responsible for assisting aget, Bransford, & Hasselbring, transfer. (Ertmer learners in organizing infor- Grabinger and Spiro). & Newby) mation in an optimal way so that it can be readily assimi- lated. (Koffka, Kohler, Lewin, Piaget, Ausubel, Bruner, Gagne)
- 5. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories What types Reasoning, clear objec- Social, vague (“ill-defined”). Classroom: k-12 and Adults Complex learning, rapid Self-directed and indepen- of learning tives, problem solving Workplace: Adults changing core, diverse dent. (Moslow and Rogers). are best ex- Task-based (Schunk, 1991) Jonnassen, 1991a, described Social: Child and Adult (Wilson, knowledge sources learning. (Skinner, three stages of knowledge ac- 1980). (Heylighen, (2008), Andragogy and critical re- plained by quisition: introductory, ad- Siemens and Downes flection. (Knowles, M. this theory? Bandura, Simplification and stan- vanced, and expert. He argues 2005). Thorndike, dardization (Bednar et 1968). Pavlov). that constructive learning envi- Multiple Intelligences (Gardner al., 1991). ronments are most effective for 1983) the stage of advanced knowl- Explain why specific things Stimulus-response Multiple Intelligences are being taught (e.tg., cer- Intelligence is a func- edge acquisition, where initial association (Winn (Gardner 1983) tain commands, functions, 1990), which tion of the number of misconceptions and biases ac- quired during the introductory operations, etc.) include connections learned. instructional cues, (Thorndike, 1927). stage can be discovered, negoti- ated, and if necessary, modified Instruction should be task- practice and oriented instead of memo- reinforcement and/or removed. rization Multiple Intelligences Jonnassee agrees that introduc- Learning that (Gardner 1983) tory knowledge acquisition is Instruction should take involves into account the wide range better supported by more ob- discriminations of different backgrounds of jectivistic approaches (behavior (recalling facts), learners. Since adults are and/or cognitive). generalizations self-directed, instruction (defining and should allow learners to illustrating discover things for them- concepts, and selves providing guidance associations Multiple Intelligences (Gard- ner 1983) and help when mistakes are (applying made. (Knowles, 1984). explanations), and chaining Multiple Intelligences (automatically performing a (Gardner 1983) specified procedure). (Schunk 1991).
- 6. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Multiple Intelligences Schema (Bartlett, Mathematical Learning theory Criterion referenced In- How is ( Gardner 1983) 1932), arrived at the (R. C. Atkinson 1972), Intranet –internal online struction (R. Mager, technology concept from studies of Maximize mean performance of information. 1975). Goal/task analysis used for the whole class, Minimize the memory he conducted LMS – Learning Man- —to identify what needs learning in variance in performance for the in which subjects re- whole class, Maximize the agement System, web to be learned, (2) perfor- your indus- called details of stories conferencing. mance objectives—exact number of students who score try? that were not actually specification of the out- at grade level, or maximize the The Cloud-based Ap- there. Suggested that mean performance for each comes to be accom- Information memory takes the form individual. plication for non-tra- plished and how they are Processing Theories (g. Miller, of schema which pro- ditional learning. to be evaluated, (3) crite- 1956).chunking – vide a mental frame- rion references testing— the idea that short- work for understanding Geo-everything, Per- evaluation of learning in term memory and remembering infor- sonal Web, Semantic- terms of the could only hold mation. knowledge/skills speci- 5-9 chunks of Aware Application – fied in the objectives, (4) information (seven Bransford & Franks to solve difficult prob- development of learning plus or minus two) (1971) involved in modules tied to specific where a chunk is lems—bottom-up and showing people pictures objectives. any meaningful and asking questions to-down approaches. unit. I.e., digits, them about what the (The Horizon Self-paced course involv- words, chess positions, or story depicted; people Report-2009) ing a variety of different people’s faces. would remember differ- media (e.g., workbooks, ent details depending videotapes, small group TOTE (Test- upon the nature of the discussion, and comput- Operate-test-Exit) picture. er-based instruction). (miller, Galanter & Pribram (1960)),
- 7. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Novice versus expert Mastery learning and performance (e.g., Chi performance-oriented in- et al., 1988) suggests struction. that the nature of ex- pertise is largely due to Feedback/Reinforcement the possession of (Markle, S. R. (1964)). schema that guides per- ception and problem- solving. TOTE replaces the stimulus-0respons e as the basic unit of behavior. The goal is tested to see if it has been achieved and if not an operation is performed to achieve the goal; this cycle of test- operate is repeated until the goal is eventually achieved or abandoned. The basis of many subsequent theories of problem solving (e.g., GPS) and Production System.
- 8. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories References: Atkinson, R. C. (1972). Ingredients for a Theory of Instruction. American Psychologist, 27, 921-931,. Ausubel, D. (1963). The Psychology of Meaningful Verbal Learning. New York:: Grune and Stratton. Bandura, A. (1977). Social Learning Theory. New Your: General Learning Press. Bandura, A. (1986). Social Foundations of Throught and Action: A Social Cognitive Theory. Englewood Cliffs: Printice Hall, p. 23 (#1). Bednar, A. K. (1991). Theory into Practice: How do we Link? In G. J. Anglin (ed.), Instructional Technology: Past, Present, and Future. Englewood, CO:: Libraries Unlimited. . Bransford, J. D. (1971). The Abstraction of Linguistic Ideas. Cognitive Psychology, 2, 331-350. Brown, J. S. (1989). Situated Cognition and the Culture of Learning. . Educational Researcher, 18(1), pp. 32-42. Bruner, J. S. (1960). The Process of Education. Cambridge Mass.: Harvard University Press. Chi, M. G. (1988). The Nature of Expertise. Hillsdale, NJ:: Erlbaum. Clancey, W. J. (1986). Review of Winograd and Flores' Understanding Computers and Cognition: A Favorable Interpretation. (STAN- CS-87-1173. Palo Alto, CA: Department of Computer Science, Standford University. Dede, C. (2005). Planning for Neomillennial Learning Styles: Implications for Investments in Technology and Faculty. In D. G. Oblinger & J. L. Oblinger (Eds.), . Educating the Net Generation, Retrieved from http://www.educause.edu/content.asp? page_id=6069&bhcp=1. Downes, S. (2005). An Introduction to Connective Knowledge. In T. Hug (Ed) (2007). Media, Knowledge and Education. Exploring New Spaces, Relations and Dynmics in Digital Media Ecologies. Dweck, C. S. (1983, (4th ed.)). Achievement Motivation, In E. M. Hetherington (Ed.) Handbook of Child Psychology: Vol. 4. Socialization, Personality, and Social Development. New York: Wiley. Eccles, J. S. (1985). Teacher Expectations and Student Motivation. In J. B. Dusek (Ed.), teacher Expectancies. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Ertmer, P. A. (n.d.). Behaviorism, Cognitivism, Constructivism: Comparing Critical Features from an Instructional Design Perspective. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 6(4), pp. 50-72.
- 9. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Gagne, R. M. (1985, (4th ed)). The Conditions of Learning . New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. Garvin, D. A. (1993). Building a Learning Organization. Harvard Business Review, 71 (4), 78-91. Guthrie, E. R. (1946). Psycholotgical Facts and Psychological Theory. Psychological Bullentin, 43, 1-20. Heylighen, F. (2008). Complexity and Self-organization. . encyclopedia of Library and Information Sciences. , Retrieved from http://pespmcl.vub.ac.be/Papers/ELIS-complexit.pdf. Hull, C. (1943). Principles of Behaviors. New York:: Appleton-Century-Crofts. Hull, C. L. (1927). Cognitive Behavior: An Introduction to Behavior Theory. New York: Appleton-Century, Crofts. Hull, C. L. (1934). The Concept of the Habit-Family Hierarchy and Maze Learning. Psychological Bullentin, 41, 33-54. Jarvis, P. (1987). The Social Contect of Adult Learning. London: Croom Helm. Jonassen, D. H. (1991a). Evaluating Constructivistic Learning. Educational Technology, 31(9), pp. 28-33. Knowles, M. (1968). Andragogy, not Pedagogy. Adult Leadership., 16(10), 350-352, 386. Knowles, M. (1984). Andragogy in Action. San Francisco:: Jossey-Bass. Ladd, G. T. (1911 (origianlly published 1902)). Philosophy of Conduct. New York:: C. Scribner's Sons. Lave, J. &. (1991). Situated Learning: Legitimate peripheral Participation. . New York: Cambridge University Press. Lawrence, R. (1996). Co-learning Communities: A hermeneutic Account of Adult Learning in Higher Education Through the Lived World of Co-horts". Northern Illinois University: Unpublished doctoral dissertation. Lewin, K. (1935). A Dynamic Theroy of Personality. New York: McGraw-Hill. Mager, R. (1975, (2nd. ed)). Preparing Instructional Objectives . Belmont, CA:: Lake Publishing Co. . Mandler, J. (1984). Stories, Scripts and Scenes: Aspects of Schema Theory. Hillsdale, NJ:: Erlbaum. Markle, S. R. (1962). Good Frames and Bad. New York:: Wiley. Merriam, S. B. (1999). Learning in Adulthood: A Comprehensive Guide. (2nd. ed.). San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. Miller, G. A. (1956). The Magical Number Seven, plus or minus two: Some Limits on our Capacity for Processing Information. . Psychological Review, 63, 81-97. [Available at http://www.musanim. com/miller1956]. Miller, G. A. (1960). Plans and the Structure of Behavior. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston. Moslaw, A. H. (1959). New Knowledge in Human Values. . New York:: Harper and Row. Newell, A. (1990). Unified Theories of Cognition. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Ormond, J. E. (1999, (3rd. ed.)). Human Learning,. Upper Saddle Rive, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Pavlov, I. P. (1927). Conditioned reflexes (G. V. Anrep, Trans). London: Oxford University Press. Piaget, J. (1926 ). The Child's Conception of the World. London: Routhledge and Kegan Paul.
- 10. Table of Definitive Questions for Learning Theories Piaget, J. (1985 (Oringinal work published 1996)). Equilibration of Cognitive Structure. Univeristy of Chicago Press. Rogers, C. R. (Orginal printed 1969, 1994, (3rd ed)). Freedom to Learn. New York:: MacMillian. Rotter, J. B. (1954). Social Learning and Clinical Psychology. New York:: Prentice-Hall. Rumelhart, D. E. (1978). Accretion, Tuning, and Restructuring: Three Modes of Learning.In J. W. Cotton & R. L. Klatzky (Eds.), Semantic Factors in Cognition. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Salomon, G. ((ed.)). Distributed Cognitions. Cambridge:: Cambridge University Press. Schon, D. (1983). The Reflective Practitioner. How Professionals Think in Action. London: Temple Smith. Schunk, D. H. (1991). Self-efficacy and Academic Motivation. . Educational Psychologist, (26), 207-231. Siemens, G. (2005). Connectivism: A Learning theory for the Digital Age. Internaltional Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning, 2(1). Skinner, B. F. (1953). Science and Human Behavior. New York:: Free Press. Spiro, R. J. (1991). Cognitive Flexibility, Constructivism, and Hypertext: Random Access Instruction for Advanced Knowledge Acquisition in ill-structureed domans. Educational technology, 31(5), pp. 24-33. Thorndike, E. (1922). The Psychology of Arithmetic. New York:: MacMillan. Thorndike, E. (1927). The Measurement of Intelligent. New York:: Teachers College Press. Tolman, E. C. (1922). A New Formula for Behaviorism. Psychological Review, 29, 44-53. Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Wilson, T. R. (1980). On-the-job Training and Social Learning Theory: A Literature Review. Special Report (#13).
