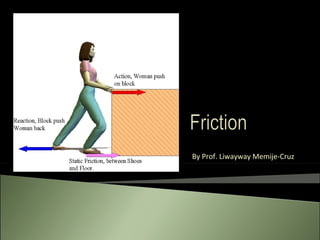
Friction
- 1. By Prof. Liwayway Memije-Cruz
- 2. a force that holds back the movement of a sliding object.
- 5. If a car needs to stop at a stop sign, it slows because of the friction between the brakes and the wheels.
- 6. If you run down the street and stop quickly, you can stop because of the friction between your shoes and the cement.
- 8. Friction is still there, but the liquid makes the surfaces smoother and the friction a lot less. Less friction means it is harder to stop.
- 9. is the friction that builds up between the tires on a car and the pavement. Rolling traction is the interaction between the tire and the surface, which results in forward motion. When water coats that surface, the tire can't obtain traction.
- 10. The low friction thing happens to cars when it rains. That's why there are often so many accidents. Even though the friction of the brakes is still there, the brakes may be wet, and the wheels are not in as much contact with the ground.
- 12. Hydroplaning occurs when your tires move over a wet surface so quickly that they don't have time to displace enough water and contact the surface. The water lifts the tire up from the surface, and the vehicle begins to hydroplane. While speed, road conditions and tire wear all play a part, the main cause of hydroplaning is water depth. Hydroplaning is possible whenever water accumulates to a depth of one-tenth of an inch (0.3 centimeters) or more for at least 30 feet (9.14 meters) and a vehicle moves through it at 50 miles per hour (22.35 meters per hour) or more Tire size and tread patterns are also important. Hydroplaning is more likely to happen if your vehicle has narrow tires. Worn tires are more dangerous in wet conditions. Certain tire tread patterns are better at channeling water away than others. All wheel driven vehicles are more likely to hydroplane than two- wheel drive vehicles, because their computerized differentials may shift power from the front to the rear tires, creating a hydroplaning situation. Heavy vehicles are less prone to hydroplaning.
- 13. Friction is the reason humans are able to control where they move or why objects can stay in one place, but it is also the reason we must use force and lose energy to move objects and why many materials wear out and break. The reality of friction allows machines to work, humans to walk and cars to drive. Friction also means that energy needs to constantly be exerted to move any object. When two surfaces are in contact, friction stops those surfaces from sliding against each other. All machines make use of friction and without it would have no use.
- 14. Without friction we are handicap. 1. It is becomes difficult to walk on a slippery road due to low friction. When we move on ice, it becomes difficult to walk due to low friction of ice. 2. We can not fix nail in the wood or wall if there is no friction. It is friction which holds the nail. 3. A horse can not pull a cart unless friction furnishes him a secure Foothold.
- 15. it makes moving large objects extremely difficult and causes surfaces to wear and break. it is a physical constraint, but also makes controlled movement and work possible. produces heat in various parts of machines. In this way some useful energy is wasted as heat energy. Due to friction we have to exert more power in machines. It opposes the motion. Due to friction, noise is also produced in machines. Due to friction, engines of automobiles consume more fuel which is a money loss.
- 18. The parts of machines which are moving over one another must be properly lubricated by using oils and lubricants of suitable viscosity.
- 19. Proper greasing between the sliding parts of machine reduces the friction
- 20. In machines where possible, sliding friction can be replaced by rolling friction by using ball bearings.
- 22. * Sliding Friction, also known as kinetic friction, takes place when an object slides over another. * The aim of sliding friction is to stop an object unlike rolling friction. It acts between objects already in motion. * Kinetic friction is caused by chemical bonding between surfaces rather than interlocking between them.
- 23. Fk = Uk N Where, F = Sliding or kinetic friction Uk= Coefficient of sliding friction N = Normal reaction due to weight
- 24. When two objects are not moving relative to each other, a force opposes or resists the lateral movement of the objects.
- 25. Fs= Fmax = UsN Example: When wepush a heavy object and areunableto do so, wepush it harder and harder, after sometimeit moves suddenly and after itsmovement it'seasier to push it. Here: 1. Becauseof Static friction we wereunableto movetheobject. 2. When it moved, we had overcomethekinetic friction which waslessthen static friction. If thecoefficient of static friction ishigh, it means, a lot of forcewill berequired to overcomethisstatic condition of theobject and to get it in motion.
- 26. occurswhen an object rolls over asurface. actson thepoint of the contact of therolling object and thesurfaceon which it is rolling. tendsto slow down the rolling motion of theobject. thecombination of various other forces.
- 27. Deformation of the object Deformation of the surface The diameter of the wheels surface The movement below the surface Sliding Surface adhesion Surface properties Material of the object Temperature
- 28. When we ride our bike through soft dirt, it is difficult to do so because rolling friction comes into action and hence opposes motion. It is very interesting to note that it is easier to drive through soft dirt if the tire also has less air, this is because the traction is increased which leads to improved driving.
- 29. F = Crr N Where, F = force of friction Crr= coefficient of rolling friction N or W = weight of the object (wheel) in this case (1) Rolling resistance is not directly dependent on the weight of the vehicle as obvious in the above equation. (2) When we apply brakes to any moving vehicle, rolling friction changes to kinetic sliding friction.
- 30. http://physics.tutorvista.com/forces/types-of-friction.html http://byjus.com/physics/rolling-friction/ http://www.physics4kids.com/files/motion_friction.html http://study.com/academy/lesson/friction-definition-and-types.html
