Lecture 2--Philosophy of Science
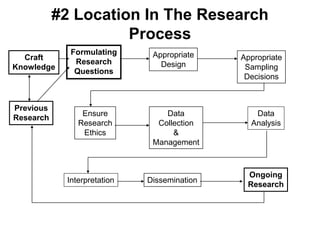
- 1. #2 Location In The Research Process Formulating Research Questions Appropriate Design Craft Knowledge Appropriate Sampling Decisions Previous Research Ensure Research Ethics Data Collection & Management Data Analysis Ongoing Research Interpretation Dissemination
- 2. Philosophy of Science Not everyone agrees how to do science. One key issue concerns the pursuit of objectivity. The Scientific Method Open to the data Provisional knowledge and refutation Evidence is basis for knowledge Evidence is based on observation Replication is important Assumes an objective reality Precise and generalizable findings Scientific Observation Systematic Comprehensive Objective Operationally specified
- 3. Philosophy of Science Scientific Methods Nomothetic Partially understand a general phenomenon Many subjects, few variables Empirical generalities Quantitative Ideographic Understand many factors underlying a specific action Few subjects, many variables and data collected Quantitative and qualitative Explanatory Assumes cause and effect Implies determinism (behavior is influenced by factors external to the individual) Probability statements – influence as causality Attempts to answer why a phenomenon is seen
- 4. Paradigms Paradigms- Assumptions that organize our observations and make sense of them. Based on ontology (study of existence) and epistemology (study of the nature of knowledge) Ones fundamental model, scheme, world view Methodology (organizing principles) stems from paradigm Postmodernism- Rejects notion of objective reality and standards of truth and logical reasoning that are the core of the scientific method; Everything is subjective. Positivism and post-positivism Objectivity Precision Generalizability Post-positivism accepts subjectivity Reality is objective, but observation and measurement are not purely objective. Post-positivism attempts to account for and/or minimize subjectivity By design Statistical control Quantitative Social Work research assumes a post-positivist paradigm
- 5. Paradigms Interpretivism- Reality is multiple, subjective, and socially constructed. Empathic understanding Understand internal states Modeling idiosyncrasy Critical Social Science- Interpret findings through the filter of their empowerment or advocacy goals. Oppression Empowerment Institutions Qualitative Methodology Subjective meanings Depth of understanding Experiential
- 6. Components of Theory Theory- A systematic set of interrelated statements intended to explain some aspect of social life or enrich our sense of how people conduct and find meaning in their daily lives. The statements are referred to as Hypotheses (predict something that should be observed in real world if Theory is true The things the hypotheses predict are called variables. Attributes are the characteristics or quantities that make up a variable
- 7. Logical Systems Deductive Method Theory Hypothesis Defines variables Observe/measure Inductive Method Observe Recognize a Pattern Develop a logical explanation for the Pattern
