Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
IB Biology 3.5 genetic modifcation and biotechnology

IB Biology 3.5 genetic modifcation and biotechnology
IB Biology 3.5 Slides: Genetic Modification & Biotechnology

IB Biology 3.5 Slides: Genetic Modification & Biotechnology
IB Biology 7.2-7.3 Slides: AHL Transcription & Translation

IB Biology 7.2-7.3 Slides: AHL Transcription & Translation
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (10)
Implications of variation adaptation and natural selection

Implications of variation adaptation and natural selection
Similar to 10.1 meiosis
Similar to 10.1 meiosis (20)
More from Bob Smullen
More from Bob Smullen (20)
Recently uploaded
Recently uploaded (20)
Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b

Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b
❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.

❤Jammu Kashmir Call Girls 8617697112 Personal Whatsapp Number 💦✅.
Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf

Pests of mustard_Identification_Management_Dr.UPR.pdf
Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf

Forensic Biology & Its biological significance.pdf
Kochi ❤CALL GIRL 84099*07087 ❤CALL GIRLS IN Kochi ESCORT SERVICE❤CALL GIRL

Kochi ❤CALL GIRL 84099*07087 ❤CALL GIRLS IN Kochi ESCORT SERVICE❤CALL GIRL
Human & Veterinary Respiratory Physilogy_DR.E.Muralinath_Associate Professor....

Human & Veterinary Respiratory Physilogy_DR.E.Muralinath_Associate Professor....
Sector 62, Noida Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified

Sector 62, Noida Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified
FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Analytical Science

FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Analytical Science
Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds

Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds
SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE

SAMASTIPUR CALL GIRL 7857803690 LOW PRICE ESCORT SERVICE
Connaught Place, Delhi Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified

Connaught Place, Delhi Call girls :8448380779 Model Escorts | 100% verified
Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young

Dubai Call Girls Beauty Face Teen O525547819 Call Girls Dubai Young
development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus

development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus
10.1 meiosis
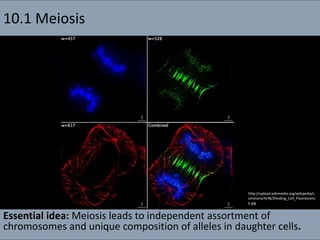
- 1. 10.1 Meiosis Essential idea: Meiosis leads to independent assortment of chromosomes and unique composition of alleles in daughter cells. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/c ommons/4/46/Dividing_Cell_Fluorescenc e.jpg
- 2. Understandings Statement Guidance 10.1 U.1 Chromosomes replicate in interphase before meiosis. 10.1 U.2 Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister homologous chromatids. 10.1 U.3 Crossing over produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells. 10.1 U.4 Chiasmata formation between non-sister chromatids can result in an exchange of alleles. 10.1 U.5 Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I. 10.1 U.6 Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II. 10.1 U.7 Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
- 3. Applications and Skills Statement Guidance 10.1 S Drawing diagrams to show chiasmata formed by crossing over.
- 4. 10.1 U1 Chromosomes replicate in interphase before meiosis. • During the S phase of the cell cycle, so that each chromosome has a copy of itself and consists of two sister chromatids. • During meiosis I, chromosomes condense and synapse to form bivalents (homologous chromosomes are aligned next to each other). http://www.columbia.edu/cu/biology/co urses/c200507/images/meiosis_19.gif
- 5. 10.1 U2 Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister homologous chromatids.
- 6. 10.1 U3 Crossing over produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells. http://www.indiana.edu/~oso/lessons/Genetics/ figs/sheep/2_fXe_sp2.jpg
- 7. 10.1 U4 Chiasmata formation between non-sister chromatids can result in an exchange of alleles. • Chiasmata are points where two homologous non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material during crossing over in meiosis. • Chromosomes intertwine and break at the exact same positions in non-sister chromatids. • The two chromosomes are now attached at the same corresponding position on the non- sister chromatid. • Once attached the non-attached portions of the chromatids actually repel each other. • Chiasmata refer to the actual break of the phosphodiester bond during crossing over. • The chiasmata are separated during anaphase 1 which can result in an exchange of alleles between the non-sister chromatids from the maternal and paternal chromosomes.
- 8. 10.1 U5 Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I. • During meiosis I, unlike mitosis homologous chromosomes separate to opposite poles; however, their sister chromatids remain attached to each other • Homologous chromosomes can exchange material in a process called crossing over • Meiosis I is considered reduction division because the chromosome number is reduced by half (2n -> n in humans) http://i.ytimg.com/vi/RfRtVDkABPI/hqdefault.jpg
- 9. 10.1 U6 Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II. • During meiosis II sister chromatids separate (some are non-identical sister chromatids due to crossing over • This type of separation is very similar to mitosis as the chromatids are separated from each other
- 10. 10.1 U7 Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I. • Independent assortment is an essential component in explaining how chromosomes align themselves during meiosis. • It also explains how unlinked genes are passed on from generation to generation. • When homologues line up along the equatorial plate in metaphase I, the orientation of each pair of is random; meaning the maternal or paternal homologue can orient towards either pole. • The orientation of how one set of homologues line up has no effect on how any of the other homologues line up. • Two young women to the right are non identical twin sisters, who because of independent assortment have different hair and skin coloring http://hellogiggles.com/bi-racial-twins/
- 11. 10.1 U7 Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I.
- 12. 10.1 S.1 Drawing diagrams to show chiasmata formed by crossing over. http://www.thestudentroom.co.uk/showthread.php?t=1561992 • The centromere is a section of DNA on the chromosome where the chromatids are closest, it's generally tightly packed, the DNA typically doesn't have a defined sequence and is often satellite DNA, non-coding. It's the point at which the mitotic spindle attaches itself. • Chiasmata are places where the chromosomes cross over, and sometimes exchanges of DNA take place. This is usually looser packed, often functional DNA