DNA Replication Sintesis
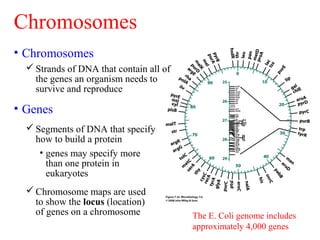
- 1. The E. Coli genome includes approximately 4,000 genes • Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Chromosomes • Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein • genes may specify more than one protein in eukaryotes Chromosome maps are used to show the locus (location) of genes on a chromosome
- 2. • Genetic Variation Phenotypic variation among organisms is due to genotypic variation (differences in the sequence of their DNA bases) Differences exist between species and within a species • Different genes (genomes) different proteins (proteomes) • Different versions of the same gene (alleles) • Differences in gene expression (epigenetics) Chromosomes
- 3. • Cell Division (mitosis) Cells must copy their chromosomes (DNA synthesis) before they divide so that each daughter cell will have a copy A region of the chromosome remains uncopied (centromere) in order to hold the sister chromatids together – Keeps chromatids organized to help make sure each daughter cell gets exactly one copy – Nondisjunction is when sister chromatids do not assort correctly and one cell ends up with both copies while the other cell ends up with none DNA Replication
- 4. • DNA Synthesis The DNA bases on each strand act as a template to synthesize a complementary strand • Recall that Adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C) The process is semiconservative because each new double-stranded DNA contains one old strand (template) and one newly-synthesized complementary strand DNA Replication A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C A G C T G T C G A C T C G A C A G C T G
- 5. DNA Replication • DNA Polymerase Enzyme that catalyzes the covalent bond between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the deoxyribose (sugar) of the next nucleotide DNA Polymerization
- 6. 3’ end has a free deoxyribose 5’ end has a free phosphate DNA polymerase: can only build the new strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction Thus scans the template strand in 3’ to 5’ direction DNA Replication
- 7. Initiation • Primase (a type of RNA polymerase) builds an RNA primer (5-10 ribonucleotides long) • DNA polymerase attaches onto the 3’ end of the RNA primer DNA Replication DNA polymerase
- 8. Elongation • DNA polymerase uses each strand as a template in the 3’ to 5’ direction to build a complementary strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction DNA Replication DNA polymerase
- 9. Elongation • DNA polymerase uses each strand as a template in the 3’ to 5’ direction to build a complementary strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction results in a leading strand and a lagging strand DNA Replication
- 10. Leading Strand 1. Topisomerase unwinds DNA and then Helicase breaks H-bonds 2. DNA primase creates a single RNA primer to start the replication 3. DNA polymerase slides along the leading strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction synthesizing the matching strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction 4. The RNA primer is degraded by RNase H and replaced with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase, and then DNA ligase connects the fragment at the start of the new strand to the end of the new strand (in circular chromosomes) DNA Replication
- 11. Lagging Strand 1. Topisomerase unwinds DNA and then Helicase breaks H-bonds 2. DNA primase creates RNA primers in spaced intervals 3. DNA polymerase slides along the leading strand in the 3’ to 5’ direction synthesizing the matching Okazaki fragments in the 5’ to 3’ direction 4. The RNA primers are degraded by RNase H and replaced with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase 5. DNA ligase connects the Okazaki fragments to one another (covalently bonds the phosphate in one nucleotide to the deoxyribose of the adjacent nucleotide) DNA Replication
- 12. Topoisomerase - unwinds DNA Helicase – enzyme that breaks H-bonds DNA Polymerase – enzyme that catalyzes connection of nucleotides to form complementary DNA strand in 5’ to 3’ direction (reads template in 3’ to 5’ direction) Leading Strand – transcribed continuously in 5’ to 3’ direction Lagging Strand – transcribed in segments in 5’ to 3’ direction (Okazaki fragments) DNA Primase – enzyme that catalyzes formation of RNA starting segment (RNA primer) DNA Ligase – enzyme that catalyzes connection of two Okazaki fragments DNA Replication
- 13. Web Resources DNA Replication (synthesis) • http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072556781/student_view0/chapter11/animation_quiz_2.html • http://www.wiley.com/college/pratt/0471393878/student/animations/dna_replication/index.html • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20DNA%20Replication%20Coordination%20Leading %20Lagging%20Strand%20Synthesis.htm • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20DNA%20Replication%20Nucleotide%20Polymerization.htm • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/DNAReplicationBasic_w_FX.html (download this video file from the website to view it without interruptions) • http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/molgenetics/dna-rna2.swf • http://www.bioteach.ubc.ca/TeachingResources/MolecularBiology/DNAReplication.swf
- 14. • DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins • Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes • The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictate the order of amino acids that make up a protein Protein Synthesis Nucleotide sequence of His gene
- 15. Protein Synthesis Nucleotide sequence of His gene Amino acid sequence of His protein • DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins • Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes • The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictate the order of amino acids that make up a protein
- 16. • Protein synthesis occurs in two primary steps Protein Synthesis mRNA (messenger RNA) copy of a gene is synthesized Cytoplasm of prokaryotes Nucleus of eukaryotes 1 mRNA is used by ribosome to build protein (Ribosomes attach to the mRNA and use its sequence of nucleotides to determine the order of amino acids in the protein) Cytoplasm of prokaryotes and eukaryotes Some proteins feed directly into rough ER in eukaryotes 2
- 17. (eukaryotes) Protein Synthesis 1) INITIATION • Transcription Initiation RNA polymerase binds to a region on DNA known as the promoter, which signals the start of a gene Promoters are specific to genes RNA polymerase does not need a primer Transcription factors assemble at the promoter forming a transcription initiation complex – activator proteins help stabilize the complex Gene expression can be regulated (turned on/off or up/down) by controlling the amount of each transcription factor
- 18. Protein Synthesis 1) INITIATION • Transcription Elongation RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA and breaks the H-bonds between the bases of the two strands, separating them from one another Base pairing occurs between incoming RNA nucleotides and the DNA nucleotides of the gene (template) • recall RNA uses uracil instead of thymine AGTCAT UCAGUA
- 19. Protein Synthesis • Transcription Elongation RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA and breaks the H-bonds between the bases of the two strands, separating them from one another. Base pairing occurs between incoming RNA nucleotides and the DNA nucleotides of the gene (template) • recall RNA uses uracil instead of thymine RNA polymerase catalyzes bond to form between ribose of 3’ nucleotide of mRNA and phosphate of incoming RNA nucleotide 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ + ATP + ADP
- 20. Protein Synthesis • Transcription Elongation The gene occurs on only one of the DNA strands; each strand possesses a separate set of genes
- 21. Protein Synthesis 1) INITIATION • Transcription Termination A region on DNA known as the terminator signals the stop of a gene RNA polymerase disengages the mRNA and the DNA
- 22. Exons are “coding” regions Introns are removed different combinations of exons form different mRNA resulting in multiple proteins from the same gene Humans have 30,000 genes but are capable of producing 100,000 proteins Protein Synthesis • Alternative Splicing (eukaryotes only)
- 23. Web Resources Transcription • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Transcription.htm • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsofH466lqk • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranscriptionBasic_withFX.html Alternative Splicing • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FVuAwBGw_pQ&feature=related
- 24. mRNA copy of a gene is synthesized Cytoplasm of prokaryotes Nucleus of eukaryotes 1 Protein Synthesis mRNA is used by ribosome to build protein (Ribosomes attach to the mRNA and use its sequence of nucleotides to determine the order of amino acids in the protein) Cytoplasm of prokaryotes and eukaryotes Some proteins feed directly into rough ER in eukaryotes 2 mRNA Transcription Translation mRNA tRNA synthesis
- 25. Transcription Translation mRNA tRNA synthesis Protein Synthesis • Translation Every three mRNA nucleotides (codon) specify an amino acid
- 26. Protein Synthesis • Translation tRNA have an anticodon region that specifically binds to its codon
- 27. Transcription Translation mRNA tRNA synthesis Protein Synthesis • Translation Each tRNA carries a specific amino acid
- 28. Transcription Translation mRNA tRNA synthesis Protein Synthesis Aminoacyl tRNA synthetases attach amino acids to their specific tRNA
- 29. Protein Synthesis • Translation Initiation Start codon signals where the gene begins (at 5’ end of mRNA) AUGGACAUUGAACCG… 5’ 3’ start codon Translation mRNA
- 30. Protein Synthesis • Translation Initiation Start codon signals where the gene begins (at 5’ end of mRNA) Ribosome binding site (Shine Dalgarno sequence) upstream from the start codon binds to small ribosomal subunit – then this complex recruits the large ribosomal subunit Small ribosomal subunit Small ribosomal subunit Ribosome Large ribosomal subunit
- 31. Protein Synthesis • Translation Scanning The ribosome moves in 5’ to 3’ direction “reading” the mRNA and assembling amino acids into the correct protein large ribosome subunit small ribosome subunit
- 32. Protein Synthesis • Translation Scanning The ribosome moves in 5’ to 3’ direction “reading” the mRNA and assembling amino acids into the correct protein
- 33. Protein Synthesis • Translation Termination Ribosome disengages from the mRNA when it encounters a stop codon
- 34. Web Resources Translation • Eukaryotic: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5bLEDd-PSTQ&feature=related • Prokaryotic: http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Protein%20Synthesis%20Prokaryotic.htm • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Peptide%20Bond%20Formation.htm • http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationBasic_withFX0.html • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationAdvanced.html
- 35. Practice Question Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACGCACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC
- 36. Practice Question Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACGCACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC Serine – Tyrosine – Histidine – Threonine – Histidine – Proline – Serine – Serine – Serine - Serine
- 37. Ser – Tyr – His – Thr – His – Pro – Ser – Ser – Ser - Ser Practice Question Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACGCACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC Serine – Tyrosine – Histidine – Threonine – Histidine – Proline – Serine – Serine – Serine - Serine
- 38. Serine – Tyrosine – Histidine – Threonine – Histidine – Proline – Serine – Serine – Serine - Serine Practice Question Translate the following mRNA sequence AGCUACCAUACGCACCCGAGUUCUUCAAGC S – Y –H– T – H – P – S – S – S - S Ser – Tyr – His – Thr – His – Pro – Ser – Ser – Ser - Ser
- 39. Protein Synthesis • Multiple RNA polymerases can engage a gene at one time • Multiple ribosomes can engage a single mRNA at one time DNA mRNAs Transcription Translation
- 40. Protein Synthesis • Eukaryotes: transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation occurs in the cytoplasm • Prokaryotes: Transcription and translation occur simultaneously in the cytoplasm
- 41. • There are four main types of RNA: 1. mRNA - RNA copy of a gene used as a template for protein synthesis 2. rRNA - part of structure of ribosomes 3. tRNA - amino acid carrier that matches to mRNA codon 4. snRNA - found in nucleus where they have several important jobs RNA
- 42. 1. Why is DNA synthesis said to be “semiconservative”? 2. What role do DNA polymerase, DNA primase (a type of RNA polymerase), helicase, topoisomerase, RNase H, and ligase play in DNA replication? 3. What is the difference between how the leading strand and lagging strand are copied during DNA replication? Why do they have to be synthesized differently in this fashion? 4. What would happen if insufficient RNase H were produced by a cell? What if insufficient ligase were produced by a cell? 5. What are four key differences between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase? (“they are difference molecules” doesn’t count as one!) 6. Compare and contrast codons and anticodons? 7. What is alternative splicing? Why is it necessary in eukaryotes? 8. During translation, what amino acid sequence would the following mRNA segment be converted into: AUGGACAUUGAACCG? 9. How come there are only 20 amino acids when there are 64 different codons? 10. How come prokaryotes can both transcribe and translate a gene at the same time, but eukaryotes cannot? Practice Questions
- 43. Web Resources Transcription • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Transcription.htm • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsofH466lqk • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranscriptionBasic_withFX.html Translation • Eukaryotic: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5bLEDd-PSTQ&feature=related • Prokaryotic: http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Protein%20Synthesis%20Prokaryotic.htm • http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Peptide%20Bond%20Formation.htm • http://www.johnkyrk.com/DNAtranslation.html • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationBasic_withFX0.html • http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/TranslationAdvanced.html Alternative Splicing • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FVuAwBGw_pQ&feature=related
- 44. Insulin Example of Protein Synthesis http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/insulinproteinstructure.html Hemoglobin Example of Protein Synthesis http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/insulinproteinstructure.html Collagen Example of Protein Synthesis http://www.biotopics.co.uk/JmolApplet/collagen.html Web Resources
- 45. Images • http://www.kscience.co.uk/as/module1/pictures/bacteria.jpg • http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/library/onlinebio/14_1.jpg • http://pharmamotion.com.ar/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/nrti_mechanism_action_antiretrovirals.jpg • http://biology200.gsu.edu/houghton/4564%20%2704/figures/lecture%204/AAAreverse.jpg • http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/pdbsum/2d8x/traces.jpg • http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov • http://xarquon.jcu.cz/edu/uvod/09nucleus/092function/images/activation3.jpg • http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov • http://bass.bio.uci.edu/~hudel/bs99a/lecture23/lecture4_4.html • http://selfhpvdna.diagcorlab.com/images/images/CervicalCancer.jpg
