The Cell Membrane
•Télécharger en tant que PPTX, PDF•
4 j'aime•3,373 vues
Brief description of the plasma cell membrane and how materials get into or out of the cell. Appropriate for 7th grade life science.
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
Presentation on Electrical Properties of Cell Membrane

Presentation on Electrical Properties of Cell Membrane
Replicative mechanisms of Plasmid and Circular Genomes

Replicative mechanisms of Plasmid and Circular Genomes
Cytoskeleton - microtubules ,microfilaments and intermediate filaments

Cytoskeleton - microtubules ,microfilaments and intermediate filaments
Cell structure, prokaryotice cell, eukaryotic cell, organization of the cell

Cell structure, prokaryotice cell, eukaryotic cell, organization of the cell
En vedette
En vedette (7)
Similaire à The Cell Membrane
Similaire à The Cell Membrane (20)
Nuclear Membrane: Active and Passive Transport (Illustrations)

Nuclear Membrane: Active and Passive Transport (Illustrations)
Cell membrane powerpoint diffusion and osmosis revised

Cell membrane powerpoint diffusion and osmosis revised
B.Sc. Microbiology/Biotech II Cell biology and Genetics Unit 3 cell transport

B.Sc. Microbiology/Biotech II Cell biology and Genetics Unit 3 cell transport
Active Transport is movement of substance against their concentration gradien...

Active Transport is movement of substance against their concentration gradien...
Dernier
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Dernier (20)
ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.

ICT role in 21st century education and it's challenges.
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...

Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom

Fostering Friendships - Enhancing Social Bonds in the Classroom
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...

Sensory_Experience_and_Emotional_Resonance_in_Gabriel_Okaras_The_Piano_and_Th...
The Cell Membrane
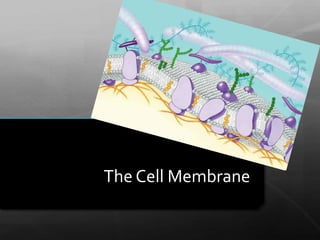
- 2. Cell Membrane Also known as the plasma membrane In both plant and animal cells Main function: to protect the cell Made of a lipid (fat) double layer with special embedded proteins
- 4. Cell Transport The membrane also controls what goes in or out of the cell (cell transport) It is semi-permeable Some molecules, like oxygen & water, are permeable go directly through the membrane Other molecules, like glucose & salt, are impermeable and only pass through a protein
- 5. Cell Transport There are lots of ways substances enter or exit a cell It depends on the size of the substance: Small Particles move through the membrane by: Passive or Active Transport Large Particles move through the membrane by: Endocytosis or Exocytosis
- 6. Passive Transport Does not require energy (thus passive…) Two Types 1. Diffusion 2. Facilitated Diffusion
- 8. 1) Diffusion Diffusion is when molecules spread from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration This is called a concentration gradient
- 9. 1) Diffusion Think about spraying air freshener into a room. It gradually spreads out. Same thing if someone farts… Or, if we pushed everyone here into a corner, but let you move where you wanted, you would tend to spread out around the room instead of staying crammed into the corner. You’re moving from an area of high concentration (the corner) to an area of low concentration (the rest of the room).
- 10. 1) Diffusion
- 11. 1) Diffusion Diffusion occurs in cells through the membrane. Oxygen needed for cellular respiration enters cells by diffusion CO2 produced by cellular respiration leaves cells by diffusion.
- 12. Osmosis Osmosis is when water diffuses through a membrane. Think about how important it is for water to get into and out of cells.
- 13. 2) Facilitated Diffusion Sometimes, molecules can’t get through the membrane without a little help (facilitation…) In facilitated diffusion, a special protein embedded in the membrane helps molecules move across No energy is required, this is still passive transport Molecules such as glucose, sodium & chloride ions get into the cell this way
- 14. Active Transport Requires energy (ATP) Sometimes, cells have to move a substance against the concentration gradient or from an area of low to high concentration
- 15. Active Transport Active transport also occurs through a special protein or pump, like with facilitated diffusion This is one of the main reasons why cells require energy – they need the ability to remove substances. For example, kidney cells filter & remove salt from your blood through active transport.
- 16. Passive versus Active Transport
- 17. Large Particles Sometimes particles are too big to simply cross the membrane. Instead, they must get pulled into or pushed out of the membrane in one of two ways 1. 2. Endocytosis Exocytosis
- 18. 1) EndoCytosis Occurs when large particle(s) are captured by a pocket in the membrane The particle is too big to fit through a protein channel The pocket breaks off & forms a package that moves into the cell Requires energy Essential nutrients, like iron, are absorbed into cells this way
- 19. 1) EndoCytosis
- 20. 2) ExoCytosis Occurs when a large bit of material needs to be removed from a cell A package of the materials travels through the cell to the membrane, joins it, and is expelled Opposite of endocytosis Requires energy Cells use this to flush out waste such as hormones
- 21. 2) ExoCytosis
- 22. Big Ideas 1. What are two functions of the cell plasma membrane? 2. What types of substances need to be transported across the membrane? 3. How does a particle’s size affect how its transported through a cell? 4. List 3 differences between passive & active transport.