Assessment forfolio questions
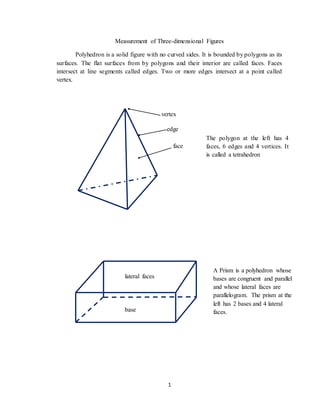
- 1. 1 Measurement of Three-dimensional Figures Polyhedron is a solid figure with no curved sides. It is bounded by polygons as its surfaces. The flat surfaces from by polygons and their interior are called faces. Faces intersect at line segments called edges. Two or more edges intersect at a point called vertex. The polygon at the left has 4 faces, 6 edges and 4 vertices. It is called a tetrahedron edge face vertex A Prism is a polyhedron whose bases are congruent and parallel and whose lateral faces are parallelogram. The prism at the left has 2 bases and 4 lateral faces. lateral faces base
- 2. 2 A Pyramid is a polyhedron with a polygon as base and triangles as lateral faces. The most common pyramids are those with triangles, square and, rectangles as bases. A Cube is a regular prism because it is bounded by a regular polygon (square) and all its angles are right angles. vertex face edge A Rectangular solid is the most common type of right prism. It is bounded by rectangles whose corners are right angles.face triangular pyramid square pyramid rectangular pyramid
- 3. 3 A Cylinder is a solid whose bases are congruent circles. A right circular cylinder is a cylinder whose altitude is perpendicular to the bases and has an endpoint in each base. A Cone is a solid with a circle as base and all line segments from the circle meet at a point called the vertex. A right circular cone is a cone whose altitude is a segment that is perpendicular to the base. Any segment that joins the vertex to a point on the circle is a slant height. A Sphere is a solid with all points of which are equidistant from the fixed point called the centre. A radius of a sphere is a segment whose endpoints are the centre and a point on the sphere. CD is a radius. A chord of a sphere is a segment whose endpoints are points on the sphere. MN is a chord. A diameter of a sphere is a segment that contains the centre and whose endpoints on the sphere. PR is a diameter. A tangent to a sphere is a line that intersects the sphere in exactly one point. XY is a tangent to the sphere at O. O Y X lateral face altitude radius radius base altitude slant height base C P R D M N
- 4. 4 Measurements of 3D Figures Surface Are of Solids is defined as the sum of the areas of the outer surfaces of a solid. These outer faces are known as faces. A. Surface Area of a Cube. To find the surface area of a cube, multiply the square f the length of a side by 6. B. Surface Area of Rectangular Prism is the total area of the surfaces of rectangular prism. Formula; SA = 6s2 Where s is the side or the edge of the cube Example; 1. s = 2.2cm SA = 6s2 = 6(2.2cm) 2 = 6(4.84cm2) SA = 29.04cm2 2. s = 0.09m SA = 6s2 = 6(0.09cm)2 = 6(0.0081m2) SA = 0.0486m2 Formula: SA = 2B + LA where B is the area of the base LA is the area of the lateral faces Examples: 1. Find the surface area of a rectangular prism whose length is 7cm, width is 4cm and thickness is 5cm. SA = 2B + LA SA = 2(lw + lh + wh) = 2[(7cm)(4cm) + (4cm)(5cm) + (7cm)(5cm)] = 2(28cm2 + 20cm2 + 35cm2) = 2(83cm2) SA = 166cm2 2. L = 12cm, w =7cm and h = 6cm SA = 2B + LA SA = 2(lw + lh + wh) = 2(12cm x 7cm) + 2(7cm x 6cm) + 2(12cm x 6cm) = 168cm2 + 84cm2 + 144cm2 SA = 396cm2
- 5. 5 C. Surface Area of Cylinder is the amount of spaces outside the sphere. D. Surface Area of a Cone is the amount of space outside the cone. E. Surface Area of Sphere is the amount of space outside the sphere. Formula; SA = 2Лr2 + 2Лrh or SA = 2Лr(r + h) where r is the radius h is the height Example: 1. Find the surface are of a cylinder having radius is equal to 7cm and height is 20m. SA = 2Лr2 + 2Лrh = 2(3.14) (5cm)2 + 2(3.14)(5cm)(20cm) = 2(3.14) (25cm2) + 2(3.14)(100cm2) = (6.28) (25cm2) + (6.28) (100cm2) = 157cm2 + 628cm2 SA = 785cm2 Formula: SA = Лr2 + Лrs where s is the slant height and r is the radius of the base Example: 1. Find the surface area of a cone having s = 7.25cm and r = 3.5cm. SA = Лr2 + Лrs = (3.14) (3.5cm)2 + (3.14) (3.5cm) (7.25cm) = (3.14) (12.25cm2) + (10.99cm2) (7.25) = 38.465cm2 + 79.6775cm2 SA = 118.1425cm2 Formula: SA = 4Лr2 where r is the radius Example: 1. Find the surface area of a sphere having r = 6cm. SA = 4Лr2 = 4(3.14) (6cm)2 = 12.56 (36cm2) SA = 452.16cm2
- 6. 6 F. Surface Area of Square Pyramid is the amount of space outside the square pyramid. Volume is used to measure space. It is the amount of space enclosed in a solid figure. It is expressed in cubic denominations. G. Volume of a Rectangular Prism is the amount of space enclosed in rectangular prism. Formula: SA = s2 + 2bs where s2 is the area of the base b side of the base s is the slant height Example: 1. Find the surface area of the square pyramid having b = 3cm, s = 5cm and s2 = (3cm)2. SA = s2 + 2bs = (3cm)2 + 2(3cm)(5cm) = 9cm2 + 30cm2 SA = 39cm2 Formula: V = l x w x h or area of the base times height SA = B x h where l is the length w is the width h is the height Example: 1. Find the length of the rectangular prism having l = 4.2cm, w = 3.7cm and h = 2.5cm. V = l x w x h = (4.2cm) (3.7cm) (2.5cm) = 15.54cm2 (2.5cm) V = 38.85cm3
- 7. 7 H. Volume of Triangular Prism is the amount of space enclosed in triangular prism. I. Volume of Square a Pyramid is the amount of space enclosed in a square pyramid. Formula: V = bh x H 2 Where b is the length of one side of the base h is the height of the altitude triangular prism H is the height of the base Example: 1. Find the volume of triangular prism having l = 3.4cm, b = 3cm and h = 3.2cm. V = bh x H 2 = (3.4cm) (3.2cm) x 3cm 2 = 10.88cm2 x 3cm 2 = 5.44cm2 x 3cm V = 16.32cm3 Formula: V = 1 (l x w) h 3 Where l is the length w is the width h is the height Example: 1. Find the volume of a pyramid having l = 9cm, w = 8cm and h = 7cm. V = 1 (l x w) h 3 = 1 (8cm x 9cm) x 7cm 3 = 1 (72cm2) x 7cm 3 = 24cm2 x 7cm V = 168cm2 In the case of square pyramid the length and the width are equal.
- 8. 8 J. Volume of a Cylinder is the amount of space enclosed in a cylinder. K. Volume of a Cone is the amount of space enclosed in a cone. L. Volume of a Sphere is the amount of space enclosed in a sphere. Formula: V = Лr2h Where is the height Example: 1. Find the volume of a cylinder having r = 3cm and h = 10cm. V = Лr2h = (3.14) (3cm)2 (10cm) = (3.14) (90cm3) V= 282.6cm3 Formula: V = 1 Лr2h 3 Where r is the radius h is the height Example: 1. Find the surface area of a cone having the r = 3cm and h = 6cm. V = 1 Лr2h 3 = 1 (3.14) (3cm)2 (6cm) 3 = 1 (3.14) (9cm2) (6cm) 3 = 1 (3.14) (54cm3) 3 = 169.56cm3 3 V = 56.52cm3 Formula: V = 4Лr3 3 Example: 1. Find the volume of a sphere having h = 0.9cm. V = 4Лr3 3 = 4 (3.14) (0.9cm)3 3 V = 3.05cm3
- 9. 9 Completion Directions: Complete the following statements by filling your answers on the blank provided. 1. A solid figure which is bounded by polygon in each space is called ______. (polyhedron) 2. The flat surfaces form by polygons and their interior are called _______. (faces) 3. The faces of polyhedron intersect at line segments called _________ (edges). 4. The edges of a polyhedron intersect at points called _________. (vertices) 5. A polyhedron whose bases are congruent and parallel and whose lateral faces are parallelogram is called _______. (prism) 6. A regular prism which is bounded by squares whose corners are right angles is called _______. (cube) 7. A right prism which is bounded by rectangles whose corners are right angles is called ________. (rectangular solid) 8. A polyhedron with a polygon as base and triangles as lateral faces is called _________. (pyramid) 9. A solid figure whose bases are congruent circles is called _______. (cylinder) 10. A solid figure with a circle as base and all line segments from the circle meet at the vertex is called ________. (cone)
- 10. 10 Short Answer Directions: Supply of what is asked in each statement. 1. What kind of cylinder whose altitude is a segment that is perpendicular to the bases and has an endpoint in each base? (right circular cylinder) 2. What kind of four sided polygon that usually made up the faces of rectangular solid? (rectangle) 3. What kind of pyramid that has rectangle as its base? ( rectangular pyramid) 4. What kind of a solid figure which all points are equidistant from the given point called centre? (sphere) 5. What is the sum of the areas of the outer surfaces of a solid figure? (surface area) 6. What is the amount of space enclosed in a solid figure? (volume) 7. What is the formula in getting the surface area of a cylinder? (SA = 2Лr2 + 2Лrh) 8. What is the formula in getting the surface area of a cone? (SA = Лr2 + Лrs) 9. What is the formula in getting the volume of a square or rectangular pyramid? (V= 1/3 (l x w) h or V = 1/3 B x h) 10. What is the formula in getting the volume of a sphere? ( V = 4/3 Лr3)
- 11. 11 Essay Directions: Answer the following statements/questions. 1. In five sentences, write an essay describing the solid figures. 2. In four to six sentences, write an essay comparing the surface area and the volume of a solid figure. 3. In five sentences, write an essay describing the formula and its importance in the real world.
- 12. 12 Multiple Choice Directions: Answer the following. Encircle the correct answers. 1. What is the missing in this formula in finding the volume of a cylinder? V = Лr2 A. w B. l C. b D. h* 2. What is the missing in this formula in finding the surface area of a cone? SA = r2 + Лrs A. Л* B. b C. l D. h 3. What is the missing in this formula in finding the volume of a sphere? V = Лr3 A. 1/3 B. 1/2 C. 4/3* D. 2/3 4. It is a solid figure with a circle as base and all line segments from the circle meet at a point called the vertex. What solid figure is referred above? A. Cone* B. Sphere C. Pyramid D. Cylinder 5. What is the surface area of a cone having slant height equal to 7.25cm and radius equal to 3.5m? A. 118.1370cm2 B. 118.1425cm2* C. 118.2000cm2 D. 118.1480cm2
- 13. 13 6. What is the volume of a triangular prism having length equal to 3.4cm, height of base is 3cm and height of the prism is 3.2cm? A. 16.35cm3 B. 16.20cm3 C. 16.32cm3* D. 16.30cm3 7. What is the height of square pyramid having length equal to 9cm, width equal to 8cm and volume equal to 168cm3. A. 6cm B. 7cm* C. 8cm D. 9cm 8. What is the formula in getting the surface area of a sphere? A. V = 4/3Лr3* B. V = 2/3Лr3 C. V = 3/4Лr3 D. V = 3/2Лr3 9. What is the volume of a cylinder having radius equal to 3cm and height equal to 10cm? A. 282.744cm3* B. 282.717cm3 C. 282.726cm3 D. 283.735cm3 10. What is the volume of a sphere having radius equal to 0.9m? A. 3.0535m3 B. 3.0536m3* C. 3.0537m3 D. 3.0534m3
- 14. 14 Matching Type Directions: Match column A with column B. Write only the letter with the correct answer. Column A Column B 1. Amount of space outside the sphere (e) 2. Amount of space enclosed in a rectangular prism (d) 3. Amount of space enclosed in a cone (c) 4. Amount of space enclosed in sphere (b) 5. Amount of space outside the rectangular prism (a) 6. Amount of space outside the cylinder (j) 7. Amount of space enclosed in a cylinder (i) 8. Amount of space enclosed in a square pyramid (h) 9. Amount of space outside the cube (g) 10. Amount of space outside the cone (f) a. SA = 2B + LA b. V = 4/3 Лr3 c. V = 1/3 Лr2h d. V = l x w x h e. SA = 4Лr2 f. SA = Лr2 + Лrs g. SA = 6s2 h. V = 1/3 (l x w) h i. V = Лr2h j. SA = 2Лr2 + 2Лrh k. SA = s2 + 2bs l. V = bh/2 x H
- 15. 15 Table of Specification Three Dimensional Figures and their Measurements Topics Time Allotment Percentage Allocation Remembering 50% Analysis 40% Evaluating 10% Total 100% 1.Basic Terminology 30min 25% 4 (Completion) 3 (Multiple Choice) 1 (Multiple Choice) 8 2. Surface Area of Solids 45min 38% 5 (Multiple Choice) 5 (Multiple Choice) 1 (Multiple Choice) 11 3.Volume of Solids 45min 37% 6 (Multiple Choice) 4 (Multiple Choice) 1 (Multiple Choice) 11 Total 12min 100% 15 12 3 30
- 16. 16 Name: ___________________________________________ Score: __________ I. Directions: Supply what is asked in each statement. Write your answer on the blank provided before each number. 1. What kind of Cone whose altitude is a segment that is perpendicular to the bases and has an endpoint in each base? 2. What kind of four sided polygon that made up the faces of a cube? 3. What kind of pyramid that has three sided polygon as base? 4. What is the sum of the areas of the outer surfaces of a solid? II. Directions: Answer the following. Encircle the correct answers. 5. It is a solid figure with a triangle as one of the lateral faces and it has any polygon as its base. It has a point in its end top and diagonal line can be seen in it. A. Cone B. Triangular Prism C. Pyramid D. Diamond 6. It is a solid with all the points in its outer surface are equidistant to the given point called center. What kind of solid figure does the statement refer to? A. Pyramid B. Sphere C. Triangular Prism D. Cone 7. This kind of solid figure can be seen typically during summer season and can be associated to a sweet and delicious kind of food. What kind of solid figure is this? A. Cone B. Cube C. Cylinder D. Rectangular Prism right circular cone square triangular pyramid surface area
- 17. 17 8. A Cone is a solid figure with a circle as base. Does this statement clearly define what a cone is? A. Yes, because it states the description of a cone. B. Yes, because it states the real definition of a cone. C. No, because it does not refer to the characteristics of a cone. D. No, because it fails to define what really a cone is. 9. What is the formula in getting the area of the lateral surface of a cylinder? A. 2Лr B. 2rh C. 2Лh D. 2Лrh 10. What is the formula in getting the area of the lateral surface of a cone? A. Лrh B. Лrs C. Лr2h D. 2rh 11. What is the formula in getting the surface area of the lateral surfaces of a sphere? A. 4Лr2 B. 4Лr3 C. 4Л2r D. 4Лrh 12. What is the formula in getting the area of the lateral surface of square pyramid? A. 4bs B. 2bs C. 2b/s D. 4s/b 13. It is a polyhedron with twenty surfaces. A. Tricosaquadrihedron B. Nonadecahedron C. Tricosahedron D. Octahedron
- 18. 18 14. Which of the following is the correct formula in finding the surface area of a cone? A. Лr2 + Лr2s B. Лr + Лrs2 C. Лr2 + Лrs D. Лr + Лrs 15. Which of the following is the correct formula in finding the surface area of a cylinder A. 2Лr (r + h)2 B. 2Лr2 + 2Лrh C. 2Лr2 + h D. 2Лr2(r + h) 16. What are the missing parts of this formula in finding the surface area of the square pyramid? SA = s + 2s A. l and h B. s and b C. b and h D. s and h 17. Which is not similar to SA= 2B +LSA A. 2s2 + 4sh B. 2Lw + (2w+2L)h C. bh + Ph D. h2 + Ph 18. Which formula does not belong to the group? A. 4Лr2 B. 4Лrh C. 4Лr D. 4Лr3h 19. The Surface Area of a solid is the area of its surface. Does this statement clearly define what surface area is? A. Yes, because it exactly states the definition of a surface area. B. Yes, because if somewhat states the meaning of what a surface area is. C. No, because it does not refer to what a surface area is.
- 19. 19 D. No, because it lacks something to clearly define what really a surface area is. 20. It is the amount of space enclosed in a figure. A. Area B. Volume C. Surface Area D. Perimeter 21. What is the formula in getting the volume of a triangular prism? A. V= bh/2 x H B. V= l x w x h C. V= BH/2 D. V = 2bh x H 22. What is the formula in getting the volume of a sphere? A. V = 4/3 Лr2h B. V= 4/3 Лr2 C. V= 4/b3r3Лh D. V = 4/3 Лr3 23. What is the formula in getting the volume of a cone? A. V= 1/3Лrh B. V= 1/3Лr2h C. V= 1/3Лr3h D. V= 1/3Лr2h 24. What is the formula in getting the volume of a cylinder? A. V= 2Лr2h B. V= 2Лh C. V= Лr2h D. V= Лr3h 25. What is the formula in getting the volume of a square pyramid? A. V= 1/3 (l x w) + h B. V= 1/3 (l x w)/h C. V= 1/3 (l x w) x h D. V= 1/3 (b x w) x h
- 20. 20 26. A square pyramid in Egypt has an amount of space in its base equal to 12,000 m2 and its altitude is equal to 205m. What is the amount of space enclosed in a pyramid? A. 820,000m2 B. 615,000m2 C. 3,280,000m2 D. 1,230,000m2 27. A basketball has a circumference equal to 29Лcm. Determine what would be the amount of space enclosed in a ball. A. 7,183.17cm3 B. 6,385.04cm3 C. 4,788.78cm3 D. 12,770.08cm3 28. Which formula does not belong to the group? A. Area of Square B. Volume of a cube C. Surface area of a cube D. Area of a circle 29. What formula of a solid figure that has distinct form/part from the group? A. Volume of a Cube B. Volume of a Sphere C. Volume of a Triangular prism D. Volume of a Rectangular prism 30. A sphere is a representation of the earth. Does this statement properly define what a sphere is? A. Yes, because the earth is in a form of sphere. B. Yes, because the sphere is like the shape of the earth. C. No, because the earth is not exactly in a form of sphere. D. No, because the earth alone is not enough to be used to define what really a sphere is all about.
