Structure of plant cell
•Télécharger en tant que PPTX, PDF•
38 j'aime•23,493 vues
This presentation shows the structure of the plant cell. Each and every part of the plant cell has explained in a language easy to understand.
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
Similaire à Structure of plant cell
Similaire à Structure of plant cell (20)
Lecture 1 -_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanisms

Lecture 1 -_cells_structure_and_transport_mechanisms
Structure, chemical_composition_and_function_of_organalles.

Structure, chemical_composition_and_function_of_organalles.
Dernier
Dernier (20)
Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b

Asymmetry in the atmosphere of the ultra-hot Jupiter WASP-76 b
GBSN - Microbiology (Unit 3)Defense Mechanism of the body 

GBSN - Microbiology (Unit 3)Defense Mechanism of the body
development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus

development of diagnostic enzyme assay to detect leuser virus
Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor

Thyroid Physiology_Dr.E. Muralinath_ Associate Professor
Selaginella: features, morphology ,anatomy and reproduction.

Selaginella: features, morphology ,anatomy and reproduction.
LUNULARIA -features, morphology, anatomy ,reproduction etc.

LUNULARIA -features, morphology, anatomy ,reproduction etc.
Early Development of Mammals (Mouse and Human).pdf

Early Development of Mammals (Mouse and Human).pdf
Cot curve, melting temperature, unique and repetitive DNA

Cot curve, melting temperature, unique and repetitive DNA
FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry

FAIRSpectra - Enabling the FAIRification of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry
Bhiwandi Bhiwandi ❤CALL GIRL 7870993772 ❤CALL GIRLS ESCORT SERVICE In Bhiwan...

Bhiwandi Bhiwandi ❤CALL GIRL 7870993772 ❤CALL GIRLS ESCORT SERVICE In Bhiwan...
Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds

Biogenic Sulfur Gases as Biosignatures on Temperate Sub-Neptune Waterworlds
Structure of plant cell
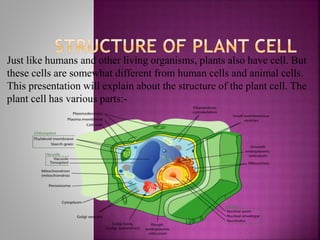
- 1. Just like humans and other living organisms, plants also have cell. But these cells are somewhat different from human cells and animal cells. This presentation will explain about the structure of the plant cell. The plant cell has various parts:-
- 2. MAIN PARTS OF THE PLANT CELL 1: Cytoplasm 2: Nucleus 3: Cell membrane 4: Cell wall 5: Chromosomes 6: Plasmodesmata 7: Filamentous cytoskeleton
- 3. Cytoplasm The jelly- like substance present between the cell membrane and nucleus is known as the cytoplasm. Various other components, or organelles, of cells are present in the cytoplasm. These are Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Ribosomes, Endoplasmic reticulum, Lysosomes, Vacuole, Peroxisomes etc. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colorless.
- 4. Nucleus The nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. The nucleus is generally spherical and located in the centre of the cell. The nucleus contains thread- like structures called chromosomes which carry genes. Gene is a unit of inheritance in living organisms. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, the nucleolus and nuclear pores. Nuclear pores regulate the transport of molecules across the envelope. The nucleolus is a smaller spherical body in the nucleus.
- 6. CELL MEMBRANE The cytoplasm and the nucleus and other parts of the cell are enclosed within the cell membrane which separates cell from one another and also the cell from the surrounding medium. The membrane is porous and allows the movement of substances or materials both inward and outward. The yellow outline in this diagram is the cell membrane.
- 7. Cell wall The cell wall is a very tough, flexible and sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds plant cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition the cell wall is acting as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. The green outline in this diagram is the cell wall:-
- 8. In eukaryotes, nuclear chromosomes are packaged by proteins into a condensed structure called chromatin. This allows the very long DNA molecules to fit into the cell nucleus. Chromosomes are even more condensed than chromatin and are an essential unit for cellular division.
- 9. Plasmodesmata are microscopic channels which allow molecules to travel between plant cells. Unlike animal cells, every plant cell is surrounded by a cell wall. Neighboring plant cells are therefore separated by a pair of cell walls, forming an extracellular domain known as the apoplast. Although cell walls allow small soluble proteins and other solutes to pass through them, Plasmodesmata enable direct, regulated, symplastic intercellular transport of substances between cells.
- 10. Filamentous cytoskeleton The filamentous cytoskeleton is a network of fibers composed of proteins contained within a cell's cytoplasm. It is a dynamic structure, parts of which are constantly destroyed, renewed or newly constructed. Here is a multitude of functions the cytoskeleton can perform: It gives the cell shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, it stabilizes entire tissues, it can actively contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate, it divides chromosomes. It is involved in the division of a mother cell into two daughter cells etc. The functions which this cytoskeleton can perform depend on the type of cell and the organism.
- 12. Thank you This presentation has been made by:- Anhad Naad Class- 8th-A Roll no.- 6