Ast Observing Project Tr03, 2010 Spring
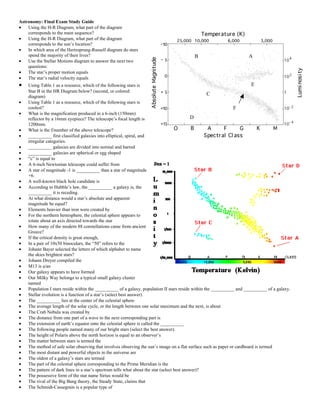
- 1. Astronomy: Final Exam Study Guide • Using the H-R Diagram, what part of the diagram corresponds to the main sequence? • Using the H-R Diagram, what part of the diagram corresponds to the sun’s location? • In which area of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram do stars spend the majority of their lives? B A • Use the Stellar Motions diagram to answer the next two questions: • The star’s proper motion equals • The star’s radial velocity equals • Using Table 1 as a resource, which of the following stars is E Star B in the HR Diagram below? (second, or colored diagram) C • Using Table 1 as a resource, which of the following stars is coolest? F • What is the magnification produced in a 6-inch (150mm) reflector by a 16mm eyepiece? The telescope’s focal length is D 1200mm. • What is the f/number of the above telescope? • __________ first classified galaxies into elliptical, spiral, and irregular categories. • __________ galaxies are divided into normal and barred • __________ galaxies are spherical or egg shaped • “c” is equal to • A 6-inch Newtonian telescope could suffer from • A star of magnitude -1 is __________ than a star of magnitude +6. • A well-known black hole candidate is • According to Hubble’s law, the __________ a galaxy is, the __________ it is receding. • At what distance would a star’s absolute and apparent magnitude be equal? • Elements heavier than iron were created by • For the northern hemisphere, the celestial sphere appears to rotate about an axis directed towards the star • How many of the modern 88 constellations came from ancient Greece? • If the critical density is great enough, • In a pair of 10x50 binoculars, the “50” refers to the • Johann Bayer selected the letters of which alphabet to name the skies brightest stars? • Johann Dreyer compiled the • M13 is a/an • Our galaxy appears to have formed • Our Milky Way belongs to a typical small galaxy cluster named • Population I stars reside within the __________ of a galaxy, population II stars reside within the __________ and __________ of a galaxy. • Stellar evolution is a function of a star’s (select best answer) • The __________ lies at the center of the celestial sphere • The average length of the solar cycle, or the length between one solar maximum and the next, is about • The Crab Nebula was created by • The distance from one part of a wave to the next corresponding part is • The extension of earth’s equator onto the celestial sphere is called the __________ • The following people named many of our bright stars (select the best answer). • The height of Polaris above the north horizon is equal to an observer’s • The matter between stars is termed the • The method of safe solar observing that involves observing the sun’s image on a flat surface such as paper or cardboard is termed • The most distant and powerful objects in the universe are • The oldest of a galaxy’s stars are termed • The part of the celestial sphere corresponding to the Prime Meridian is the • The pattern of dark lines in a star’s spectrum tells what about the star (select best answer)? • The possessive form of the star name Sirius would be • The rival of the Big Bang theory, the Steady State, claims that • The Schmidt-Cassegrain is a popular type of
- 2. • The star Aldebaran lies in which constellation? • The study of the origin, structure, evolution, and destiny of the universe is • The sun travels about ____ along the ecliptic each day. This apparent motion of the sun is caused by earth’s __________. • The theory of rapid acceleration just after the Big Bang occurred is termed • This astronomer compiled 110 of the skies brightest deep sky objects in a list. • This astronomer created the magnitude scale. • Vega is a bright star in which constellation? • What constellation is termed the Great Bear? • What constellation is termed the Hunter? • What does the Doppler Effect indicate about our universe? • What form of electromagnetic radiation has the longest wavelengths? • What is albireo? • What is the general term for the creation of elements within a star? • What is the major element that formed the stars and sun? • What is the name of the point directly overhead? • What is the name of the sun’s direction of motion in space? • What is the significance of the zodiac? • What magnitude is the approximate limit of human vision? • What phenomenon accounts for a 26,000-year shift in the position of the north celestial pole? • What star will be the North Star in 14,000 AD? • What use do Cepheid variable stars have for astronomers? • Where is our sun in the following list of stellar evolution milestones? • Which celestial coordinate is analogous to longitude on a terrestrial globe? • Which celestial coordinate ranges 90º above or below the celestial equator? • Which celestial coordinate ranges from 0-24 hours along the celestial equator? • Which constellation is considered the 13th member of the zodiac • Which of the following are apparent outbursts or arches of gases visible along the edge of the sun? • Which of the following are north circumpolar constellations? • Which of the following describes an absorption spectrum? • Which of the following describes the oscillating Big Bang model of the universe? (best answer) • Which of the following is a famous planetary nebula? • Which of the following is used to measure the distances to nearby stars? • Which of the following stars is brightest? • Which star has the greatest proper motion? • Which type of telescope uses only lenses to collect light? • Which types of stars were originally thought to emit signals from an alien civilization? • Why are astronomers searching for missing mass? • Your fist measures an angle of about _____ on the sky? Table 01 Star Apparent Magnitude Spectral Class Distance (light years) Absolute Magnitude Barnard’s Star 9.56 M3 6 13.4 Betelgeuse 0.50 M2 1400 -7.2 Procyon 0.38 F5 11.4 2.6 Rigel 0.12 B8 1400 -8.1 Sirius -1.46 A1 8.6 1.4 Sirius b 8.11 White Dwarf 8.6 11.3 Spica 0.98 B1 220 -3.2 Vega 0.03 A0 25 0.6 HR Diagram for underlined questions (right)
