The Periodic Table
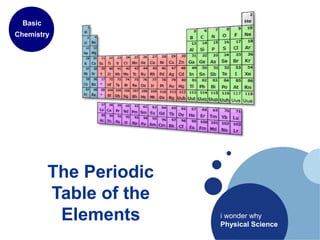
- 1. The Periodic Table of the Elements Basic Chemistry i wonder why Physical Science
- 2. In your lab notebook, please answer as best you can: 1. What is an atom which has donated an electron in order to form a full energy level called? What charge does it have? • Ion (cation); positive charge 2. What does C6H12O6 represent? • A sugar molecule of 6 Carbon atoms bonded to 12 Hydrogen and 6 Oxygen atoms 3. Draw a Bohr Model diagram of a stable, neutral Aluminum atom. 4. Draw a Lewis Dot Structure of a stable, neutral Aluminum atom. 5. What is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas? • The boiling point (varies with each substance) Bonus Question: Is it possible for a liquid to turn into a gas without boiling? Yes! (evaporation) Review Quiz 4
- 3. Chemical Bonding - Ionic, Covalent, Metallic Review
- 4. All matter is made of atoms Atoms of the same kind are pure elements with distinct properties What gives each element its unique characteristics? What makes gold soft and shiny? What causes salt to form into crystals? Why is Helium "lighter than air" MatterMatter Interactive Periodic TableInteractive Periodic Table Review Answer: The number and arrangement of particles in each atom determines the properties of the elements.
- 5. • Rows (called periods) highlight the repeating nature of elements • Displayed in order of increasing atomic number • Share the same number of occupied electron energy levels • Atomic radius decreases as you move left to right (more protons = tighter pull) • Ionization energy increases left to right (tendency to capture electrons) • Columns (called groups) have similar chemical & physical properties • Same # of valence electrons (electrons in outermost shell) Periodic Table of the Elements - What patterns do you see?
- 6. Periodic Table of Elements - Bohr Diagrams • What similarity do you see among periods (horizontal rows)?
- 7. Periodic Table of Elements - Lewis Dot Structures • Can you see the patterns among the groups (vertical columns)?
- 8. Three General Classes of Elements • Metals ~ 80% of all elements • Shiny, solid (except Hg) • Malleable (soft, can reshape) • Conduct heat & electricity • Ductile (drawn into thin wires) • Metalloids - only 7 • Have properties of both metals and nonmetals • All are solids • Semiconductors • Nonmetals - 2nd largest group • Dull (not shiny) • Brittle (shatter, not bendable) • Good insulators • More than half are gases
- 9. Group 1: Alkali Metals • Physical Properties • Soft (can be cut with knife) • Shiny and silver • Low densities Bohr Diagram Lewis Structure • Chemical Properties • Have 1 valence electron • VERY REACTIVE! – Usually lose 1 electron in reactions – More stable (happy) as cations • Never found as pure elements in nature • Must be stored under oil in sealed containers to prevent violent reactions Sodium in Water
- 10. Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals • Physical Properties • Hard • Gray-white • Good electrical conductors Bohr Diagram Lewis Structure • Chemical Properties • Have 2 valence electrons • Less reactive than alkali metals, but more than the other metals • Usually react by losing both valence electrons to form +2 cations • Never found as pure elements in nature Berryllium Magnesium Calcium Strontium Barium Radium Sr Calcium & Barium in Water
- 11. Group 3-12: Transition Metals & Lanthanide and Actinide Series • Physical Properties • Form colored compounds • Most are hard & shiny • Good electrical conductors Bohr Diagram Lewis Structure • Chemical Properties • have 1 or 2 valence electrons • Less reactive, but unpredictable reactions • Can help speed up reactions (catalysts) • Form cations or metallic bonds Au * Lanthanides **Actinides Copper & Zinc Reactions
- 12. Group 13: Boron Family • Physical Properties • Boron (metalloid) is hard, black solid and very brittle • Good conductor at high temps • Poor conductor at low temps • Al, Ga, In, & Ti are metals • mixed conductivity, soft/malleable Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Have 3 valence electrons • Reactivity varies within this group • General form cations and ionic bonds Boron Aluminum Gallium Indium Thallium Lewis Structure Al Metal Salts Flame Test
- 13. • Physical Properties • Carbon (nonmetal) is found in nearly every living thing • Elemental forms in nature: – Graphite & diamonds • Si & Ge are metalloids • Sn & Pb are metals Group 14: Carbon Family Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Have 4 valence electrons • May gain or lose electrons • Often covalently shares 4 electrons when reacting with other elements Carbon Silicon Germanium Tin Lead Lewis Structure Bronze from Tin & Copper Ge
- 14. • Physical Properties • N & P are nonmetals • Nitrogen is a gas at room temp • All others are solids • As & Sb are metalloids • Bismuth is a metal Group 15: Nitrogen Family Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Have 5 valence electrons • Elements vary in reactivity Nitrogen Phosphorus Arsenic Antimony Bismuth Lewis Structure Phosphorus video As Phosphorus Bismuth
- 15. • Physical Properties • Oxygen is a nonmetal gas • Most abundant element in Earth's crust (1/5 Earth's atmosphere) • Sulfur is a yellow, nonmetal solid • Smells like rotten eggs Group 16: Oxygen Family Bohr Diagram • Selenium is a nonmetal solid • Conducts electricity with sunlight • Te & Po are metalloids • Chemical Properties • Have 6 valence electrons • Elements vary in reactivity Oxygen Sulfur Selenium Tellurium Polonium Lewis Structure Sulfuric Acid on Sugar Cubes Tellurium S
- 16. • Physical Properties • Fluorine & Chlorine are greenish- yellow gases, toxic in their pure form • Bromine is a smelly, reddish-brown liquid that causes burns • Iodine is a dark-gray solid • Astatine is a radioactive solid Group 17: Halogens P:53 N:74 Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Have 7 valence electrons • Generally gain (to form +1 anions) or share 1 electron • All very reactive Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Astatine Lewis Structure Halogen Reactions I
- 17. • Physical Properties • All are gases easily found in the atmosphere • Each noble gas creates a different color in "neon" lights Group 18: Noble Gases Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Have 8 valence electrons (except He) • Have full valence shells, so NOT very reactive • Sometimes called “inert” Helium Neon Argon Krypton Xenon Radon Lewis Structure Lead Balloon Demo Ar
- 18. • Physical Properties • Most abundant element in the universe • Doesn't fit in any group • Invisible gas (nonmetal), very flammable • Pure hydrogen is lighter than air Hydrogen Bohr Diagram • Chemical Properties • Has only 1 valence electron • Forms many different compounds • Has NO neutrons Lewis Structure Hydrogen Bomb H
Notes de l'éditeur
- All because of the atoms that form them - different atoms have different properties that react depending on their number of protons, electrons & neutrons
- Like the days of the month, the chemical elements can be arranged in a way that shows a repeating, or PERIODIC pattern. DRY ERASE EXERCISE Patterns: atomic # increases as you move left to right Groups share same # of valence electron Energy levels increase as you move down a group
- luster is a measure of shinyness
- Common uses: Sodium chloride is table salt, lithium in batteries, Cesium in clocks, potassium in fireworks, liquid detergents, fertilizers and vitamins, rubidium in photocells (motion detectors) Pure sodium in water = flames
- Common uses: Beryllium in high-speed aircraft, missiles, spacecraft & satellites, Magnesium combined with other metals to form strong but lightweight alloys. Calcium in limestone & marble, essential for strong teeth & bones, Strontium gives fireworks their red color, barium in ceramics and some types of glass (and GI x-rays). Radium is radioactive (too many protons or too few neutrons causes unstable atom where particles are released) and used in cancer chemotherapy.
- Elements with atomic number greater than 92 are manufactured in laboratories and are highly unstable (radioactive)
- Common uses: Boron makes boric acid (mild antiseptic), borax (laundry water softener & ant killer) and a small component of silly putty - produces green flame when burned Aluminum (most abundant metal in Earth's crust) is soft and light - found in baseball bats, drink cans, bikes & cooking utensils. Gallium is solid at room temp but melts in your hand - used in electronic devices Indium also has a low melting point - used in alloys in thermometers and flat-screen TV's Thallium is poisonous - not many uses, but sometimes mixed with other compounds to form types of glass.
- Common uses: Graphite in pencils and powder lubricant, silicon comprises sand and used in semiconductors (computer chips), Tin lines steel food cans, mixed with copper makes bronze, Lead resists corrosion - used in ceramics, plumbing, glassmaking
- Common uses: Nitrogen (largest component of air), builds proteins in cells, DNA/RNA Phosphorus - highly reactive/corrosive solid, also found in human body, used in match heads (very flammable) Arsenic - pesticides, pyrotechnics Antimony - hardens & strengthens lead, semiconductors, batteries Bismuth - carrier for uranium fuel in nuclear reactors, fire extinguishing systems, cosmetics, medicine
- Common uses: Sulfur - food preservative, rubber product, bleaching & refrigeration Selenium - solar cells, light meters, photocopiers Tellurium - semiconductors, ceramics, tinting glass Polonium - rare radioactive element, named after Poland (discoverers Marie & Pierre Curie's native country)
- Common uses: Fluorine - fluoride toothpaste, teflon Chlorine - table salt, disinfectant, bleaching of paper product or clothing Bromine - dye, disinfectant, photographic chemicals Iodine - essential for thyroid function
- Common uses:
- The Eagle Nebula. (External Sample)By weight, 75 percent of the visible universe is hydrogen. Ordinarily it is a colorless gas, but vast quantities of it in space absorb starlight, creating spectacular sights such as the Eagle Nebula (seen by the Hubble Space telescope). Found in: water, sugar, ammonia, rocket fuel, stars & nebulae, and air
- Beauty salon peroxide to show how difference in concentration affects rate of reaction
- Like the days of the month, the chemical elements can be arranged in a way that shows a repeating, or PERIODIC pattern. DRY ERASE EXERCISE Patterns: atomic # increases as you move left to right Groups share same # of valence electron Energy levels increase as you move down a group
