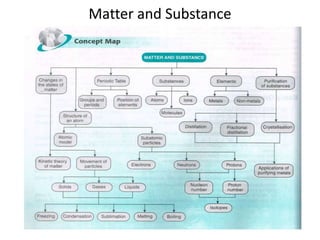
Science assignment- Form 4 Chapter 4
- 2. Kinetic Theory of Matter 1) Kinetic Theory of Matter states that • Matter is made up of tiny and discrete particles. • The particles are always moving in random motion. • The moving energy is called the kinetic energy of particles. • The kinetic energy of particles depends on the temperature of matter and increases when the temperature increases. 2) Importance of Kinetic Theory of Matter: a) It explains the movement of particles in three states, which are solid, liquid and gaseous states. b) It explains the basic structure of matter.
- 3. Interconversion of the Three States of Matter
- 5. Kinetic Theory of Matter can be applied to explain the changes in the states of matter through the processes as shown.
- 8. Structure of an Atom •Matter is made up of tiny, discrete particles called atoms. •An atom is the smallest particle in an element which is able to react chemically. •An atom is indivisible. •It is impossible to observe an atom with the naked eye. However, you may be able to see a crude picture of atoms taken with an electron microscope called the scanning tunnelling microscope. The atoms are magnified millions of times as shown in Photograph 4.1.
- 9. Subatomic Particles of Atoms • An atom is made up of three subatomic particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. • The atom consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by subatomic particles known as electrons as shown in the Figure 4.8.
- 10. Properties of Subatomic Particles
- 11. 4.3 Proton Number and Nucleon Number in Atoms of Elements • An element is a substance which cannot be split by any known chemical method into two or more simpler substances. • An element is made up of atoms, for example, element iron contains iron atoms. • The element either occur naturally or are man-made by scientists. • A neutral atom contains an equal number of protons and electrons as shown in Table 4.5. Element Number of protons Number of electrons Hydrogen 1 1 Oxygen 8 8 Iron 26 26 Table 4.5 Neutral atoms
- 12. • Proton number = number of protons = number of electrons of a neutral atom • Nucleon number = number of protons + number of neutrons • Number of neutrons = nucleon number – proton number • An atom can be represented by the symbol as shown in Figure 4.10 :
- 13. Isotopes • Isotopes are atoms of the same element and contain the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. • Each isotopes is named by inserting the nucleon number after the name of the element. • Example of hydrogen isotopes include a) Hydrogen-1 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutron b) Hydrogen-2 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 1 neutron c) Hydrogen-3 : a hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 2 neutrons
- 14. Table below shows the isotopes for different elements.
- 15. Classification of Elements in the Periodic Table • In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, introduced a table which was known as the Periodic Table. It contained all 63 elements in the table were arranged from left to right in the order of their increasing atomic masses. • The importance of the Periodic Table : – Important in systematic and methodical study of elements. – Help us to determine the properties of elements. – Uses to forecast the properties and uses of particular element.
- 17. Properties of Substances – Atoms, Molecules and Ions • An atom is the smallest, indivisible particle of an element which can take part in a chemical reaction. • A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same type or different types which are chemically combined together. • There are two types of molecules : – Molecules of an element ( combination of the same type of atoms. For example : oxygen, hydrogen and chlorine) – Molecules of a compound ( combination of the different types of atoms. For example : water, carbon dioxide and ammonia) • An ion is when an atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes a charged particle. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positive ion and it has more protons than electrons but if gains electrons, it becomes a negative ion which has more electrons than protons.
- 18. Comparison of properties among three groups of substances
- 19. Metals and non-metals • Most elements can be classified as metals or non-metals. • Examples of metals include iron, sliver, copper, aluminium, gold and tin. • Argon, hydrogen gas and diamonds are examples of non-metals. • Uses of metals and non-metals in daily life : Examples of Metals • Iron is used in making cars, bridges and railway tracks. • Sliver is often used to make jewellery. • Copper is used in make wires for electric circuits. • Aluminium is used to make power lines as it is very light. Examples of non-metals •Diamond are mostly used to make beautiful jewellery. •Phosphorus is used to make matchstick tips. •Sulphur is a key ingredient in making paint. •Graphite is used to manufacture lubricants.
- 20. Similarities and differences between metals and non-metals
- 21. Method of Purification • Purification is a process in which impurities are separated from a particular substance so that it becomes a pure substance. • Purification is carried out using diverse physical techniques. No chemical changes take place. • Purification is carried out through: – Distillation – Crystallisation
- 22. Distillation • Distillation involves the evaporation of a liquid to form a gas or a vapour. The vapour is then condensed to obtain a pure liquid known as distillation. © TutorVista (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xxNfJLMNS4E)
- 23. Crystallisation • Crystallisation is a process carried out to obtain crystals from a saturated solution. © KClassScienceChannel (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QdwKhbtzsug)
- 24. Characteristics of substances to the purification methods used.
- 25. Conclusion • As conclude, matter exists in three states – solid, liquid and gas. • Heat energy is absorbed during boiling, melting and sublimation ; Heat energy is released during freezing and condensation. • An atom is made of three subatomic particles – protons, neutrons and electrons. • Isotopes are atoms of an element that have the same proton number but different nucleon numbers. • The Periodic Table is a table of elements arranged from left to right in the order of their increasing proton numbers. • Metals are hard, shiny, ductile, malleable and can conduct electricity and heat. • Non-metals are dull, brittle and poor conductors of electricity and heat. • Purification carried out through distillation and crystallisation.