Foundations grp 1
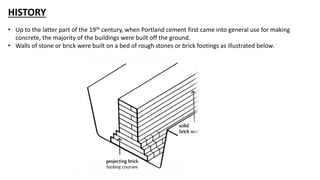
- 1. HISTORY • Up to the latter part of the 19th century, when Portland cement first came into general use for making concrete, the majority of the buildings were built off the ground. • Walls of stone or brick were built on a bed of rough stones or brick footings as illustrated below.
- 2. HISTORY • Local experiences of the behaviour of soil and rocks under the load buildings gave sufficient information to choose a foundation of required depth and spread of this method of construction. • From the beginning of the 20th century concrete was increasingly used as a foundation base • However, initially it was used as a base for laying stones . This massive and unnecessary form of construction was accepted practice for some years. • The move from the practical, common sense approach of the 19th century to the closely regulated system resulted in some foundations so massive as to exceed the anticipated combined loads onto the foundations. • The tendency to over design has been exacerbated by the willingness of the building owners to seek compensation for damage, caused by claimed negligence of architects, engineers and builders who in order to avoid paying for such claims tended to over design.
- 3. Definition A foundation is that part of a building structure which is in direct contact with the ground to which the weight of the structure and other loads of the structure are transmitted. The soil or rock on which the base directly rests is called a natural foundation while the wall or column base itself is called an artificial foundation.
- 4. Functions of Foundations Following are the main functions of foundations : 1.To transmit and distribute the total load of the structure to a larger area of underlying support. 2.To prevent differential settlement of the structure. 3.To provide stability to the structure.
- 5. STRIP FOUNDATION The commonest type adopted on one or two storey buildings on firm, non- shrinkage sub‐soils such as gravel. Normally consists of a continuous strip of concrete which provides a continuous ground bearing for load‐bearing walls.
- 6. TRADITIONAL STRIP FOUNDATION The wall footing is a continuous slab strip along the length of the wall. Stone, brick, reinforced concrete etc. is used for the construction of wall foundations.
- 7. WIDE STRIP FOUNDATION • Wide strip opted for where the soil has a low bearing capacity such as in marshy, soft • Clay soils and filled areas.
- 8. DEEP STRIP FOOTING This type of strip footing to be used when depth of more than 900mm has to be reached in clayey or marshy soils.
- 9. SHALLOW FOUNDATIONS Shallow foundations are also called spread footings or open footings. The 'open' refers to the fact that the foundations are made by first excavating all the earth till the bottom of the footing, and then constructing the footing. RAFT OR MAT FOUNDATIONS These are large concrete slab laid on the ground to support columns and walls The slab is spread out under the entire building or at least a large part of it which lowers the contact pressure compared to the traditionally used strip or trench footings. Raft Foundations, also called Mat Foundations, are most often used when basements are to be constructed Mat Foundations are also used where the soil is week, and therefore building loads have to be spread over a large area, or where columns are closely spaced, which means that if individual footings were used, they would touch each other. They are usually used where the strata is unstable with risky of the building sinking They are also suitable where the are movements of strata for example in mining areas where dynamites are normally used
- 10. How raft foundation works • A raft foundation spread the weight of the building on the whole ground floor area • These foundations are placed on the hard rock or firm strata to ensure minimum movement • They usually have thick edges for stability • The foundation may be stiffened by inserting ribs and beams for extra strength and rigidity
- 11. Where raft foundations is used • Heavy buildings such as commercial buildings with large loads • Low bearing capacity soils to spread the loads and improve stability • When the ratio of footings to the total floor area is high • When footing have a risk of overlapping due to closeness of walls to each other
- 12. Advantages of raft foundation • The raft can act as a foundation and slab at the same time saving material and time • Less excavation is required • Reduces differential settlement an hence less risky of cracking Disadvantage • Unsuitable for point loads
- 13. Raft foundation on multistory Cont…. • The ground is excavated up to the firm strata or hard core for stability • Reinforcements are laid on the excavated area and concrete is poured • Ground beams can be introduced
- 14. Raft foundations on multistory buildings
- 15. Materials Used for Raft Foundation Construction Here are some materials used for the erection of Raft foundation- • Formwork • Spacer • Reinforcement • Concrete. Construction Process of Raft foundation Key steps of Raft foundation construction are noted below. 1. Identify the desired depth at which foundation is to be provided. 2. Excavate soil up to the required depth. 3. Compact the soil. 4. Provide a waterproofing membrane. 5. Pour 3” of plane cement-sand paste. 6. Lay reinforcement maintaining the required spacing using spacers. 7. Pour concrete to the desired depth. 8. Curing.
- 16. 1Flat Plate Mat • This is the simplest form of raft foundation. This type of mat is used when the columns and walls are uniformly spaced at small intervals and the subjected loads are relatively small. Reinforcement is placed in both directions and more reinforcement is required at the column locations and load-bearing walls. The thickness of this types of raft foundation is generally restricted within 300mm for economic reason. A thicker slab would not be economical.
- 17. Piled Raft • This type of raft foundation is supported on piles. A piled raft is used when the soil at a shallow depth is highly compressible and the water table is high. Piles under raft help in reducing settlement and provides resistance against buoyancy.
- 18. Rigid Frame Mat/Cellular Raft Foundation • In this type of raft, the foundation walls act as a deep beam. Rigid frame mat is referred when columns carry extremely heavy loads and the connecting beams exceeds 90cm depth. Here two concrete slabs are placed, one on top of another and connected with foundation walls in both directions and thus forms a cellular raft foundation. This type of raft is very rigid and is economical when the required slab thickness is very high.
- 19. • Group 1 Building construction
- 20. Raft foundations • These are large concrete slab laid on the ground to support columns and walls • The slab is spread out under the entire building or at least a large part of it which lowers the contact pressure compared to the traditionally used strip or trench footings.
- 21. Raft foundations
- 22. Raft foundation cont.. • They are usually used where the strata is unstable with risky of the building sinking • They are also suitable where the are movements of strata for example in mining areas where dynamites are normally used
- 23. How raft foundation works • A raft foundation spread the weight of the building on the whole ground floor area • These foundations are placed on the hard rock or firm strata to ensure minimum movement • They usually have thick edges for stability • The foundation may be stiffened by inserting ribs and beams for extra strength and rigidity
- 24. Where raft foundations is used • Heavy buildings such as commercial buildings with large loads • Low bearing capacity soils to spread the loads and improve stability • When the ratio of footings to the total floor area is high • When footing have a risk of overlapping due to closeness of walls to each other
- 25. Advantages of raft foundation • The raft can act as a foundation and slab at the same time saving material and time • Less excavation is required • Reduces differential settlement an hence less risky of cracking
- 26. Disadvantage • Unsuitable for point loads
- 27. Raft foundations on multistory buildings
- 28. Raft foundation on multistory Cont…. • The ground is excavated up to the firm strata or hard core for stability • Reinforcements are laid on the excavated area and concrete is poured • Ground beams can be introduced
- 29. Pile foundations
- 30. Piled Foundation Classification of Piles ~ can be by basic design function or by their method of construction :-
- 31. DEFINITION • Pile foundation is kind of deep foundation, is actually a slender column or long cylinder made of materials such as concrete or steel which are used to support the structure and transfer the load at desired depth either by end bearing or skin friction • A foundation is described as 'piled' when its depth is more than three times its breadth.
- 32. WHEN TO USE •Heavy and un-uniform loads from superstructure are imposed. •When the groundwater table is high. •Other types of foundations are costlier or not feasible. •When the soil at shallow depth is compressible. •When there is the possibility of scouring, due to its location near the river bed or seashore, etc. •When there is a canal or deep drainage systems near the structure. • When soil excavation is not possible up to the desired depth due to poor soil condition. • When it becomes impossible to keep the foundation trenches dry by pumping or by any other measure due to heavy inflow of seepage.
- 33. PILE FOUNDATIONS
- 35. FACTORS AFFECTING SELECTION • Type and loads from the superstructure. • Properties of soil. • The depth of the soil layer capable of supporting the piles. • Variations in length of pile required. • Availability of materials. • Durability required. • Available equipment for pile driving. • Budget. • The depth of water level and intensity of underground water flow. • Types of surrounding structures.
- 36. CAUSES OF PILE FOUNDATION FAILURE 1.Load implied on the pile is greater than designed load. 2.Defecting workmanship. 3.Dislocation of reinforcement of pile. 4.End bearing pile resting on soft strata. 5.Faulty soil investigation. 6.Selecting the wrong type of pile. 7.Under-reinforcement of the pile. 8.A decay of piles. (like attack of insects, corrosion etc.) 9.Deformation of piles due to lateral loads. 10.Incorrect assessment of pile capacity. 11.Not considering lateral forces for designing of piles.
- 37. Pile foundations
- 38. DEFINITION • Pile foundation is kind of deep foundation, is actually a slender column or long cylinder made of materials such as concrete or steel which are used to support the structure and transfer the load at desired depth either by end bearing or skin friction • A foundation is described as 'piled' when its depth is more than three times its breadth.
- 39. WHEN TO USE •Heavy and un-uniform loads from superstructure are imposed. •When the groundwater table is high. •Other types of foundations are costlier or not feasible. •When the soil at shallow depth is compressible. •When there is the possibility of scouring, due to its location near the river bed or seashore, etc. •When there is a canal or deep drainage systems near the structure. • When soil excavation is not possible up to the desired depth due to poor soil condition. • When it becomes impossible to keep the foundation trenches dry by pumping or by any other measure due to heavy inflow of seepage.
- 40. PILE FOUNDATIONS
- 42. Piled Foundation Classification of Piles ~ can be by basic design function or by their method of construction :-
- 43. Pile Installation Methods 1.Boring methods (non-displacement piles Continuous flight auger (CFA): If boring and pouring takes place simultaneously during pile driving Negative skin friction
- 44. Pile Installation Methods 2.Pile driving methods • Pile driving using hammer • Dropping weight: A hammer with approximately the weight of the pile is raised to a suitable height and is released to strike the pile head • Vibration: The amplitude of vibration used here should be sufficient to break the skin friction on sides of pile. This is bested suited for sandy or gravelly soils. • Jacking (only for micro piles): To install jacking piles, Hydraulic rams are used to push piles into ground • Jetting: To aid the penetration of piles in to sand or sand gravel, water jetting can be employed.
- 45. DIAMETER • Pile diameter: 600 to 3500 mm depending on soil diameter and consistency. Pile depth: 60 to 100 m depending on soil diameter and consistency. • 40 meters deep , in soft ground or in aggressive or contaminated soils.
- 46. FACTORS AFFECTING SELECTION • Type and loads from the superstructure. • Properties of soil. • The depth of the soil layer capable of supporting the piles. • Variations in length of pile required. • Availability of materials. • Durability required. • Available equipment for pile driving. • Budget. • The depth of water level and intensity of underground water flow. • Types of surrounding structures.
- 47. CAUSES OF PILE FOUNDATION FAILURE
- 48. CAUSES OF PILE FOUNDATION FAILURE 1.Load implied on the pile is greater than designed load. 2.Defecting workmanship. 3.Dislocation of reinforcement of pile. 4.End bearing pile resting on soft strata. 5.Faulty soil investigation. 6.Selecting the wrong type of pile. 7.Under-reinforcement of the pile. 8.A decay of piles. (like attack of insects, corrosion etc.) 9.Deformation of piles due to lateral loads. 10.Incorrect assessment of pile capacity. 11.Not considering lateral forces for designing of piles.
- 49. UNDER PINNING • This is a process of strengthening foundations of existing structures. • The abovementioned process can be used to repair faulty foundations. • Also if one desires to increase the storeys of a structure.
- 50. REASONS FOR UNDER PINNING • 1. Uneven Settlement - this could be caused by uneven loading of the building, unequal resistance of the soil action of tree roots or cohesive soil settlement. • Increase in Loading -this could be due to the addition of an extra storey or an increase in imposed loadings such as that which may occur with a change of use • Lowering of Adjacent Ground -usually required when constructing a basement adjacent to existing foundations
- 51. TYPES OF UNDER PINNING • Pile method. • Pier and beam method. • Cantilever needle beam method.
- 52. PILE METHOD • This method is effectively applicable in areas with clay soils and in water logged areas. • This method greatly relieves the load previously imposed on the existing foundation. • The maximum depth possible is 15m • A needle penetrates through the wall that is in turn connected to the piles as illustrated below.
- 53. PILE METHOD
- 54. PILE METHOD
- 55. PROCEDURE • Piles are driven at regular intervals along both side of wall • The piles are then connected by concrete or steel needle which penetrates through the existing wall.
- 56. ADVANTAGES • Suitable for sites with restricted access. • It is faster than the traditional underpinning. • It can support great loads.
- 57. DISADVANTAGES. • The piles should be properly reinforced to withstand handling stresses during transit. • Foundations of the adjacent structures can be affected by the vibrations generated during the process of driving the piles into the ground.
- 58. PIER AND BEAM METHOD. • It is also termed as a base and beam method. • It came as a successor of mass concrete method which had limitations. • RC beams are placed to transfer the load to the base or piers. • The size and depth of beams is based on the soil’s bearing capacity. • It is a thrift method for depths shallower than 6m.
- 59. PIER AND BEAM METHOD.
- 60. PIER AND BEAM METHOD.
- 61. PIER AND BEAM METHOD.
- 62. CANTILEVER NEEDLE BEAM METHOD • This method is used to repair existing wall foundations either internal or external.
- 63. PROCEDURE. • Construction of piles
- 66. CANTILEVER NEEDLE BEAM METHOD
- 67. ADVANTAGES • Access from one side • Occupants can use the property during construction • Cantilever beam can be at a higher level if the existing foundation is too deep • Suitable for restricted areas
- 68. DISADVANTAGES • There is need for specialised equipment • It requires skilled personnel to be done
- 69. References • Building Construction Illustrated 4th edition F. Ching • Construction Technology by Chudley and Greeno fourth Edition(2)