Contenu connexe Similaire à Next Generation Network Automation (20) 2. © 2018 Nokia2
Next Generation
Network Automation
Tutorial at IEEE IM 2019
Laurent Ciavaglia
April 2019
3. © 2018 Nokia3
General messages
Confidential
• First tutorial on this topic, ask for your indulgence
• Not comprehensive, many missing areas and projects (e.g. ONAP)…
– Next tutorial
• Work from many inside and outside Nokia. My deep thanks.
• Learn with you
• Interactive, open loop,
• Don’t hesitate to ask questions, most importantly if I’m wrong
• Slides will be available after the session at: https://www.slideshare.net/LaurentCiavaglia
or send me an email at laurent.ciavaglia@nokia.com
• 30 min. break at 10:30 ?
4. © 2018 Nokia4
Agenda
Confidential
• Motivations
• Architectural Vision
• ETSI ZSM
• The Automation Journey
• The Automation Continuum
• Next Generation Platform as a Service
• Concluding remarks
• Q & A
6. © 2018 Nokia6
• Focus on “elephant” mass-
market services that can justify
the cost & time
• Expensive and slow to get new
service to market due to
complex OSS/BSS systems, and
manual processes
The future of digital service delivery from Digital Service Providers (DSPs)
New Markets | Faster New Services | Faster Time to Revenue | Higher Customer Satisfaction
• Webscales deliver rapid,
personalized, on-demand
services - leverage cloud
automation but mainly over
the top delivery
• CSPs starting to evolve with
NFV/SDN to speed the
delivery of network services
Traditional CSP
Cloud Transformation
Future DSP
• Digital experience: broad array of
new services that combine cloud
services and network resources
• Tailor virtual networks for each
use case: latency, bandwidth,
security, choice of functions
• Agile network: services are rapidly
trialed, deployed & scaled
• Open platform: ecosystem of
cloud and network players
Source: Analysys Mason
7. © 2018 Nokia7
Network Slicing - The foundation for future value creation.
Network slices are end-to-end ‘virtual private services’
Composable Network
& Service Resources
Application
Logic
Virtual Network
Functions
Cloud
Infrastructure
SW-Defined
Connectivity
Service
Request
Slice Request
Attributes
Latency:
Throughput:
Reliability:
Mobility:
Geography:
Security:
Analytics:
Cost profile:
…
Network & Cloud
Orchestration
Service Specific Network Slices
4K,VR
Automated
composition
& operations
Service
Delivery
High performance
localized delivery
UEAccessCore TransportApplication
E2E virtual network optimized for specific tenant, service or service class with dynamic
adaption and automated monitoring and control
Augmented
Services
8. © 2018 Nokia8
Network and Service Automation are essential to DSP economics
Without E2E automation NFV/SDN & network slicing add significant cost and complexity
9. © 2018 Nokia9
The shift: Transformation from CSP to DSP requires a new automation stack
Evolution
DIGITAL SERVICE
LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT (LCM)
OPERATIONAL SUPPORT
SYSTEMS (OSS)
BUSINESS SUPPORT SYSTEMS (BSS)
PHYSICAL
RESOURCES AND INFRASTRUCTURE
DIGITAL STOREFRONT
CUSTOMER AND BUSINESS AUTOMATION
VIRTUAL & PHYSICAL
RESOURCES AND INFRASTRUCTURE
CLOUDINFRA&IT
PROPRIETARYTELECOM
TRADITIONAL DIGITAL Service Provider
Managing complexity and agility of digital services requires fully automated delivery platform
• Service operations
• Network & cloud resource management
• Data layer management
10. © 2018 Nokia10
The essential value path from CSP to DSP
Containing operations
cost of NFV Life Cycle
Management (LCM)
NFV Deployment
at Scale
Network
Objectives
Automation
Imperatives
Rapidly adapting VNF
scale, placement &
resilience to conditions
Containing operations
cost of NFV LCM
Efficient
Dynamic NFV
Continuously adapting
resource allocations
across network slices
for SLA performance
Containing operations
cost of NFV LCM
Operator 5G Service
Delivery Slices
Digital Partner
Delivery Slices
Instantly fulfilling on-
demand network slice
service requests
Containing operations
cost of NFV LCM
Resource allocations
across network slices
Operations Automation Automated Value Creation
VNF scale, placement
& resilience
VNF scale, placement
& resilience
Multiple value stages to the automation transformation
11. © 2018 Nokia11
Industry perspective: Automation is a real and emerging priority
Industry wide Automation requires coherent action and strategy now
13. © 2018 Nokia13
The future architecture: What are we aiming for?
Service operations and network domain management with closed loop automation
DIGITAL SERVICE
LIFECYCLE
MANAGEMENT (LCM)
DIGITAL STOREFRONT
CUSTOMER AND
BUSINESS AUTOMATION
VIRTUAL & PHYSICAL
RESOURCES AND
INFRASTRUCTURE
DIGITAL Service Provider
Service Operations &
Cross-Domain Orchestration
Fixed Access Domain
IP Routing DomainNetwork Domain Management
IP/Optical Domain
Fixed Access Domain, etc.
Cross Domain
Data Layer
Two level architecture, each with
similar operations functions
including:
• Orchestration and fulfilment
• Topology and inventory
• Assurance and analytics
• DevOps
(physical or virtual)Virtual & Physical Resources
Areas of focus for this discussion
14. © 2018 Nokia14
From silos and custom integration to full multi-domain automation
Perspective: Evolution of network management architectures
1980 - 2000
Single-Vendor Domains
2000 - 2012
Multi-Vendor Domains
2012 - 2018
Network Virtualization
Beyond 2018
Network Automation
A new architecture is required to enable network and service automation
Increasing operational complexity Operational agility and efficiency
15. © 2018 Nokia17
From reactivity to zero-touch automation
Perspective: Evolution of network management automation
Zero-TouchProactiveReactive
Network/service
operations
Closed-loop network and
service automation
Partially automated processesLow: single task
Level of
automation
Prescriptive analytics &
machine intelligence
Predictive analytics,
e.g. for maintenance/repair
Descriptive & diagnostic
analytics, for example
anomaly detection
Intelligence
Fully programmable with
embedded software control
More dynamic with partial
software control overlay
Static networkNetwork agility
Past Present Future
Source: adapted from Analysis Mason
16. © 2018 Nokia18
Vision of future network and service automation architecture
Service operations:
• Catalog-driven e2e service orchestration for automated
cross-domain service delivery
• Intelligence-driven service lifecycle operations enabling
automated closed loop service fulfillment & assurance
• Abstract service inventory through federation & open APIs
Network domain management:
• Domain-level automation driven by network intelligence
and domain service/resource orchestration across the
domain’s NFs
• Model-driven resource assurance and control
• Shared domain data enables inter-domain data exposure
and optimization
• Multi-vendor VNF / PNF management
17. © 2018 Nokia19
Fixed Access Domain
IP Routing Domain
Wireless Domain
Partial Custom
Integration
EMS1 EMS2 EMS3 EMS4
VNFM VNFM VNFM VNFM
NFV
Orchestrator
IP/Optical Domain
Fixed Access Domain, etc.
Enterprise
Service
Management
Voice
Service
Management
Data
Service
Management
Vendor1
NetworkResources
Vendor2
NetworkResources
Vendor3
NetworkResources
Vendor4
NetworkResources
6 Key architectural transformations to support E2E automation
Required transformation: Silos and custom integration moves to full multi-domain automation
More autonomous
cloud native VNFs
5
Silo-less closed loop
automation
1
Shared network data
layer key for cross
domain cohesion
4
Open industry
standard NF
interfaces essential
6
EMS functions
decomposed &
subsumed in framework
2
Model-driven control
displaces vendor-
specific code
3
20. © 2018 Nokia22
Vision of the FMO architecture
More detailed view for each of the three areas above
1
2
3
21. © 2018 Nokia23
Detailed view of the service operations architecture
Service operations includes cross-domain coordination role
1
DA: Driving APIs of domain
management systems
(virtual domain controller)
SA: Processing real time
data to derive insights and
KPIs for service monitoring
and assurance
SI: Service-specific
cognitive applications for
intelligent decisions &
recommendations
SO: Catalog-driven e2e
orchestration of multiple
domains to create a
customer-facing service
Service AssuranceDomain Adaptation
Analytics/Reporting
Service Intelligence
Monetization &
Demand Monitoring
Intent-based
Service Optimization
Customer
Experience Mgt.
Action Triggering
Service
Catalog
Service Orchestration
Cross-Domain
Orchestrator
Service Policy
Topology/Inventory
Domain Management
ApplicationsIP/Routing
Wireless Access Fixed Access
Service Operations & Cross-Domain Management
Service AvailabilityService Quality
Business & Product Management
Data Collection / Mediation
Service & Cross
Domain Data
22. © 2018 Nokia24
Service Orchestration Service Intelligence Service Assurance
Detailed view of the network domain management architecture
Resource AssuranceResource Control
PM FM SM Logs
Analytics/Reporting
Network Intelligence
Network Security
Incident Mgmt
Network Resources
(physical or virtual)
Configuration &
Optimization
Capacity
Adjustment
Trouble Resolution
Topology Manager
Basic Root Cause &
Impact Analysis
Network Resource Orchestration
Topology
Discovery
Policy Manager
Network Resource
Orchestrator
Inventory Manager
Service Operations & Cross-Domain Management
Closed-loop automation requires a new domain management architecture
RC: Controls the state of
a single resource (network
element, microservice)
RA: Processing real time
data to derive insights and
KPIs for use by other
applications
NI: Domain-specific
cognitive applications for
intelligent decisions &
recommendations
NRO: Domain-level
orchestration of multiple
resources to create a
network service
VNF InstantiationSoftware Manager
Resource
Controller
Cloud Resource
Management
Domain Management
2
Shared & Domain
Specific Data
23. © 2018 Nokia26
Detailed view of the network data layer
Data Integration
Generic libraries for big data processing,
data visualization and machine learning
Access Control
(Meta)Data
Management
The Network Data Layer contains a real-time operational image of the network domain: topology &
inventory, resources, object models and templates, CM master database, telemetry data, logs, …
Data integration: data abstraction and
distributed computing using data from
data storage and streaming
(e.g. based on Apache Spark)
Data storage: several database
technologies optimized for use cases
(time series, topology, …) plus data lake
for big data storage (e.g. Hadoop)
Data Streaming
Workflows and tasks
Publish/Subscribe
Message Bus
3
Data layer components can leverage open source software building blocks
Data streaming: data and event distribution
based on pub/sub message bus (e.g. Kafka).
Data is forwarded to a database for storage
or directly to applications for processing.
Data Storage
Various DatabasesBig Data Storage
24. © 2018 Nokia27
New monitoring and control interfaces simplify integration of NRO/NI functions
Resource AssuranceResource Control
PM FM SM Logs
Analytics/Reporting
Network Intelligence
Network Security
Incident Mgmt
Network Resources
Configuration &
Optimization
Capacity
Adjustment
Trouble Resolution
Topology Manager
Basic Root Cause &
Impact Analysis
Network Resource Orchestration
Topology
Discovery
Policy Manager
Network Resource
Orchestrator
Inventory Manager
Service Operations & Cross-Domain ManagementNorthbound interface:
Provides abstracted
network domain view
towards service
operations
VNF InstantiationSoftware Manager
Resource
Controller
Cloud Resource
Management
Domain Management
Southbound interface:
Open interface to
network resources
(e.g. Netconf)
Monitoring & control
interface (new):
supports integration of
management functions
on top of open (ONAP)
and traditional control
platforms
NetworkDataLayer
25. © 2018 Nokia28
Standards & Fora
TMForum (*)
ETSI ZSM
ONAP
ETSI ZSM
3GPP
NGMN
BBF
MEF
IETF
ETSI NFV
ONF
OASIS (TOSCA)
OpenStack
Open vSwitch
(*) TMForum also covers BSS
27. © 2018 Nokia30
➢ Reduced need to involve VNF
manager in CM, healing, scaling
➢ VNFs can execute policies
autonomously
➢ Remaining VNFM functions (VNF
instantiation, cloud resource
management and software
management) can be logically
combined with CM micro-services
(generic “resource controller”)
VNFs must have cloud-native designs
Breaking monolithic software into
self-contained, loosely-coupled
services, which:
• implement a business capability
• are independently deployable and
scalable
• can be shared between multiple
users (multi-tenancy)
• enable continuous delivery and
deployment of large, complex
applications
• leads to increasing complexity on
operability plane
Microservices
Autonomous applications which are
decoupled from infrastructure and
support:
• portability: deployment in different
cloud environments
• auto-configuration
• self-healing and self-resilient
• auto-scaling
• self-secure
Cloud-native VNFs
VNF operability
Operability requirements of cloud-native autonomous VNFs are changing
28. © 2018 Nokia31
Topology is essential for connectivity management and orchestration
• Topology micro-service is used by other services
• The topology micro-service captures real-time
state of the services, networks and resources.
• There may be a single topology service or multiple
ones.
• The level of abstraction will differ depending on the
level of the topology service.
• The service is natively multi-tenanted
• Topology managers are federated. This enables an
accurate multi-layer view
Topology
(Inventory)
Manager
Management/ControlContinuum
Pub/Sub Data Bus
Resource
Orchestrator
Service
Impact
Service
Domain A
Topology
Manager
Domain B
Topology
Manager
Domain C
Topology
Manager
Federated Topology Services
Federated real-time abstract topology micro services drive responsive multi-layer services
Domain examples: optical,
IP routing, mobile backhaul
Service Management
30. © 2018 Nokia33
State of the industry
• Currently there are multiple inconsistent management frameworks in the industry, many
silos, a lack of alignment and a lack of interoperability.
It is essential to move to an environment that leverages
synergies and achieves alignment through convergence on a
single end-to-end network and service management
architecture.
31. © 2018 Nokia34
ETSI ISG ZSM
Formed in December 2017; first meeting in January 2018
14 founding members
Formed under the auspices
of the ETSI ISG
Key objective
Enable future operational
processes and tasks to be
executed automatically, end-to-
end
Industry convergence
Facilitate collaboration with the
relevant open-source projects,
standardization bodies and fora
Goal
Accelerate the definition of the
end-to-end service management
architecture, spanning both legacy
and virtualized network
infrastructures
Interoperability
Provide a common foundation to
enable a diverse ecosystem of
open source groups to produce
interoperable solutions
32. © 2018 Nokia35
The ISG ZSM continues growing in a steady and healthy pace
– 65 members; 18 operators
33. © 2018 Nokia36
Industry alignment: ETSI ZSM has a central role in the automation ecosystem
• ETSI Zero touch network and Service
Management (ZSM) has a pivotal role in
bridging between holistic end-end
automation and other standardization bodies
or open source projects
• Requirements derived from use cases
• Architecture for management/automation
• Open-source projects like ONAP should focus
on implementation and validation
• Alignment discussion with LNF and ONAP
already started
34. © 2018 Nokia37
Note: the ZSM DRAFT specifications are publicly available via the ZSM open area (Link).
ZSM deliverables
Work item Title
ZSM 001 Use cases and requirements (specification)
ZSM 002 Reference Architecture (specification)
ZSM 003 End to end management and orchestration of network slicing (specification)
ZSM 004 ZSM Landscape (report)
ZSM 005
Means for Automation (report)
ZSM 006 Proof of Concept Framework (specification)
ZSM 007 Terminology
ZSM 008 Inter management domain lifecycle management
35. © 2018 Nokia38
© ETSI 38
Motivation
• Virtualization allows networks to evolve much quicker than in the past.
Network management needs to keep pace.
→ No „one size fits all“, need flexible composition of network management
services
→ Decoupled evolution
• Introduction of NFV and Network slicing increase scale,
complexity and TCO
→ Automation of network management is the answer
36. © 2018 Nokia39
© ETSI 39
ETSI ZSM: A framework rather than a system
• We need a flexible management framework, not a fixed management
system.
✓ Management services that can be composed; support for service exposure
and service integration
✓ Model-driven, open, intent based interfaces
✓ Separation of management concerns: Domains and End-to-End;
encapsulation of complexity
✓ Shared data (stored, streamed) as the lifeblood of automation
✓ Closed loops at various levels as the driver of automation
• → Deployment flexibility, open for evolution!
37. © 2018 Nokia40
© ETSI
The ETSI ZSM framework
reference architecture
(Source: ETSI GS ZSM002)
• ZSM service aka management service: A set
of offerend management capabilities.
• Management function: Logical entity playing
the roles of service consumer and/or service
producer.
• Integration fabric: A management function,
playing the roles of both service consumer
and service producer, that enables
interoperation and communication between
management functions within and across
management domains.
• Cross-domain data services: Services that
allow to share data with authorized
consumers across domains.
• Management domain: A scope of
management delineated by a business,
administrative, technological or other
boundary.
• E2E service management domain: A
manage-ment domain specialized to manage
E2E services.
38. © 2018 Nokia41
© ETSI
ZSM architecture feature:
Separation of concerns in management
• Management Domain (aka Network Management Domain)
• Scope of management delineated by e.g. organizational or
technological boundaries
• Manages resources and services based on these
• Provides management services and decouples the inner domain
details from the outside world
• Can consume management services from other management
domains
• E2E Service Management Domain
• Manages E2E services that span multiple management
domains
• Provides management services
• Coordinates between management domains
Provided Management Services
Provided Management Services
39. © 2018 Nokia42
© ETSI 42
ZSM architecture feature:
Service-based
(Source: ETSI GS ZSM002)
The ZSM architecture defines management services which
can be provided and consumed by management functions.
(The realization of management functions is out of scope.)
40. © 2018 Nokia43
© ETSI
ZSM architecture feature:
Integration fabric
• The integration fabric allows cross-domain service interoperation & communication
• Management services communication
→ synchronous & asynchronous, e.g. event notifications and streaming data
• Management services registration and discovery
• Management service invocation, including access control
Service producer Service producer Service producer Service producer…
Integration Fabric
Mgmt Services Communication Mgmt Services Registration & Discovery
Service consumer
Mgmt Services Invocation
Service consumer Service consumer…
41. © 2018 Nokia44
© ETSI
ZSM architecture feature:
Cross-domain data services
• Data are the lifeblood of automation.
• Cross-domain Data Services allow
• Storing of management data
• Sharing of management data with
authorized consumers across domains
• Supporting big data analysis
• Rapidly providing data to support
control loops
Cross-
domain
Data
Services
Examples of shared data related to
managed entities:
• performance monitoring data
(e.g. performance counters)
• assurance data (e.g.
performance/fault alarm events)
• trace data (e.g. packet capture
data)
• configuration data
• miscellaneous log data
• network/service topology data
• network/service inventory data
42. © 2018 Nokia45
© ETSI
ZSM architecture feature:
Enabling automation based on closed loops
• Domain orchestration
services
• Automate workflows and
processes to handle
instantiation and lifecycle
management of
the services provided
by the domain.
Domain control services
Individually steer the state of
each managed entity (resource,
consumed service).
Domain intelligence services
Provide domain-specific decisions
and recommendations, to drive
domain-level closed-loop
automation.
Domain data collection services
Monitor the managed entities (resources
and consumed services), and provide live
performance and fault data to support
closed-loop automation.
(Source: ETSI GS ZSM002)
Domain analytics services
Provide domain-specific
insights based on data
collected by
domain data collection
services and on
other data.
Observe
Orient
Decide
Act
OODA
43. © 2018 Nokia46
© ETSI
Integration fabric
Domain
Data
Collection
Analyze
Learn
Domain Analytics
Domain
Control
Config mgmt
service
producer
Resources
Management Domain
Domain
Intelligence
Data
Services
(3a) Consumes
fault
notification
(3b) Consumes
fault notification;
stores fault data
(4)
Determines
root cause:
Bad link
(9)
Produces
“Configure
Resource”
service
(9) Changes
configuration on
router to reroute
traffic
Fault events
service producer
(1) Fault event: SGW
not responding
(2) Provides fault
notification
Closed loop example:
Automatic fault mitigation
Decide
Learn
(8)
Consumes
“Configure
Resource”
service
(6)
Consumes
insight
(5) Provides
insight
(7)
Decides:
Re-route
Domain
Orchestration
44. © 2018 Nokia47
© ETSI
Specification Work: ETSI GS ZSM002
• This presentation is based on the current status of
the ETSI ZSM002 specification work
• Work in progress, expected to reach „Stable Draft“
milestone soon
• Drafts of the specification availble here:
https://docbox.etsi.org/ISG/ZSM/Open/Drafts/002ed111_RefArch
V 0.10.0 (2019-
03)
ETSI GS ZSM 002
Zero-touch Network and
Service Management (ZSM);
Reference Architecture
45. © 2018 Nokia48
© ETSI 48
Conclusion
✓ The ZSM framework architecture is flexible and service based.
✓ The ZSM framework architecture separates the concerns of Network
Domain Management and E2E Service Management.
✓ Integration Fabric and Cross-domain Data Services in the ZSM framework
architecture provide flexibility to
• integrate and compose management services and
• build closed automation loops
• across domains.
47. 50 © Nokia 201850 © Nokia 2018
Roadbook
Plan your trip
Why go? Why not
go?
What to
bring?
What to
do?
49. 52 © Nokia 2018
Challenging the status quo
Create and deploy services more rapidly
Hours
& days
How do we get there
Planning cycles Response to threatsAdapting to changes
?
Seconds
& minutes
50. 53 © Nokia 2018
AutomationVirtualization & slicing
Virtualization and slicing are not enough
Automation is essential to economics
Physical network
T R A N S F O R M A T I O N
T C O
(source Nokia Bell Labs)
Flexibility also brings complexity +30%
-30%Automation brings cost down
51. 54 © Nokia 2018
The Automation Journey
Why not go
52. 55 © Nokia 2018
Roadblocks on the automation journey
54. 57 © Nokia 2018
Machine-assisted human activity
Repetitive tasks Creative tasks
55. 58 © Nokia 2018
Machine-assisted human activity
Creating time for more creative tasks
CREA TING TIMERepetitive tasks Creative tasks
56. 59 © Nokia 2018
Automation
The customer
centric view
The network
centric view
You are here
A shift in skills required!
NFV, programmability, DevOps,
open source, model-driven,
Netconf, YANG, AI, ML, …
57. 60 © Nokia 2018
Roadblocks on the automation journey
58. 61 © Nokia 2018
Automation can help!
Small mistake…
… big impact!
90 minutes to solve the issue
Monday's outages reinforce how precarious
connectivity really is, and how certain aspects
of the internet's architecture—offering
flexibility and ease-of-use—can introduce
instability into what has become a vital service.
“
59. 62 © Nokia 2018
Machine
learning
The machine finds
the rules
Step
3
Policy-driven
automatic action
You define the
rules
Step
2
Automation journey
Example: Assurance
Correlation,
visualization,
root-cause
analysis
Step
1
Manual
data/alarm
analysis
Visualize
Trust what’s happening
behind the scenes
60. 63 © Nokia 2018
Confidence
Trust but monitor and keep control
Full automationManual validation
Roll back
Pause
61. 64 © Nokia 2018
The Automation Journey
What to bring
62. 65 © Nokia 2018
Insight-driven automation
Closing the loop between intent and outcome
• Programmable carrier SDN control
• Network provisioning/optimization
• Service automation and assurance
• Software programmability
• Flow-driven telemetry
• Analytics correlation engine
• Deduction & recommendation
Information
ActionInsight
Intent
63. 66 © Nokia 2018
The NMS must transform to enable automation
NMS is becoming independent from network equipment and captures part of their brain power
Single-vendor element
management systems
Physical
equipment
Past
Single-vendor, single-domain silos,
distributed control plane
Future
Physical + virtual
equipment
Network management
and control
Centralized intelligence
Decoupling from the equipment
Multi-vendor, multi-domain network,
centralized control plane
64. 67 © Nokia 2018
The Automation Journey
What to do (and see)
65. 68 © Nokia 2018
WAN automation
Equipment
configuration
1
Network
service
delivery
2
Network
& service
assurance
Traffic
optimization
4
→Take
a tour
3
66. 69 © Nokia 2018
WAN automation
Equipment
configuration
1
Network
service
delivery
2
Network
& service
assurance
Traffic
optimization
4
→Take
a tour
3
67. 70 © Nokia 2018
Problem
Automated commissioning & provisioning
Zero-touch provisioning (ZTP)
!!
Manual installation and
commissioning is complex,
time and resource intensive
(costly), and prone to errors
Network
New equipment needed
for upgrade, repair, etc.
+
Benefits
Solution Equipment self-registers in
the network and gets
automatically configured
and commissioned
• Accelerate infrastructure &
service deployment
• Improve network quality and
reduce the risk of human
error
NSP
Equipment:
1. Comes with pre-installed certificates
2. Gets network connectivity from DHCP
3. Contacts the management system
4. Gets configuration and intended
firmware pushed via NETCONF
68. 71 © Nokia 2018
WAN automation
Equipment
configuration
1
Network
service
delivery
2
Network
& service
assurance
Traffic
optimization
4
→Take
a tour
3
69. 72 © Nokia 2018
Network service delivery for 5G and IoT
Introducing network function interconnect (NF-IX) architecture
!
Problem
!
How to dynamically adjust
transport network resource
needs to match fluctuating 5G
and IoT service demands Access
Humans
& Machines Telco Cloud
Public Cloud
Private Cloud
Unified transport
network fabric
MEC MEC
CPC
Solution
Benefits
NF-IX automatically engineers
the necessary data path
connectivity in appropriate
network slices
• Fast service provisioning
• Guarantee transport SLAs for
each service
• Optimize network resources
as load conditions change
Mobility service slice
Enterprise service slice
Residential service slice
IoT, M2M service slice
Virtualized overlay servicesNetwork functions
Automatic SLA policy mapping
NSP
70. 73 © Nokia 2018
Network service delivery for enterprises
Virtual networks orchestration (VNO)
!
Problem
!
Enterprises expect
instantaneous software-
defined (SD) connectivity from
branches to datacenters Service provider
datacenter
Customer
premises
(branch sites)
Service provider
network (or Internet)
Public cloud
datacenter
WAN
Benefits
Solution Automate branch site
connectivity, including
provisioning, configuration,
and optimization of the
network and security policies
• Achieve faster ROI for
enterprise services
• Launch new services faster
• Improve the end-customer
experience
NSP
Control
VNO
Orchestration
71. 74 © Nokia 2018
WAN automation
Equipment
configuration
1
Network
service
delivery
2
Network
& service
assurance
Traffic
optimization
4
→Take
a tour
3
72. 75 © Nokia 2018
Network and service assurance
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Problem
!
It’s impossible to process the
volume, velocity and variety of
streaming data to anticipate
or fix network issues
Real-time data
• Alarms
• Test results
• Environmental data
• Route, state and
configuration changes
Network
Events storm
Solution
Benefits
Let the machine learn how to
correlate events to assist in
predicting, detecting and
solving incidents
• Improve network availability
• Fix problems before they arise
• Detect silent failures
• Accelerate troubleshooting
Operator
…and get better with time!
Network state
• Equipment inventory
• Configuration
• Network topology
• Service topology
Feedback=
Learning!
NSP
Recommendation
Automated
Manual
Action
73. 76 © Nokia 2018
WAN automation
Equipment
configuration
1
Network
service
delivery
2
Network
& service
assurance
Traffic
optimization
4
→Take
a tour
3
74. 77 © Nokia 2018
Traffic optimization
Peer engineering
Problem
!
Peering points with transit
providers are source of
congestion, performance
degradation and cost Peer 1 Peer 2 Peer 3
End user
Traffic spikes:
cyber Monday,
iOS update,
binge viewing,
etc.
Solution
Benefits
Leverage real-time analytics
to dynamically select optimal
peer links or transit provider
and steer traffic per
application flows, per route,
AS, or per BGP communities
• Avoid traffic congestion and
manual misconfiguration
• Optimize performance
(latency, packet loss)
• Control peering costs
Visibility &
Control Action
NSP
Insight
+
75. 78 © Nokia 2018
Network and traffic optimization
IP-Optical coordination and cross-domain control
Problem
!
Benefits
Inefficient operations in
heterogeneous networks
impact resources utilization
and service availability
• Simplify operation (OPEX)
• Increase network utilization
(CAPEX)
• Improve network resiliency
• Speed up planning and
troubleshooting processes
Control &
management
NSP
IP/MPLS
Optical
Multi-layer
• Discovery
• Visualization
• Provisioning
• Resource control
• Protection/restoration
• Maintenance coordination
Solution Establish unified network
visualization and coordination
across IP and Optical layers
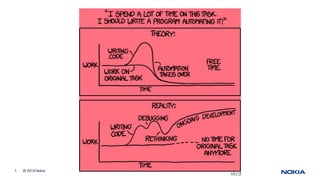
77. 80 © Nokia 2015
The automation challenge is
network complexity
Public
78. 81 © Nokia 2015
Networks growth in scale, scope, features and
interactions generates ever higher number of
operations, amount of data, and more complex process
orchestration
Public
We create network complexity
(and it’s okay!)
Public
79. 82 © Nokia 2015
More automation and more insights
However…
“Automation is only as good as the insight that drives it”
Public
We can control complexity
(hopefully…)
Public
80. 83 © Nokia 2015 Public
Automation without insight = Operating “in the dark”
Insight without automation = Operating “in the past”
Automation InsightsAutomation Insights
81. 84 © Nokia 2015
In its simplest form automation is the
action of making a task executable
without human intervention.
Public
82. 85 © Nokia 2015
Networks are already well but
fragmentarily automated systems.
Public
83. 86 © Nokia 2015
Label - Blue-
black
Label - Blue-
black
The Automation Continuum
Public
Deep
Wide
access edge core ixc
application
service
network
resources
AF Automated Feature
Process interaction
Label - Blue-
black
Label - Blue-
black
Label - Blue-
black
Label - Blue-
black
Label - Blue-
black
AF AF AF
AF AF AF AF AFAFAF
AF AFAFAF AF
84. 87 © Nokia 2015
An approach for combining function automation with
process automation
Applies from individual functions to orchestration of
entire chain of automation i.e. workflows
Public
The Automation Continuum
Public
85. 88 © Nokia 2015
• “Deep” automation: vertically end-to-end
across the protocol stack or from the service-layer to the physical-layer
• “Wide” automation: horizontally end-to-end
across different technologies or administrative domains
• Repeatable and reusable in different contexts
relies on standardized or best current practices for interfaces and models
• Provisioning customizable “control or touch points” in the end-to-end
automation loop for human supervision
Public
The Automation Continuum
Public
86. 89 © Nokia 2015
Challenges and enablers
Public
87. 90 © Nokia 2015
Challenges
Public
Automation challenges
• Diversity. How to design
automation patterns applicable to
the heterogeneity of devices and
components
• Reliability. How to avoid massive
error propagation when extreme
automation is deployed
• Uncertainty. How to automate
when faced with lack of knowledge
or variability of the environment or
conditions
Automation means
• Measurement
by using streaming telemetry and analytics
to generate actionable insights
• Learning
by using machine learning to identify
patterns and enable predictive operations
• Decision
by using cognitive and adaptive closed
control loops to produce effective (re)action
plans
• Governance
by using powerful, declarative abstractions
(e.g. intents)
88. 91 © Nokia 2015
From reactivity to zero-touch automation
Zero-TouchProactiveReactive
Network/service
operations
Closed-loop network and
service automation
Partially automated
processes
Low: single task
Level of
automation
Prescriptive analytics &
machine intelligence
Predictive analytics,
e.g. for maintenance/repair
Descriptive & diagnostic
analytics, for example
anomaly detection
Intelligence
Fully programmable with
embedded software control
More dynamic with partial
software control overlay
Static networkNetwork
agility
Past Present Future
Source: adapted from Analysis Mason
Public
Evolution of network management automation
89. 92 © Nokia 2015
Closed-Loop Zero-Touch Network Automation
Public
Drive ChangeExtract Insights
Specification
/ Descriptor
Implementation (Network)
Policy
On-boarding
Network
Data
Layer
Network
Data
Layer
Rules
Instantiation
Observation
Analytics
Prediction
Recommendations
Execution
Decision
Intent
Catalog
Orchestrator
ControllerBig Data
Intelligence
Public
91. © 2017 Nokia94
The ideal platform will…
Be Cloud-native
Reuse latest open-
source
components
Reuse multi-vendor
inner source /
proprietary components
Other
vendor
s
Evolve fast
1
2
3
4
Be model-driven
with an editor
view
Supports
deterministics/repeatabl
e and ubiquitous
deployments workflows
6 7Support telco-
grade workloads
8
92. © 2017 Nokia95
The ideal platform will… (con’t)
Service
Platform
Execution
Environment
Properly separate concerns
beween the « what »
(services), the « how »
(platform) and the
« where » (execution
environment)
8
Support
recursivity
(vertical
dimension)
9
Support
composability
(horizontal
dimension)
10
Verticadimension
Horizontal dimension
97. © 2017 Nokia100
It yes, this platform is specified by TM Forum and follows Platform
concepts
98. © 2017 Nokia101
NGPaaS is a prototype “embodiment” of a TM-Forum-compliant platform
RFB is the standardized technology to provide
key features
- model-driven approach with a deployment
workflow
- Poymorphic and recursive ➔ As complex as
needed
- Enables « universal » integration, deployment
and operations of various components
coming from open and inner source
99. © 2017 Nokia102
Why NGPaaS is actually working
NGPaaS provides the 3 views required to ensure a TM-Forum compliant system
100. © 2017 Nokia103
NGPaaS supports horizontal & vertical dimensions
BaaS Blueprints
Blueprint Execution Engine
BaaS
Nova Policies
Policy Engine
Nova
Nt Intents
Policy Engine
ONOS
Nt Intents
Policy Engine
OpenDayLight
Virtual
Switches
Hardware
Switches
COTS
Servers
VMs
Containers
Specialized
Hardware
PaaSIaaS
BaaS
blueprint
Admin/
Tenant Service blueprints
Tech. specific
policies
Tech. specific
policies
Policy datastores
PaaS Policy Engine
XOS Orchestrator PaaS 2 Orchestrator
PaaS Policy Engine
Policy datastores
Docker Policies
Policy Engine
Docker
Verticadimension
Horizontal dimension
SLICING
MULTI-LEVEL CONTROL
101. © 2017 Nokia104
Summary
• NGPaaS is a TM-Forum compliant
technology that enables true and
complete control of telecom systems
over vertical and horizontal dimensions
• NGPaaS is by nature compliant with many
existing open-source projects
• OSM
• Kubernetes
• CORD
• Openstack
• ONAP
• It is our ambition to push NGPaaS as
much as possible to « stress-test » its
flexibility, in particular for automation
102. © 2017 Nokia105
NGPaaS in a nutshell
EU funded R&D project (Horizon 2020) and part
of 5G-PPP Initiative, aiming on building next
Generation Platform as a Service: be
customizable, support acceleration and
flexibility, enable transformation across the
industry (operator, IoT/verticals and vendors).
Duration: June’17 – May’19 (24 months)
Project Mgmt: Bessem Sayadi, Nokia Bell-Labs
Technical Mgmt: Michail Flouris, OnAPP
Innov Mgmt: Michele Paolino, VOSYS
Connect to NGPaaS
Webpage: http://ngpaas.eu
Twitter: @NGPaaS_5GPPP
Contact: ngpaas-contact@5g-ppp.eu
104. © 2017 Nokia107
Network Element 1
Application/NF
Network Element 2
Compute
Network
Storage
Application/NF
Network Element 3
Compute
Network
Storage
Application/NF
• Monolithic Applications
• Bare Metal Servers
• HW – SW coupling
• Manual Management and operationnal process
• Network of Entities
Compute
Network
Storage
Compute NetworkStorage
Hypervisor
NFVI (Private Clouds)
Virtual Network
Element 1
Virtual Network
Element 2
Virtual Network
Element 3
• VM, KVM, Vmware, OpenStack (10 years Old)
• Monolithic Applications
• Multi-Tenant
• VNF model (remove HW dependency)
• Automation with Orchestration
• Life Cycle Management
• Network of VNFs
Compute NetworkStorage
Container Manager
NFVI (Hybrid Clouds)
Micro-Services
Micro-Services
Micro-Services
• Docker, Kubernetes (5 years Old)
• Micro-services Architecture
• Cloud-Native
• Horizontal elasticity
• Stateless
Network Architecture Evolution
106. © 2017 Nokia109
What model ?
▪ 5G must become the ubiquitous fabric blending
universal connectivity (to humans, robots, sensors…)
with cloud versatility and scalability.
▪ Another model than IaaS must be adopted, a model
derived from the cloud service providers themselves,
a model made by developers for the developers, the
Platform-As-A-Service (PaaS).
▪ One size PaaS does not fits all 5G business cases and
verticals markets (public/private clouds, specific
requirements on latency, heterogeneity, different
SLA per µservice,…)
Next Generation PaaS
107. © 2017 Nokia110
Needed technologies
NGPaaSCloud-
Native
Dev-For-
Operations
Multi-Sided
Platform
Build-to-
Order
Platform
Decentra-
lized OSS
Carrier-
Grades
Acceleration
(FPGA, GPU)
108. © 2017 Nokia111
• Platforms = “useful components” (RAN, CORE, MEC, apps, xHAUL...) + “ancillary
components” (orchestrator, intent-based controllers, message bus...) components
• Any element of the system shall be considered as a component (modular function)
RAN
EPC
Apps
MEC
Useful Components
Orchestration
Networking/Connectivity
Security
Pub/Sub Message
Virtualization
Ancillary components
CI/CD
Monitoring
Platform
110. © 2017 Nokia113
RFB overview
« 1 size does not fit all » => domains Polymorphic and recursive modelling
Everything is an RFB Recursive OSS
111. © 2017 Nokia114
By their modularity, composability, recursivity and
polymorphism RFB can model any kind of system..
• OSM
• Microservice (Kubernetes & Swarm)
• CORD
• ONAP
• Edge cloud
• …
By “standardizing” Platforms modelling, RFB makes it
possible to master ever-increasing complexity in telecom
systems composed from:
- mix of open-source & inner-source
- Heterogeneous systems
RFB in telco platforms
RFBs