QMS Deployment Sept09
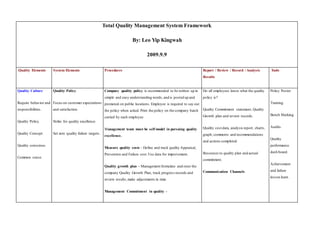
- 1. Total Quality Management System Framework By: Leo Yip Kingwah 2009.9.9 Quality Elements System Elements Procedures Report / Review / Record / Analysis Results Tools Quality Culture Require behavior and responsibilities. Quality Policy. Quality Concept. Quality conscious. Common sense. Quality Policy Focus on customer expectations and satisfaction. Strike for quality excellence. Set zero quality failure targets. Company quality policy is recommended to be written up in simple and easy understanding words,and is posted up and promoted on public locations. Employee is required to say out the policy when asked. Print the policy on the company batch carried by each employee. Management team must be self model in pursuing quality excellence. Measure quality costs - Define and track quality Appraisal, Prevention and Failure cost.Use data for improvement. Quality growth plan - Management formulate and steer the company Quality Growth Plan, track progress records and review results,make adjustments in time. Management Commitment in quality - Do all employees know what the quality policy is? Quality Commitment statement, Quality Growth plan and review records. Quality cost data, analysis report, charts, graph; comments and recommendations and actions completed. Resources to quality plan and actual commitment. Communication Channels Policy Poster. Training. Bench Marking. Audits. Quality performance dash board. Achievement and failure lesson learn.
- 2. There is clear Top Management Quality Commitment Statement. Top executives present annualquality performance KI to company board, and communicate to whole company. Formulate yearly quality direction statement and objectives. Plan and approve resources support quality functions. Quality Mindset Customer first. Meet and exceed customer requirements. Quality Owner of process owner. Do it right right the first time. Zero defect target. Problem owner. Build Quality Mindset amongst all employees Concept of internal and external customers and employee is liable to understand theirquality requirements and expectations. Process owner is responsible for the quality. Employee for producing right quality requirement in their process. Job Skills and Knowledge are well defined and identified for each position Trainings to employee with right skills, knowledge, use of tools and judgment of accept / reject quality. Qualify operators before allow them to engage a task. Ensure < How do employee contribute to the achievement of their organization’s objectives? How are training needs determined? What kind of orientation training is provided when employees are hired? How are personnelmade aware of the mission, values, and measurable objectives of the organization? How is the effectiveness of training evaluated? Management self model. Training and orientation to employee. Leadership role in problem solving culture. Quality circle. 6S. Quality tools box
- 3. Do thing right right the first time >. Define problem owner and problem solver Problem owners are those supervisors,managers, and executive leaders who own problems happened in their areas of responsibility. They are responsible for leading their team to solve the problems happened in their area. Problem owners play a significant role in reinforcing the cultural change. What happens when training is ineffective? What training records are maintained? trainings. Feedback, reward right behavior system. Mission Achieve objectives as integral part of job responsibility. Department and Employee understand specifically what they can do to improve the organization. This kind of knowledge creates strategic focus throughout the organization. Clear Role Define Quality responsibility in job description. Employee are communicated what matters most to the company's success. They know the significance of their roles and are prepared to carry them out. Clear objectives Set clear objectives. Instead of just having a micro view of activities and tasks,personnel begin to understand howtheir jobs link to the larger mission of the organization. Measurable objectives be established at relevant functions and levels. All personnelmust be able to communicate, in their own words, how they help move objectives in the right direction. Clear desirable behavior Practice immediately feedback. Economics award and How is progress against objectives communicated to the organization? Is there evidence of achieving objectives? How do employees contribute to the achievement of organization’s objectives? Dash Board showing performance trend to all employee. What’s the most important thing about your job? What’s the hardest thing about your job? What are some things you’d like to change QFD (Quality function deployment) Dash board management Set quality target achievement as one of base employee performance review. Set quality care as one of core behavior in performance
- 4. promotion are linked to performance results. about your job? What is a resource that would help you be more effective? What should your manager know that he or she currently doesn’t know? If you were the manager here, what would you do differently? review. Management Commitment Financial support. Power authorization. Action quality, no lip quality. A Quality Management System. Top management committed to finance and execute : A Quality Organization to implement, manage, maintain, monitor and lead to improve the QMS. A Documentation Systemto define the authority, responsibility, execution, control, monitoring, maintenance, change, review, upgrading and improvement of the QMS. Build and well define an infrastructure of QMS. Have a detailed total quality control blue print. Quality Management System Organization Build up Quality Management Team, define responsibility and authority, appoint Quality Management Representative.All Managers are member of Quality Management Team, Department / Functional manager is quality representative of department. Quality Management System Documentation Build up Comprehensive processes procedure to provide well defined guidelines and steps to operations.There is a Document Control System to define document creation, authorization of use, maintain, change,obsolete, retain. QMS Organization Chart. QMS Product Realization Flow Chart CI project and CAR records. CI project, CA follows up review, completion and effectiveness. Tools training, Customer feedback review and action plan, QMS effectiveness assessment and recommendations. Company/Department have updated document list, training record of all employee. MRM records, Improvement Plan. Regular audits and reviews on documented procedure and processes. CI on area of weakness. LEAN
- 5. Execution of procedures. Functional departments commit to follow 100% process procedures,set and achieve departmental targets align with company goals. Have detailed action plan and resources to pursue the targets. Targets be achievable and measurable. Product Quality Control Flow Chart A clear processes flow chart to show clear control steps of product realization. Strict rules are set to govern sideways and deviations. Regular periodical Management Reviews Managers take the lead to track company and departmental KPI performance trend, and take actions for under performance. General Manageris owner of annual quality MRM. Product Quality Company does not allow existence of quality-in-doubt products,in house or on field. Before sales,sales, and after sales services to customers are integral parts of Quality by Design Written requirements, criteria and standards must be part of design inputs. Requirements stated by the customer; Requirements not stated by the customer but necessary for intended Professional Sales Services See customer satisfaction section below. Contract Review There is specific contract review procedures and forms to complete before starting formal product development. Customer Services, Sales, Quality, Engineering, legal and Operation are required to review and sign confirmation in respect to their control and responsible area. There is standardize product design and development Are product requirements completed? How does the organization ensure that correct versions are available? How do requirements get reviewed prior to acceptance? How to ensure that product meets the stated requirements? Electronic approval system. Qualification system.
- 6. product quality. Process owner product (materials, WIP, finished goods) knowledge and quality criteria. use; Statutory and legal requirements; and Additional requirements determined by the organization. procedure with clear steps and approval gates Apply Product design tools in product design as appropriated : APQP, DFSS, QFD, MSA, FMEA, PPAP Product Qualification There is procedure of product qualification plan for every new product to qualify for mass production.Qualification criteria approval gates are well defined and must meet. Approvalgates must be signed off and closed based on test data and results. What happens when changes are made to product requirements? Product development file and record must be completed and well maintained with FAI report and samples. Product qualification record shows approval date and signature. Quality by Process All processes is defined with SIPOC. LEAN the flow. Necessary aids and/ortools are in place to facilitate achievement of objectives and prevent mistakes. Eliminate the wastes. Define Yield Rate (quantity Process Qualification Each and all process steps shallbe well defined the objective matrix : criteria and standard of SIPOC (Supplier, Input, Process-steps,Output,Customer) Qualify the processes with 5 M 1 E Qualification (Man, Materials, Machine, Method, and Environment) – Each needs specific qualification procedure and criteria of acceptance. 1. Man – Skill and training; 2. Material – Specification and sample; 3. Machine – Setting and maintenance; Production FAI, LAI record. Improvement actions, projects. Training records. Control Plan available. WI Control data, graph, chart. Yield records. IPQA SPC 6S
- 7. and/ortime) at logical and financial affordable level. Mechanism to stop the processes at doubtfulquality. 4. Method – SOE / WI / VA; 5. Measurement SystemAnalysis – G R & R 6. Environment – temperature, humidity, lighting, noise, dust etc. 7. Control Plan. 8. Ensure Yield rates. 9. 6S FAI and LAI There is First Article Approval systemto govern production take place. Last Article to verify variation to indicate Sigma [σ] level within specification. WIP quality control Have in-process sampling plan for each product and execute seriously. Verify process SOE and disciplines are followed exactly. To minimize the Rolled Throughput Yield (RTY) by applying self check, Poke-yoke in each process station. QC records. Repair records.
- 8. Define stop line criteria and trigger points. Prevent materials damages from handling , transferring and storage 1. Find the best fit container / packaging for materials, protect them from damaging, deterioration during transits,storage.Specify container / packaging used for each material, WIP and finished goods in material specification. 2. Consider material environmental requirements always. 3. Always be cautious of human direct contact that could cause later defect (example – Oxidization). 4. Clear Identification of materials.
- 9. Quality Assurance Quality Knowledge and skills. Trained personnel. Quality supplies. Strict process disciplines. Supplies Quality Assurance Build up supplier and supplies Selection systems,including performance monitoring method. Impose incoming material quality control to prevent source of problem from incoming materials. Periodical review materials on quality, price and improvement / new versions. Supplier Qualification procedure There is Suppliers selection process and criteria to ensure supplier capacity and capability of meeting quantity and quality requirements. Develop comprehensive supplier assessment quality feedback forms. There is purchase order review and confirmation processes with suppliers to secure right quality requirements are understood and confirmed achievable by suppliers. Regular Supplier communication. Supplier support:training in technology and industrial standards,legal requirements. Material qualification procedure There is materials selection and approval process to ensure materials are met with specification. Develop qualification form and approval gates. Incoming material quality assurance There is incoming inspection plan and approved reference sample for each material. The plan shall have specific acceptance criteria, such as sampling plan and accepting level, COC or supplier inspection report in lieu of tests. Supplier approval records and performance data. Material approval records,samples. Incoming material control records. How incoming non-conformance is handled and record or rectification. Supplier performance evaluation and improvement action taken. Supplier evaluation audit. Sample approval system. Approval sample regular review. Supplier performance system. Reliability test. Incoming material quality assurance method -COC sampling, supplier test reports.
- 10. Carry out periodical reliability test to ensure variation is within control. In-process Quality Assurance Have a reliable in-process quality assurance (IPQA) plant and team. Strictly follow process disciplines. Updated WI. Tailor made SPC tools to monitor and check the production variations. Minimize the possibility of defected products reaching the customers. In-process quality control See quality by process. Outgoing quality assurance There is either in-process sampling plan or outgoing sampling plan procedure or both to ensure product quality, before shipping to customer are conformed to defined quality requirements. There is clear guidelines and authority to trigger production line / shipment stop when quality is diversified from control point(s). Collect and analyze performance data to ensure process is stable or need to take action to reinstall. In-process audit records, data, samples. Statistics of acceptance and reject records of finished products. FA reports and CAR and result records. control plan, FAI record, prints, IPQA/IPQC FAI, LAI WI SOE Quality samples. Trained operators. SPC MSA
- 11. Engineering Change Management Make strict written procedure and detailed processes to guide all kinds of changes. Engineering Change Control For all changes,first study the impacts to customers. No Changes are allowed if they affect customers form and fit, and agreed quality, unless obtained their approval. Follow strictly change procedure and processes.Acheck sheet to monitor completion of change process activities. A change center shall monitor the flow and task to guarantee 100% completed and correct. There are actions to verify no multiple systems/formats,missing information, wait time/responsiveness,manual re-keying of information, translation/interpretation, conflicting changes. It is recommended a to see the final authorized signal before a change is taken place. Change records, customer approval records. Trace back to specifications, FMEA, control plan, FAI, prints. Paper or electronic process and approval gate system. Engineering Change completion and effectiveness verification log book. Control nonconforming Control nonconforming materials including supplies, WIP, stocks,customer returns to prevent pollution to clean materials. Handle nonconforming There are detailed instructions of how to handle nonconforming. There are specific locations to quarantine nonconforming. Find Root causes of nonconforming and eliminate them. Preventive and improvement actions are formulated and their Ask employee how they to control non- conformance. Ask employee how they can trace the material with lot number. Disposition records. Nonconforming data collection and Physical and Book quarantine system. Monitor quality costs trend chart. Logical and meaningful part
- 12. results are verified. Update process flow. Nonconforming cases are needed to close and nonconforming materials are required to dispose within specific time limit. Nonconforming quantity and values are collected for management review and identify area of improvement. Traceability Structure the lot number of material, WIP, finished goods so that they can be traced back to origination at any time. The lot number shall be able to tell where, when, which. A material lot number can trace to which WIP, finished goods lots; a finished goods lot number can trace to which materials lots. Materials, WIP, finished good always travel with ID. Structure the part number of material to maximize information to detect there is a material problem. (Categories, model/class, size, color, distinct characteristics (hardness,thickness, voltage, watt, etc), maker. Every employee is trained to know how to trace materials with part numbers and lot numbers. analysis records. Improvement records. numbering and lot numbering system. Regulatory Compliance There is responsible person and mechanism to ensure legal requirements, regulatory rules and restrictions, industrial Verify compliance certificate, approval Specialist overseeing this
- 13. standards,environmental regulations, technical approval etc are compliant. Maintain a table of compliance requirements for all categories of materials. Ensure material compliant from beginning of product development. Ensure compliance of supplies.COC must be supported by qualified lab test result. Might need to reconfirm by 3rd party lab test irregularly. documents,test reports. area. Compliant reference table Quality Problem prevention & Solving Prevent quality problem happened rather than discover quality problem by inspection. Openly shares data and encourages its analysis on a broad scale, employees are made known the problems so as to make preventive action becomes easy. Have specific systemand personnelresponsible for Problem prevention Apply quality tools such as Poke-yoke, auto counting,sensors to prevent quality problem from happening. Detect potential problem by collecting and analyzing data. Generate preventive action through data analysis indicators rather than seeing actual problem happened. Data analysis is a primary job of identify quality problems. Regular maintenance program, calibration plan are fixed for Machine, equipment, measurement tools,software. SPC detect process variation. MSA ensure precise and precision of measurement system. Maintenance program and records. Calibration plan and proof records. FMEA records. Problem solving tools training. Ask employee how they handle a problem. What does your organization do to solve customer problems better than competitors so that customers old and new will pay good money for yourservices and goods LEAN 6 Sigma 7 QC tools.
- 14. problem solving process.: locate problem owner and problem solver, monitoring progresses, ensure corrective actions are taken, validate effectiveness of actions before confirming problem solved. Poke-yoke to prevent human error. Problem Solving There is procedure to set up problem solving team and select members for the team for each problem. Quality personnel shall always take the lead for the problem solving process – 1. Locate problem area, problem owner and problem solver. 2. Monitor, follow up progress,and verify solution and validate effectiveness. The team shall use cause and effect tool (5M1E : Man, Machine, Material, Method,Measurement and Environment - Fishbone and 5 why ) Problem owners are those supervisors,managers,and executive leaders who own problems happened in their areas of responsibility. They are responsible for leading the problem solvers to get the problems solved.The members of problem solving team from other functional departments shall support as needed to solve the problem. All employees within the organization, no matter what their levels, find themselves in the role of problem solver from time to time. 1. Set expectations for your employees, at a local level, to use effective problem solving method and tools as part of and buy more over time? Problem solving training and CI process training to employee.
- 15. their jobs. 1. Know how to expose and clearly define problems. 2. Actively coach employees on effective problem solving process. 3. Take responsibility to standardize the process once a problem has been solved. 4. Recognize and reward employees for successfully solving problems. Problem solvers are our employee who are given appropriated trainings in skill and knowledge. They will act as change agent, be a power force in the workplace by both adopting and promoting new behaviors to others across and up the organizational structure.The management shall : 1. Employees are trained with skills and knowledge so that they can see problems. They are trained to be capable of recognizing that a current situation may be a problem and to define the problem clearly in measurable terms. 2. Build up quality mindset that it is the responsibility of employee to take up and solve problems as culture. Problem solvers must be willing and able to accept ownership for solving the problems in their area of responsibility, to communicate the existence of a problem to leadership if it’s
- 16. too large for the problem solver to solve, and to point out problems to others if they are outside the problem solver’s area of responsibility. Problem solvers must take immediate actions to contain and solve problems in their area of responsibility. 3. Apply structured,data-driven problem solving process to solve problems. Customer Satisfaction Contract review: Changes (Engineering, specifications, delivery schedule) communication. After sales services and technical supports. Meet and exceed Customer expectations. Sales and Customer Services are well verse of product knowledge, common legal sense. Product knowledge shall include their quality specifications and standards, and regulatory requirements (name of specification and standard such as Industrial standards,IEC, UL, VDE, RoHS, FCC, legal restrictions etc, but not the detailed content).They should conclude the quality requirements with the customers at selling point and take the lead to review the contract before processing the There is process to verify and take care of customer requirements. Sales, customer services are responsible for obtaining and confirming specific quality requirements, including criteria and standard,from customers. Company provides trainings to them. There is confirmed formal and written quality requirements document for each business/sales contract / order. The document is communicated to all relevant personneland implemented in a Control Plan. Quality personnel are responsible for conforming the products that are shipped to customers are conformed to customer requirements, industrial standards,and legal specifications. Sales and customer services carry out detailed customer satisfaction survey activities (visit, telephone,letter, email). Publish and communicate to all employees. How are customer perceptions captured on a proactive basis? Daily meeting to follow up progress on customer complaint and recovery plan progress and completion.
- 17. orders. Contract review team should include Sales, Production, Design, Quality and legal personnel. Their confirmation of capability and on time delivery is essential. Response Customer feedback Collect and analyze customer satisfaction data. Formulate improvement strategy. Communicate actions to customers. Install sufficient resource for customer complaint. Take serious and fast Response to customer complaint. There is strict customer complaint procedure with specific response times, response format (such as 5D, 8D, CAR), and response personnel.Customer quality services team responsibilities are strictly defined. The Quality Department shall organize the response to customer complaint. There are personneland mechanism monitors the progresses,actions follow up, validation of actions effectiveness and closed records. Lesson learns are shared broadly. Design teams (product and process)are compulsory required to review the lesson learns. Steps to execute the customercomplaint process in a way that meets the customer’s reasonable exceptions andneeds, but does not compromise the true resolution of the problem. 1. Know the details of how the product works in the customer’s process and product. Know how thefailure modes of the product affect thecustomer. For a given thing that goes wrong with the process or product, what is the How are customer perceptions captured on a proactive basis? How is data on customer satisfaction analyzed? How are opportunities identified and prioritized? What is the connection to the corrective and preventive action system? What are the organization’s long term trends in customer satisfaction? How are resources for customer satisfaction identified and provided? What connections exist between customer satisfaction and the organization’s objectives? 5D, 8D, CAR
- 18. exact effect on the customer? 2. React quickly to a customer notification. CQE should take a customer notification of a problem as an alarm for the organization. Containment should be a priority, with all investigation started after containment is achieved. 3. Be sure to obtain as much detail from the customer as possible. Make sure you listen to the customer for the details of what is occurring. Makerequests for data, samples, etc. 4. Develop a plan for theproblem-solving efforts and stick to it. Be realistic with the customer on the time-frame that is needed for a thorough investigation and resolution of the problem. Once a plan is developed and agreed to, the timing must be considered sacred. 5. Communicate with thecustomer regularly on thestatus of the problem-solving efforts. Makesure the customer knows exactly where you are in the problem-solving process. Ensure that the customer understands all that is being done, including verification of containment measures as the process proceeds. How are customer complaints handled? What is the largest complaint category? What is being done about it? How has the number of complaints changed over time? How are personnel trained to prevent complaints? How customers are made aware of actions on their complaints? What tools are used to identify the causes of complaints?
- 19. Continuous Improvement LEAN approach to eliminate wastes. Re-engineering to add values. Improve sigma of defectives. Keep competitiveness Keep in space with customer's expectation growth by upgrading products and technology. Product improvement - 1. Improve failed product to prevent repeat failure. 2. Improve product to exceed customer requirements. Process improvement - 1. Improve process to prevent producing poor quality. 2. Improve process to increase profit margin. Strengthen competitiveness by improving total quality. Benchmarking with competitors all the time to keep an eye on competitiveness. Publish and communicate strength and weakness to all employees to make them know what are needed to improve. Regular periodical review on quality performance report and identify improvement needs.Lesson learns are shared broadly. Design teams (product and process)are compulsory required to review the lesson learns. Organize process owners into improvement team, equip them with CI skills. Improve product quality in two folds 1. Products failed to meet quality in field and in house shall be examined and provide failure analysis, hence take improvement action to prevent repeat problem. 2. Products are reviewed after launch to seek opportunity of adding more values both to customer and the company. Improve process in two folds 1. Processes that identified to create quality problem How do data trends get analyzed? How do employees communicate their improvement ideas? How do preventive actions get recorded? Are statistical techniques being used? How are customer perceptions captured on a proactive basis? How does top management reviewthe organization’s performance? Who is involved in reviewing the organization’s performance? What actions have resulted from these reviews? How are records of the reviews generated? Are all required inputs and outputs addressed by records? How does the rest of the organization learn of actions and decisions that are determined during reviews? What evidence are seen to show continual improvement? Quality Scorecard. Fishbone LEAN Sigma.
- 20. shall be re-engineered to prevent repeat problem. 2. Processes are reviewed after launch to look for room to improve in yield and eliminate variations. Challenge but not exceed process limits.
- 21. Risk Management How to protect company and customer business from risk of operations breaking down. Recovery Plan Prepare a recovery plan for facing disasteror serious accident that forces the production down. Back Up System Prepare an emergency plan to include: 1. An emergency team list with full name and emergency contact number. The General Managershall be team leader. Functional managers are compulsory members. Each member has kept a copy an emergency recovery procedure. 2. Keep a back up copy of important documents outside the site. The backup copy is updated every day if possible. 3. Prepare a back up production facilities list that an alternative production location can be easily located. 4. There is employee evacuation plan for fire, power failure, poison gas etc possible accident. Practice the plan regularly. 5. There is trained emergency outbreak handling volunteer team, such as fire fighting, first aid. Ask to describe how to act upon an accident happened in the plant. Ask how many emergency evacuation practices a year. Verify documents backup and recovery team information. Photos and records of practices. Periodical practices plan.