An PPT on Consumer Behaviour and Market Segmentation
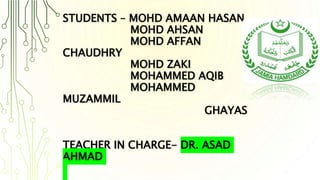
- 1. STUDENTS – MOHD AMAAN HASAN MOHD AHSAN MOHD AFFAN CHAUDHRY MOHD ZAKI MOHAMMED AQIB MOHAMMED MUZAMMIL GHAYAS TEACHER IN CHARGE- DR. ASAD AHMAD
- 3. WHAT IS CONSUMER BEHAVIOR ?
- 4. Consumer behavior is the study of individuals and organizations and how they select and use products and services. It is mainly concerned with psychology, motivations, and behavior.
- 5. The study of consumer behavior includes: - How consumers think and feel about different alternatives (brands, products, services, and retailers). - How consumers reason and select between different alternatives. - The behavior of consumers while researching and shopping. - How consumer behavior is influenced by their environment (peers, culture, media).
- 6. WHY UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR IS IMPORTANT FOR A MARKETER ?
- 7. Studying consumer behavior is important because this way marketers can understand what influences consumers' buying decisions. By understanding how consumers decide on a product they can fill in the gap in the market and identify the products that are needed and the products that are obsolete.
- 8. A consumer behavior analysis should reveal: -What consumers think and how they feel about various alternatives (brands, products, etc.); -What influences consumers to choose between various options; -Consumers’ behavior while researching and shopping; -How consumers’ environment (friends, family, media, etc.) influences their behavior. -Consumer behavior is often influenced by different factors. Marketers should study consumer purchase patterns and figure out buyer trends.
- 9. STUDYING CONSUMER BEHAVIOR ALSO HELPS MARKETERS DECIDE HOW TO PRESENT THEIR PRODUCTS IN A WAY THAT GENERATES MAXIMUM IMPACT ON CONSUMERS. UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIOR IS THE KEY SECRET TO REACHING AND ENGAGING YOUR CLIENTS, AND CONVERT THEM TO PURCHASE FROM YOU.
- 12. 4 Types of Consumer Behaviour A consumer’s buying decision depends on the type of products that they need to buy. The behavior of a consumer while buying a coffee is a lot different while buying a car. Based on observations, it is clear that purchases that are more complex and expensive involve higher deliberation and many more participants. There are four types of consumer behavior: 1.Complex buying behavior 2.Dissonance-reducing buying behavior 3.Habitual buying behavior 4.Variety seeking behavior
- 13. Complex buying behaviour Complex buying behavior is encountered particularly when consumers are buying an expensive product. In this infrequent transaction, consumers are highly involved in the purchase decision. Consumers will research thoroughly before committing to invest. Consumer behaves very different when buying an expensive product or a product that is unfamiliar to him. When the risk of buying a product is very high, a consumer consults friends, family and experts before making the decision. For example, when a consumer is buying a car for the first time, it’s a big decision as it involves high economic risk. There is a lot of thought on how it looks, how his friends and family will react, how will his social status change after buying the car, and so on.
- 14. Dissonance-reducing buying behaviour In dissonance-reducing buying behavior consumer involvement is very high. This might be due to high price and infrequent purchase. In addition, there is a low availability of choices with less significance differences among brands. In this type, a consumer buys a product that is easily available. Consumers will be forced to buy goods that do not have too many choices and therefore consumers will be left with limited decision making. Based on the products available, time limitation or the budget limitation, consumers buy certain products without a lot of research. For example, a consumer who is looking for a new collapsible table that can be taken for a camping, quickly decides on the product based on few brands available. The main criteria here will be the use and the feature of the collapsible table and the budget available with him.
- 15. Habitual buying behaviour Habitual Buying Behavior is depicted when a consumer has low involvement in a purchase decision. In this case the consumer is perceiving only a few significant differences between brands. When consumers are buying products that they use for their daily routine, they do not put a lot of thought. They either buy their favorite brand or the one that they use regularly – or the one available in the store or the one that costs the least. For example, while a consumer buys a loaf of bread, he tends to buy the brand that he is familiar with without actually putting a lot of research and time. Many products fit into this category. Everyday use products, such as salt, sugar, biscuits, toilet paper, and black pepper all fit into this product category.
- 16. Variety seeking buying behaviour In variety seeking consumer behavior, consumer involvement is low. There are significant differences between brands. Here consumers often do a lot of brand switching. The cost of switching products is low, and hence consumers might want to try out new products just out of curiosity or boredom. Consumers here, generally buy different products not because of dissatisfaction but mainly with an urge to seek variety. For example, a consumer likes to buy a cookie and choose a brand without putting much thought to it. Next time, the same consumer might may choose a different brand out of a wish for a different taste. Brand switching occurs often and without intention.
- 19. WHAT IS MARKER SEGMENTATION # The process of creating small segments comprising of like minded individual within a broad market refers to market segmentation # It helps in the division market into small segment including individuals who show inclination towards identical brands and have similar interests attitudes and perception.
- 20. NEED FOR MARKET SEGMENTATION • Market segmentation helps the marketers to device appropriate marketing strategies and promotional schemes according to the tastes of the individual • Market segmentation also gives the customer a clear view of what to buy and what not to buy . • It helps to organization to target the right product to the right customers at the right time . • It helps the marketers to understand the needs of the target audience and adopt specific marketing plans accordingly.
- 21. BENEFITS OF MARKET SEGMENTATION 1. When you know whom you are talking to, you can develop stronger marketing messages you can avoid generic, vague, language that speaks to a broad audience . 2. On digital services ,you can target audience by their age location interests and more 3. When your message are clear direct and targeted they attracted the right people . 4. It also helps business to focus their efforts which enables them to establish a brand identify and specialize in a particular type of product 5. Market segmentation can also help to inform other important business decisions regarding how you get your product to customers
- 23. Demographic segmentation is one of the most popular and commonly used types of market segmentation. It refers to statistical data about a group of people. Demographic Market Segmentation Examples • Age • Gender • Income • Location • Family Situation • Annual Income • Education • Ethnicity
- 24. Psychographic Segmentation categorizes audiences and customers by factors that relate to their personalities and characteristics. Psychographic Market Segmentation Examples • Personality traits • Values • Attitudes • Interests • Lifestyles • Psychological influences • Motivations
- 25. While demographic and psychographic segmentation focus on who a customer is, behavioral segmentation focuses on how the customer acts. Behavioral Market Segmentation Examples • Purchasing habits • Spending habits • User status • Brand interactions Behavioral segmentation requires you to know about your customer’s actions. These activities may relate to how a customer interacts with your brand or to other activities that happen away from your brand.
- 26. Geographic segmentation is the simplest type of market segmentation. It categorizes customers based on geographic borders. Geographic Market Segmentation Examples • ZIP code • City • Country • Radius around a certain location • Climate • Urban or rural
- 27. CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AUDIT THE CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AUDIT IS A FUNDAMENTAL PART OF THE MARKETING PLANNING PROCESS. IT IS CONDUCTED NOT ONLY AT THE BEGINNING OF THE PROCESS, BUT ALSO AT A SERIES OF POINTS DURING THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PLAN. THE CONSUMER BEHAVIOR AUDIT CONSISTS OF TWO TYPES : - 1. INTERNAL INFLUENCES. 2. EXTERNAL INFLUENCES.
- 28. INTERNAL INFLUENCES The Internal Influences also known as Internal Marketing Environment refers to components INSIDE the firm that are unique to the firm. An analysis of the internal environment is critical in the development of marketing strategy to ensure to that the firm's strategy is based upon its situation, resources and goals.
- 29. As a marketer you must know that : - How does a marketing team organized… How efficient is their marketing team… How effective is their marketing team… How does their marketing team interface with other organisations and internal functions…, etc…
- 30. External Influence The external marketing environment consists of social, demographic, economic, technological, political and legal, and competitive variables. ... Within the external environment, social factors are perhaps the most difficult for marketers to anticipate.
- 31. • A market orientated organization must know the nature of the customer such as their needs and how to satisfy them. • Their buyer decision process and consumer behavior. • Their perception of the brand and loyalty to it. • The nature of segmentation, targeting and positioning in the markets. • What customers 'value' and how we provide that value to them.
- 32. CONCLUSION CONSUMER BEHAVIOR • Consumer buying behaviors is very importance in the industry because consumers will make many buying decisions every day. There are many consumer buying decisions in great detail to answer questions about what consumers buy, where they buy, how and how much they buy, when they buy, and why they buy.
- 33. •MARKET SEGMENTATION • The underlying principle of market segmentation is that the product and services needs of individual customers differ. Market segmentation involves the grouping of customers together with the aim of better satisfying their needs whilst maintaining economies of scale. • It consists of three stages and if properly executed should deliver more satisfy customers, few direct confrontations with competitors and better designed marketing programmers.
