Topic 7 perfect competition revision (3)
•Télécharger en tant que DOC, PDF•
0 j'aime•17 vues
Perfect Competition
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (16)
Agri 2312 chapter 7 economics of input and product substitution

Agri 2312 chapter 7 economics of input and product substitution
Similaire à Topic 7 perfect competition revision (3)
Similaire à Topic 7 perfect competition revision (3) (17)
Economics 2106 (Fall 2012) — Prof. Greg Trandel — Homework Ass.docx

Economics 2106 (Fall 2012) — Prof. Greg Trandel — Homework Ass.docx
Fundamentals of EconomicsA. Profit MaximizationProfit Maximi.docx

Fundamentals of EconomicsA. Profit MaximizationProfit Maximi.docx
Page 1 Microeconomics CH 9-10 Take home quiz. Mar.docx

Page 1 Microeconomics CH 9-10 Take home quiz. Mar.docx
1. Suppose that a firm is currently charging $45 for its product. Th.docx

1. Suppose that a firm is currently charging $45 for its product. Th.docx
Outline for Lecture 15Long-Run Production CostsThe Lon.docx

Outline for Lecture 15Long-Run Production CostsThe Lon.docx
MBA 681 Economics for Strategic DecisionsPrepared by Yun Wan.docx

MBA 681 Economics for Strategic DecisionsPrepared by Yun Wan.docx
Complete the following questions on cost function 1.Write the.docx

Complete the following questions on cost function 1.Write the.docx
ECON 1102 Test 3 (061416) Test 3 ECON 1102 Sec. 711 (Mic.docx

ECON 1102 Test 3 (061416) Test 3 ECON 1102 Sec. 711 (Mic.docx
1. In the perfectly competitive market, a firm’s marginal revenue .docx

1. In the perfectly competitive market, a firm’s marginal revenue .docx
1. Which is a characteristic of monopolistic competitionA).docx

1. Which is a characteristic of monopolistic competitionA).docx
Dernier
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Dernier (20)
Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions

Salient Features of India constitution especially power and functions
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...

Jual Obat Aborsi Hongkong ( Asli No.1 ) 085657271886 Obat Penggugur Kandungan...
Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...

Beyond_Borders_Understanding_Anime_and_Manga_Fandom_A_Comprehensive_Audience_...
Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...

Kodo Millet PPT made by Ghanshyam bairwa college of Agriculture kumher bhara...
NO1 Top Black Magic Specialist In Lahore Black magic In Pakistan Kala Ilam Ex...

NO1 Top Black Magic Specialist In Lahore Black magic In Pakistan Kala Ilam Ex...
HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx

HMCS Max Bernays Pre-Deployment Brief (May 2024).pptx
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx

Python Notes for mca i year students osmania university.docx
Topic 7 perfect competition revision (3)
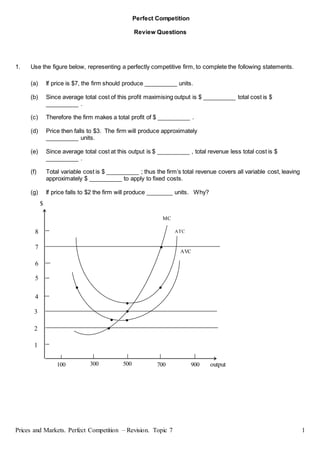
- 1. Prices and Markets. Perfect Competition – Revision. Topic 7 1 Perfect Competition Review Questions 1. Use the figure below, representing a perfectly competitive firm, to complete the following statements. (a) If price is $7, the firm should produce __________ units. (b) Since average total cost of this profit maximising output is $ __________ total cost is $ __________ . (c) Therefore the firm makes a total profit of $ __________ . (d) Price then falls to $3. The firm will produce approximately __________ units. (e) Since average total cost at this output is $ __________ , total revenue less total cost is $ __________ . (f) Total variable cost is $ __________ ; thus the firm’s total revenue covers all variable cost, leaving approximately $ __________ to apply to fixed costs. (g) If price falls to $2 the firm will produce ________ units. Why? $ 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 output 100 300 500 700 900 MC ATC AVC
- 2. Prices and Markets. Perfect Competition – Revision. Topic 7 2 2. A small scale grower supplies tomatoes to local fruit shops. Fixed costs facing the grower are $100, and the variable cost data is given in the table below: Output (Q) Total Variable Cost (TVC) 50 100 60 110 70 130 80 160 90 200 100 250 110 310 120 380 (a) For the output and cost figures given above, calculate the average variable cost (AVC) and marginal cost (MC). (b) Assume the grower operates under perfectly competitive conditions, and the price he receives is currently $6 per kilogram. Determine the output level that would maximise the grower’s profits. What are profits at this output level? (c) If, due to an influx of new competition, the price of tomatoes falls to $3 per kilogram, explain whether the grower should continue to produce in the short run and in the long run. 3. Using a perfectly competitive firm operating in the short run as a basis for your diagram, show and explain the prices associated with the break even and shut down points, and explain the output ranges over which the firm produces to make a positive economic profit and/or to minimise economic losses. 4. In long-run equilibrium, P = AC = MC. Of what significance for the allocation of resources is the equality of MC and AC? Of what significance for the allocation of resources is the equality of P and MC? 5. Using a perfectly competitive firm operating in the short run as a basis for your diagrams, show and explain how the firm can make economic profit, normal profit and minimum economic loss; and show also the break even and shut down points.
- 3. Prices and Markets. Perfect Competition – Revision. Topic 7 3 6. A perfectly competitive firm producing X has the following monthly cost data (Q = total output, MC = marginal cost): Q (units) MC ($) 1 40 2 37 3 32 4 28 5 30 6 32 7 35 8 40 9 46 10 56 (a) For each of the following prices determine this firm’s optimal output per month in the short run. Show your calculations. (i) $30.50 (ii) $32.40 (iii) $42.00 (b) Suppose the market price of X is $49.00. Calculate the total fixed cost that would result in zero economic profit for this firm. Show your calculations. (c) Suppose there are 400 firms in the perfectly competitive market for X, each with the same monthly cost data as the above firm. Draw this market’s short run supply curve, indicating the specific prices and quantities of output, on the assumption that the cost data are not affected by the summation of the firms’ outputs. (d) Suppose the market price of X is $60.00 and the total fixed cost of the above firm is $140 per month. (i) Initially, how would this firm react to the situation in the long run? Explain with the aid of your calculations. (ii) With the aid of diagrams (sketches will be sufficient – there is no need to plot the exact data) showing both the firm and the market, explain how this market adjusts to long run equilibrium.
- 4. Prices and Markets. Perfect Competition – Revision. Topic 7 4 7. A perfectly competitive firm has the following cost data: Q AFC TVC (units per day) ($) ($) 1 90 20 2 45 36 3 30 49 4 22.50 60 5 18 73 6 15 88 7 12.86 106 8 11.25 129 9 10 159 10 9 199 (a) For each of the following prices determine this firm’s profit-maximising (or loss-minimising) output per day, in the short run, and calculate the daily profit or loss. Show your calculations. (a.1) $13.20 (a.2) $16.50 (a.3) $39.00 (b) Draw this firm’s short run supply curve, indicating the relevant numerical values for price and output. (c) Suppose this firm’s costs are the same as those of other firms in the perfectly competitive industry. Indicate, together with a brief explanation, the numerical value of the critical price level below which this firm will leave the industry in the long run, and above which new firms will enter that industry in the long run.
- 5. Prices and Markets. Perfect Competition – Revision. Topic 7 5 8. A perfectly competitive firm producing X has the following monthly cost data (Q = total output, MC = marginal cost): Q (units) MC ($) 1 40 2 37 3 32 4 28 5 30 6 32 7 35 8 40 9 46 10 56 (a) For each of the following prices determine this firm’s optimal output per month in the short run. Show your calculations. (a.i) $30.50 (a.ii) $32.40 (a.iii) $42.00 (b) Suppose the market price of X is $49.00. Calculate the total fixed cost that would result in a normal profit for this firm. Show your calculations. (c) Suppose there are 400 firms in the perfectly competitive X industry, each with the same monthly cost data as the above firm. Draw this industry’s short run supply curve, indicating the specific prices and quantities of output, on the assumption that the cost data are not affected by the summation of the firms’ outputs. (d) Suppose the market price of X is $44.00 and the total fixed cost of the above firm is $140 per month. How will this firm react to this situation in the long run? Explain with the aid of your calculations.