Tracheostomy ( for medical students )
- 1. Y
- 2. PRESENTED TO:- Mrs.mamta toppo Associate professor College of nursing RIMS, Ranchi PRESENTED BY :-
- 3. Trachea -General characteristics - trachea relation TRACHEOSTOMY Introduction Definition Tracheostomy history Tracheostomy indications Types of tracheostomy - Permanent tracheostomy -Temporary tracheostomy Tracheostomy tube Parts of tracheostomy tube Advantages Pre operative work up Types of surgical airway technique in tracheostomy Procedure of open tracheostomy Post operative tracheostomy care Routine tracheostomy care Care of stoma Suctioning technique in tracheostomy Procedure of suctioning Complications Recent research work Bibliography Evaluation
- 4. Trachea or wind pipe is a cartilaginous tube that connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs allowing the passage of air. Trachea lies in the midline of the neck. Trachea extends from larynx (at the level of C6)and branches into two primary bronchi (at the level of T4-T5). It is located anterior to the esophagus.
- 6. Trachea contains rings of hyaline cartilage which are C shaped, connected to each other by the smooth trachealis muscles. C shaped design of the trachea helps to ensure that the trachea will not collapse. At the top of trachea the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx- the only complete ring. Length : 9-15 cm Outer diameter : 21-27 mm Internal diameter : 12-18 mm Distance infracricoid-carina about 11 cm 18-22 C-shaped cartilaginous rings In adults the cartilages are 3to 5 mm wide and upto 2mm thick Annular ligament – between two rings The crico tracheal ligament connects the cricoid cartilage with the 1st ring of trachea.
- 8. CERVICAL TRACHEA POSTERIOR -Esophagus,Trachealis muscle ANTERIOR - 2nd and 4th rings are covered by the isthmus of thyroid. LATERAL - 2 lateral lobes (thyroid gland) THORACIC TRACHEA ANTERIOR - Thymus gland - Left brachio cephalic vein, aortic arch LATERAL - Vagus nerve
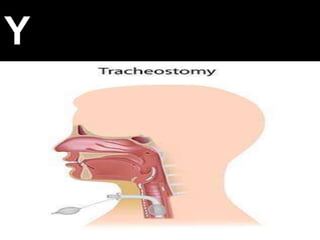
- 9. It is a surgical opening into the trachea below the larynx through which an indwelling tube is placed to overcome upper airway obstruction, facilitate mechanical ventilator support and or the removal of tracheobronchial secretions .The opening is called stoma . Tracheostomy is indicated when oral or nasal intubation is insufficient to manage acute airway obstruction. It is performed for airway protection after major head and neck surgery or when client is unable to maintain adequate oxygenation
- 11. An artificial ( usually ) surgically created airway fashioned by making a hole in the anterior wall of the trachea and the insertion of the tracheostomy tube which may or may not be permanent
- 12. It is one of the oldest surgical procedure In 1546 first well documented tracheostomy by Antonius Musa Brasavola In 1921 Chevaliar Jackson standardized the technique of tracheostomy In 1916Toye and Weinstain developed the Modern Percutaneous tracheostomy ( PCT ).
- 13. UPPER AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION RELIEVE 1.Trauma 2. Foreign body 3. Infections like acute epiglottitis etc. 4.Tumors of the larynx 5. Atresia 6. Glottic oedema TO IMPROVE RESPIRATORY FUNCTIONS 1. Fulminating bronchopneumonia 2. Chronic bronchitis 3. Chest injuries RESPIRATORY PARALYSIS 1.Unconcious head injury 2. Bulbar poliomyelitis 3.Tetanus PULMONARY TOILET 1.Those who cannot cough and clear their chest 2. Prevent aspiration by low pressure high volume cuff tracheostomy tube ELECTIVE PROCEDURES 1. For major head and neck operations
- 14. A. Depending on the timing 1. Elective 2. Emergency B. Depending on the causes 1. Permanent 2.Temporary
- 15. PERMANENT TRACHEOSTOMY The trachea is permanently disconnected from the pharynx and the proximal end of the trachea is sutured to the skin. Permanent tracheostomy is an elective procedure carried out as a part of an operation And the stoma is kept open by the rigidity of the tracheal cartilage.The patient will breathe through this stoma for remainder of his / her life.
- 16. TEMPORARY TRACHEOSTOMY It can be formed when patients require long term respiratory support or are unable to protect their own airways. A tracheostomy tube will be inserted to maintain patency of the airway.This can remove when patient recovers. It is long term procedure.
- 17. It differs from a permanent tracheostomy in that there is still a communication between the pharynx and the lower airway area via larynx. In permanent tracheostomy the only access to the lower airway is via the tracheostome.
- 18. It is an indwelling tube used to maintain patency of the tracheostomy. There are different types of tracheostomy tube available :- 1.Metal tracheostomy tube (for long term use) 2.Plastic tracheostomy tube (for short term use)
- 20. It consists of 3 parts:- 1. Outer cannula with flange (neck plate) :-It holds the tracheostomy open. 2. Inner cannula :- It fits inside outer cannula. It has a lock to keep it from being coughed out and removed for cleaning. 3. Obturator :- used to insert a tracheostomy tube.
- 22. Tracheostomy has certain advantages over the temporary tube called endotracheal tube because it :- • Reduces patient discomfort • Reduces need for sedation • Improves ability to maintain oral and bronchial hygiene • Reduces risk of trauma to the wind pipe and trachea • Make breathing easier with less effort for a sick patient • Easier to move off assisted breathing using a ventilator
- 23. History taking Physical assessment Anesthesiological assessment CBC Caugulation profile Informed consent
- 24. CRICOTHYROIDOTOMY- It is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life threatening situations, such as airway obstructions by foreign body , angioedema, or massive facial trauma. OPENTRACHEOSTOMY- It involves the creation of a stoma at the skin surface of the anterior neck leading to the trachea. It is one of the oldest described surgical intervention. . PERCUTANEOUSTRACHEOSTOMY-It is generally carried out in the ICU on a patient who is intubated and ventilated with continuous monitoring under deep intravenous sedation/ anesthesia.
- 25. A. Airway control B. Patient position :- Supine , neck and head extended by keeping pillow under the shoulder. C. Anesthesia :- (0) Not necessary if patient is unconscious or in emergency situation. (0) If patient is conscious local anesthesia or general anesthesia is used for procedure
- 26. D. Identify the landmarks :- (0) Horizontal out is made across the neck 1cm above the sternal notch . Incision should extended to sternomastoid muscles (0) Retractors are placed, skin is retracted to expose the trachea. (0) Dissect through fascial planes and retract anterior jugular vein, retract the strap muscles and divide thyroid isthmus. (0) Place cricoid hook on 2nd tracheal ring. 3rd and 4th tracheal rings are incised for the tracheostomy tube to be placed. (0) Before inserting tracheostomy tube trachea is suctioned thoroughly to remove secretions and blood . (0) A suitable size tracheostomy tube is introduced inside using obturator . A general rule is that the tube should be 3/4th of the diameter of trachea. (0) The cuff of tube is inflated by using a necktie . (0) Incision closed using skin sutures by side of tracheostomy tube. Dressing is applied for the wound to heal.
- 28. 1. Maintain patency of tracheostomy tube and airway - Frequent atraumatic suction - Humidification of inspired air or oxygen - Fowler’s position to aid in breathing - Maintain adequate fluid intake - Provide frequent mouth wash - Coughing and physiotherapy - Occasional bronchial lavage 2. Prevent infections and complications - Aseptic tube suction , handling and tube changing - Prophylactic antibiotics - Deflate cuff for 5 minutes every hours - Avoid tube impinging on posterior tracheal wall 3.Tube position - To prevent decubitus of trachea - Not to cover with blanket
- 29. 4.Suctioning - Regular gentle suctioning - Not aggressive and not too much deep 5. Inner tube care - Once or more daily removed and clean. 6. Humidification - Artificial nose to prevent crusting of secretions. ROUTINE TRACHEOSTOMY CARE Rubbing of the trachea tube and secretions can irritate the skin around the stoma . Daily care of the trach site is needed to prevent infections and skin breakdown under the tracheostomy tube and ties. Care should be done at least once a day.
- 30. Care of stoma is done in the immediate post operative period, and is ongoing. The stoma site is covered with a small square guaze and then by an occlusive dressing. Inspect the stoma area at least daily to ensure the skin is clean and dry to maintain skin integrity and avoid breakdown. Daily cleaning of the stoma is recommended using 0.9% sterile saline solution. After daily cleaning , ensure dressing inserted at stoma site
- 32. Suctioning techniques is necessary to remove mucus, maintain a patent airway, and avoid tracheostomy tube blockage of tracheostomy tube. The frequency of suctioning varies and is based on individual patient assessment. EQUIPMENTS USED IN SUCTIONING: 0 Suction apparatus 0 Suction catheter 0 Tubing 0 Sterile water
- 33. 1. Explain about the suction of tracheostomy tube to the patient and his family. 2. Perform hand hygiene 3. Peel open suction catheter end and attach to suction tubing , check and adjust suction pressure gauge to between 80-120 mmHg. 4. Utilizing a non touch technique gently introduce the suction catheter tip into the tracheostomy tube to the pre measured depth. 5. Apply finger to suction catheter hole and gently rotate the catheter while withdrawing( each suction should not be any longer than 5-10 seconds). 6. Assess the patients respiratory rate , skin color and oximetry reading. 7. Repeat the suction as indicated by the patients individual condition. 8. Look at the secretions in the suction tubing- they should be normally be clear or white and move easily through the tubing. 9. Rinse the suction catheter with sterile water decanted into container 10. Replace suction catheter into the packaging. 11. Dispose of waste, remove gloves and perform hand hygiene
- 34. A. Immediate Cardiac arrest , apnea, air embolism , haemorrhage , surgical trauma , oesophagus pneumothorax etc. B. Intermediate Dysphagia , infection , tracheal erosion , tube obstruction , lung abscess , aspiration , emphysema C. Late Persistent tracheocutaneous fistula , tracheomalacia and tracheo oesophageal fistula , tracheal stenosis
- 36. I n recent research an interprofessional team approach to tracheostomy care in which a mixed method investigation into the mechanisms explaining tracheostomy team effectiveness. The aim of the research is to investigate the mechanisms through which an interprofessional team approach can improve the management of patient with a tracheostomy After research it is concluded that tracheostomy teams enhances consistency of care through the development and the implementation of interprofessional protocol. In addition, such team allowed more efficient and effective communication and decision making consequent to the collocation of diverse professionals.
- 37. JAVEDANSARI “ATEXTBOOK OF MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING II “ PV PUBLI- CATION PAGE NO. 211-217 WWW.SLIDESHARE.COM WWW.WIKIPEDIA.COM
- 38. WHAT ISTRACHEOSTOMY ? HOW LONGWILL HAVETACHTUBE PLACED IN A PATIENT? WHYTHERE IS NEED OF INNER CANNULAWITH A TRACHEOSTOMY? WHO DEVELOPEDTHE MODERN PERCUTANEOUS TRACHEOSTOMY (PCT) AND INWHICHYEAR ? WHAT ARETHE INDICATIONS OFTRACHEOSTOMY ? TRACHEOSTOMYTUBE CONSISTS OF HOW MANY PARTS ? WHAT ARETHE ADVANTAGESOFTRACHEOSTOMY ? WHAT ARETHE COMPLICATIONS OF IMMEDIATE TRACHEOSTOMY ? TRACHEOSTOMY IS USUALLY PERFORMED BETWEEN WHICHTRACHEAL RINGS OF CARTILAGE?