Complement regulation
•Télécharger en tant que DOCX, PDF•
1 j'aime•254 vues
This document contains information about complement regulation, proteins involved in it and various diseases associated with defects in complement regulation.
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Similaire à Complement regulation
Similaire à Complement regulation (20)
A. Stathis - Lymphomas - New drugs in the treatment of lymphomas

A. Stathis - Lymphomas - New drugs in the treatment of lymphomas
5-1. Review of complement system. Khadizha Emirova (eng)

5-1. Review of complement system. Khadizha Emirova (eng)
Complement system in association with the immune response.pptx

Complement system in association with the immune response.pptx
Plus de Nidhi Jodhwani
Plus de Nidhi Jodhwani (17)
photosynthetic microorganisms (microbial metabolism)

photosynthetic microorganisms (microbial metabolism)
Smear preparation for differential leucocyte count

Smear preparation for differential leucocyte count
Dernier
Dernier (20)
Seismic Method Estimate velocity from seismic data.pptx

Seismic Method Estimate velocity from seismic data.pptx
Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)

Recombinant DNA technology (Immunological screening)
Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks

Formation of low mass protostars and their circumstellar disks
Creating and Analyzing Definitive Screening Designs

Creating and Analyzing Definitive Screening Designs
Discovery of an Accretion Streamer and a Slow Wide-angle Outflow around FUOri...

Discovery of an Accretion Streamer and a Slow Wide-angle Outflow around FUOri...
VIRUSES structure and classification ppt by Dr.Prince C P

VIRUSES structure and classification ppt by Dr.Prince C P
TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...

TEST BANK For Radiologic Science for Technologists, 12th Edition by Stewart C...
Hubble Asteroid Hunter III. Physical properties of newly found asteroids

Hubble Asteroid Hunter III. Physical properties of newly found asteroids
Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR

Stunning ➥8448380779▻ Call Girls In Panchshil Enclave Delhi NCR
Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...

Biopesticide (2).pptx .This slides helps to know the different types of biop...
Complement regulation
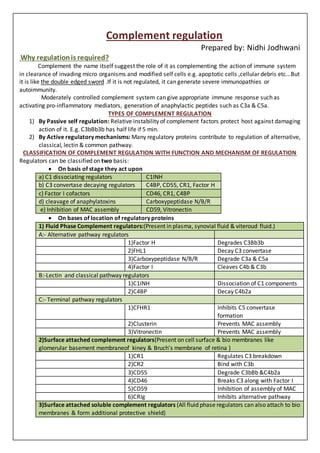
- 1. Complement regulation Prepared by: Nidhi Jodhwani Why regulationis required? Complement the name itself suggest the role of it as complementing the action of immune system in clearance of invading micro organisms and modified self cells e.g. apoptotic cells ,cellular debris etc...But it is like the double edged sword .If it is not regulated, it can generate severe immunopathies or autoimmunity. Moderately controlled complement system can give appropriate immune response such as activating pro-inflammatory mediators, generation of anaphylactic peptides such as C3a & C5a. TYPES OF COMPLEMENT REGULATION 1) By Passive self regulation: Relative instability of complement factors protect host against damaging action of it. E.g. C3bBb3b has half life if 5 min. 2) By Active regulatory mechanisms: Many regulatory proteins contribute to regulation of alternative, classical, lectin & common pathway. CLASSIFICATION OF COMPLEMENT REGULATION WITH FUNCTION AND MECHANISM OF REGULATION Regulators can be classified on two basis: On basis of stage they act upon a) C1 dissociating regulators C1INH b) C3 convertase decaying regulators C4BP, CD55, CR1, Factor H c) Factor I cofactors CD46, CR1, C4BP d) cleavage of anaphylatoxins Carboxypeptidase N/B/R e) Inhibition of MAC assembly CD59, Vitronectin On bases of location of regulatory proteins 1) Fluid Phase Complement regulators:(Present in plasma, synovial fluid & viteroud fluid.) A:- Alternative pathway regulators 1)Factor H Degrades C3Bb3b 2)FHL1 Decay C3 convertase 3)Carboxypeptidase N/B/R Degrade C3a & C5a 4)Factor I Cleaves C4b & C3b B:-Lectin and classical pathway regulators 1)C1INH Dissociation of C1 components 2)C4BP Decay C4b2a C:- Terminal pathway regulators 1)CFHR1 Inhibits C5 convertase formation 2)Clusterin Prevents MAC assembly 3)Vitronectin Prevents MAC assembly 2)Surface attached complement regulators(Present on cell surface & bio membranes like glomerular basement membraneof kiney & Bruch’s membrane of retina ) 1)CR1 Regulates C3 breakdown 2)CR2 Bind with C3b 3)CD55 Degrade C3bBb &C4b2a 4)CD46 Breaks C3 along with Factor I 5)CD59 Inhibition of assembly of MAC 6)CRIg Inhibits alternative pathway 3)Surface attached soluble complement regulators (All fluid phase regulators can also attach to bio membranes & form additional protective shield)
- 2. VARIOUS DISEASES CAN OCCUR IN HUMANS AS THE OUTCOME OF DEFECT IN COMPLEMENT REGULATION As the complement regulation is important in protection of host cell along with removal of invading micro organisms, any disturbance in this regulation can result into host cell damage and accumulation of immune debris. Some of them are described below:- 1) Hereditary angioedema: Affected regulator:C1INH Function of regulator: Dissociation of C1 complement Ratio: occurs 1 in 1000 Pathophysiology: Leads to excessive production of vasoactive mediators -Results into tissue swelling and extracellular fluid accumulation -Abdominal pain and upper respiratory track pain 2) aHUS (atypical Haemolytic Uremia): Affected regulator: Factor H, Factor I Function of regulator:Degrade C3 convertase Pathophysiology: Antibody against Factor H produced which binds with C terminal of Factor H -No degradation of C3 convertase -More C3 cleavage results into more C3a production(anaphylatoxin) -Damage to kidney 3)AMD (Age relatedMacular Degeneration): Affected regulator: Factor H Function of regulator: Degrade C3 convertase Pathophysiology: No Factor H because of defect in gene coding for that factor -No degradation of C3 convertase -More C3 cleavage results into more C3a production(anaphylatoxin) -Severe inflammation results into vasodialation -Accumulation of exudates in center of retina -Blurred central vision 4)MPGN type II(Membrane Proliferative GlomeruloNephritis type II) OR DDD (Dense Deposit Disease) Affected regulator: Factor H Function of regulator: Degrade C3 convertase Pathophysiology: Uncontrolled complement activation -Excess C3 convertase -Excess of C3 cleavage results into overproduction of C3a -C3a deposits on glomerular basement-membrane of kidney & Bruch’s membrane of retina. 5)SLE(systemic lupus erythematosus): An auto immune disease in which more amount of immune- complexes are generated and defect in regulation can result into defective clearance of these complexes thus local chronic inflammation occurs. Referance:1)Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins;Peter F. Zipfel and ChristineSkera,2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited. 2) OEWN, PUNT, SANFORD; Kuby Immunology; seventh edition;2013; W.H. Freeman and company; New York 3)Wikipedia.org