Cell membrane
- 1. The Cell Membrane and Transport Systems
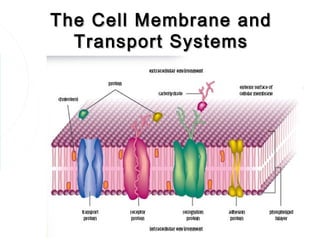
- 2. The Cell Membrane The boundary of all living cells is a cell membrane which controls the entry of dissolved substances into and out of the cell. A cell membrane consists of both lipid and protein. The membrane is formed of a double – layer of lipids. Proteins are embedded in this layer forming channels that allow water – soluble substances pass through
- 3. The Cell Membrane Phospholipid bi-layer
- 5. Crossing The Membrane All cells must be able to take in & expel various substances in order to survive, grow & reproduce. As a cell membrane only allows some dissolved substances to cross it, it is described as being semi – permeable OR partially – permeable.
- 6. Main Types of Transport Passive Transport: diffusion & osmosis Active Transport Endocytosis and Exocytosis Passive – movement across membranes that does not require any energy Active – movement across membranes that does require energy
- 7. Diffusion Net movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
- 8. Diffusion Difference in concentration between two regions = concentration gradient Diffusion occurs when a gradient exists and continues until equilibrium Factors can effect the rate of diffusion when the concentration gradient is large when heat is applied when molecules are smaller when movement occurs through a gaseous membrane
- 9. Diffusion Water, carbon dioxide and other small uncharged particles
- 10. Osmosis Net movement of a solvent, (usually water) across a differentially permeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to high solute concentration. That is, water molecules move from a region of high solvent concentration to low concentration.
- 11. Osmosis
- 12. Osmosis in Animal Cells Isotonic – when the extracellular fluid and intracellular fluids are at equal concentrations. Hypotonic – when the extracellular fluid has a higher water concentration than the intracellular fluid. Hypertonic – when the intracellular fluid has a higher water concentration than the extracellular fluid.
- 13. Osmosis High Water Low water Concentration concentration means means the solution the solution is is Hypotonic Hypertonic Loses water by Gains water by osmosis osmosis Solute molecules cannot Water molecules pass through the partially permeable Partially membrane permeable membrane There is a net movement of water molecules towards the less concentrated side (in terms of water molecules) until water concentrations equalize.
- 14. Osmosis in Animal Cells
- 15. Osmosis in Animal Cells Isotonic solution No net movement of solvent = equilibrium Red blood cell = 0.9% saline Solution = 0.9% saline
- 16. Osmosis in Animal Cells Hypotonic solution Solvent moves into the cell Red blood cell = 0.9% saline Solution = 0.4% saline
- 17. Osmosis in Animal Cells Hypertonic solution Solvent moves out of the cell into the solution Red blood cell = 0.9% saline Solution = 1.2% saline
- 18. Osmosis in Plant Cells Different to animal cells because of the cell wall
- 19. Osmosis in Plant Cells Isotonic solution No net movement of solvent = equilibrium Cell placed in solution that has the same concentration as the cell sap
- 20. Osmosis in Plant Cells Hypotonic solution Plant cell placed in solution that has a lower concentration than the cell sap •Water enters the vacuole •The vacuole expands •Cytoplasm is pushed outwards •‘Turgid’ cell
- 21. Osmosis in Plant Cells Hypertonic solution Plant cell placed in solution that has a higher concentration than the cell sap •Water exits the vacuole •Vacuole shrinks •Cytoplasm moves inwards •‘Plasmolysis’
- 22. Active Transport Diffusion is very slow & it moves substances down a concentration gradient. Many substances are needed by organisms in much greater amounts than what can be provided by diffusion alone. Additionally, some substances need to be accumulated in cells against the concentration gradient. In order for this to occur, energy must be used to move the needed substances across the cell membrane.
- 23. Active Transport Active transport occurs through protein channels.