Michael porter
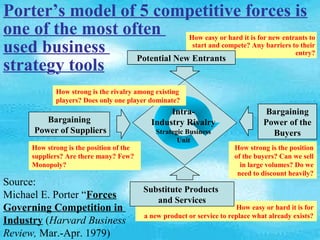
- 1. Porter’s model of 5 competitive forces is one of the most often How easy or hard it is for new entrants to used business Potential New Entrants start and compete? Any barriers to their entry? strategy tools How strong is the rivalry among existing players? Does only one player dominate? Intra- Bargaining Bargaining Industry Rivalry Power of the Power of Suppliers Strategic Business Buyers Unit How strong is the position of the How strong is the position suppliers? Are there many? Few? of the buyers? Can we sell Monopoly? in large volumes? Do we need to discount heavily? Source: Substitute Products Michael E. Porter “Forces and Services Governing Competition in How easy or hard it is for a new product or service to replace what already exists? Industry (Harvard Business Review, Mar.-Apr. 1979)
- 2. Porter’s Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy www.youtube.com/watch?v=mYF2_FBCvXw Porter’s Competitive Forces http://www.bbc.co.uk/dna/h2g2/alabaster/A583120 Michael Porter on why America needs an economic
- 4. Generic Strategies and Industry Forces Generic Strategies Industry Force Cost Differentiation Focus Leadership Entry Ability to cut price in retaliation deters potential Customer loyalty can discourage potential Focusing develops core competencies that can act Barriers entrants. entrants. as an entry barrier. Large buyers have less Large buyers have less Buyer Ability to offer lower price power to negotiate power to negotiate Power to powerful buyers. because of few close because of few alternatives. alternatives. Suppliers have power because of low volumes, Supplier Better able to pass on Better insulated from but a differentiation- supplier price increases to Power powerful suppliers. customers. focused firm is better able to pass on supplier price increases. Customer's become Threat of Can use low price to defend against attached to differentiating Specialized products & core competency protect Substitutes attributes, reducing threat substitutes. against substitutes. of substitutes. Rivals cannot meet Better able to compete on Brand loyalty to keep Rivalry price. customers from rivals. differentiation-focused customer needs.
- 5. Applying the Porter Competitive Model to Wal-Mart Foreign General Merchandisers Potential or Discounters New Entrants Established Retailer Shifting Strategy to Discounting or Megastores Intra-Industry Rivalry Bargaining SBU: Wal-Mart Rivals: Kmart, Target, Bargaining Power Toys R Us, Specialty Stores Power of Buyers of Suppliers U.S. Product Manufacturers Consumers in Small Foreign Manufacturers Town U.S.A. Local Governments Substitute Consumers in the I/T Product and Service Products Metropolitans Areas Suppliers in the U.S. and Services Canadian and Mexican Consumers Mail Order Telemarketing Home Shopping Network Buying Clubs Other Foreign Electronic Shopping Door-to-door Sales Consumers
- 7. Porter Competitive Model Education Industry: U.S. Universities Potential Foreign Universities Distance Learning New Entrants Motorola University Phoenix, DeVry, National Bargaining Intra-Industry Rivalry Bargaining Power Strategic Business Unit Power of Buyers of Suppliers Faculty and Staff Students Equipment, Service, Substitute Parents Suppliers Products Business Alumni and Services Employers Foundations, Business Legislators Government Books and Videotapes Computer-Based Training Training Companies Consulting Firms
- 8. Porter’s Model and the Role of the Government: The government plays an important role in Porter’s diamond model. Like everybody else, Porter argues that there are some things that governments do that they shouldn't, and other things that they do not do but should. He says, "Government’s proper role is as a catalyst and challenger; it is to encourage - or even push - companies to raise their aspirations and move to higher levels of competitive performance …" Governments can influence all four of Porter’s determinants through a variety of actions such as – Subsidies to firms, either directly (money) or indirectly (through infrastructure). – Tax codes applicable to corporation, business or property ownership. – Educational policies that affect the skill level of workers. – They should focus on specialized factor creation. (How can they do this?) – They should enforce tough standards. (This prescription may seem counterintuitive. What is his rationale? Maybe to establish high technical and product standards including environmental regulations.) The problem, of course, is through these actions, it becomes clear which industries they are choosing to help innovate. What methods do they use to choose? What happens if they pick the wrong industries?
- 9. Criticisms Although Porter theory is renowned, it has a number of critics. Porter developed this paper based on case studies and these tend to only apply to developed economies. Porter argues that only outward-FDI is valuable in creating competitive advantage, and inbound-FDI does not increase domestic competition significantly because the domestic firms lack the capability to defend their own markets and face a process of market-share erosion and decline. However, there seems to be little empirical evidence to support that claim. The Porter model does not adequately address the role of MNCs. There seems to be ample evidence that the diamond is influenced by factors outside the home country.
