Organic chemistry
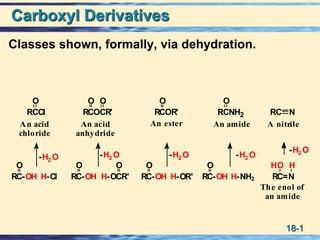
- 1. 18-1 Carboxyl Derivatives Classes shown, formally, via dehydration. H-NH2H-Cl H-OR'RC-OH O H-OCR' O RC=N HO H RC-OH O RC-OH O RC-OH O -H2 O -H2 O -H2 O -H2 O -H2 O RC NRCNH2 O RCCl O RCOR' O RCOCR' O O The enol of an amide An acid chloride An esterAn acid anhydride An amide A nitrile
- 2. 18-2 Structure: Acid Chlorides The functional group of an acid halide is an acyl group bonded to a halogen. • The most common are the acid chlorides. • To name, change the suffix -oic acid to -oyl halide. CH3CCl OO RC- Cl O Cl O Cl O Benzoyl chlorideEthanoyl chloride (Acetyl chloride) An acyl group Hexanedioyl chloride (Adipoyl chloride)
- 3. 18-3 Related: Sulfonyl Chlorides • Replacement of -OH in a sulfonic acid by -Cl gives a sulfonyl chloride. SOHH3 C O O CH3SOH O O SClH3 C O O CH3 SCl O O Methanesulfonic acid p-Toluenesulfonic acid Methanesulfonyl chloride (Mesyl chloride, MsCl) p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (Tosyl chloride, TsCl)
- 4. 18-4 Structure: Acid Anhydrides Two acyl groups bonded to an oxygen atom. • The anhydride may be symmetrical (two identical acyl groups) or mixed (two different acyl groups). • To name, replace acid of the parent acid by anhydride. COC O O CH3 COCCH3 O O Benzoic anhydrideAcetic anhydride
- 5. 18-5 Acid Anhydrides Cyclic anhydrides are named from the dicarboxylic acids from which they are derived. Maleic anhydride O O O Phthalic anhydride Succinic anhydride O O O O O O
- 6. 18-7 Esters The functional group of an ester is an acyl group bonded to -OR or -OAr. • Name the alkyl or aryl group bonded to oxygen followed by the name of the acid. • Change the suffix -ic acid to -ate. O O EtO O OEt O O O Ethyl ethanoate (Ethyl acetate) Diethyl butanedioate (Diethyl succinate) Isopropyl benzoate
- 7. 18-8 Esters; Lactones Lactone: A cyclic ester. • name the parent carboxylic acid, drop the suffix -ic acid and add -olactone. 4-Butanolactone -Butyrolactone) 3-Butanolactone -Butyrolactone) O O O O H3 C 2 3 1 2 1 3 4 6-Hexanolactone -Caprolactone) O O 2 13 4 5 6
- 8. 18-10 Amides The functional group of an amide is an acyl group bonded to a nitrogen atom. • drop -oic acid from the name of the parent acid and add -amide. (For the common acid name, drop -ic of the acid name and add -amide.) • an alkyl or aryl group bonded to the N: name the group and show its location on nitrogen by N-. CH3CNH2 O CH3 C-N H CH3 O H-C-N CH3 CH3 O N-Methylacetamide (a 2° amide) Acetamide (a 1° amide) N,N-Dimethyl- formamide (DMF) (a 3° amide) ethanamide
- 11. 18-13 Amides; Lactams Lactams: A cyclic amides are called lactams. • Name the parent carboxylic acid, drop the suffix -ic acid and add -lactam. 6-Hexanolactam -Caprolactam) H3 C O NH O NH 1 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 3 3-Butanolactam -Butyrolactam) Indicates where the N is located.
- 12. 18-14 Imides The functional group of an imide is two acyl groups bonded to nitrogen. • Both succinimide and phthalimide are cyclic imides. PhthalimideSuccinimide NH NH O O OO
- 13. 18-15 Related: Nitriles The functional group of a nitrile is a cyano group • IUPAC names: name as an alkanenitrile. • common names: drop the -ic acid and add -onitrile. CH3 C N C N CH2 C N Ethanenitrile (Acetonitrile) Benzonitrile Phenylethanenitrile (Phenylacetonitrile)
- 14. 18-16 Acidity of N-H bonds Amides are comparable in acidity to alcohols. • Water-insoluble amides do not react with NaOH or other alkali metal hydroxides to form water-soluble salts. Sulfonamides and imides are more acidic than amides. CH3CNH2 O O O SNH2 NH O O NH O O pKa 8.3pKa 9.7pKa 10 PhthalimideSuccinimideBenzenesulfonamideAcetamide pKa 15-17
- 15. 18-17 Acidity of N-H bonds Effect of neighboring carbonyl groups. 1.0
- 16. 18-18 Acidity of N-H • Imides such as phthalimide readily dissolve in aqueous NaOH as water-soluble salts. (stronger acid) (weaker acid) (weaker base) (stronger base) pKa 15.7pKa 8.3 ++ O O NH N - Na + O O NaOH H2 O
- 17. 18-19 Acidity of N-H bonds Imides are more acidic than amides because 1. the electron-withdrawing inductive of the two adjacent C=O groups weakens the N-H bond, and 2. More resonance delocalization of the negative charge. O O N N O O A resonance-stabilized anion N O O
- 18. 18-20 Lab related: Sulfonamides (Hinsberg) Experimental test to distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines. In acidIn base Reaction replaces one H with the sulfonyl group. In an H remains it is soluble in base. 1 2 3 soluble soluble insoluble insoluble
- 19. 18-21 Characteristic Reactions: Ketones & Aldehydes Nucleophilic acyl Addition: Protonation makes carbonyl better electrophile. Ok with poor nucleophile. Carbonyl weaker electrophile. Need good nucleophile.
- 20. 18-22 Characteristic Reactions: Derivatives Nucleophilic acyl substitution: An addition- elimination sequence resulting in substitution of one nucleophile for another. Tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate ++ C NuR C Y R C NuR O Y O :Nu :Y Substitution product O Dominant for derivatives due to good leaving group (Y), uncommon for ketones or aldehydes.
- 21. 18-23 Characteristic Reactions Poor bases make good leaving groups. R2 N- RO- O RCO- X- Increasing basicity Increasing leaving ability Halide ion is the weakest base and the best leaving group; acid halides are the most reactive toward nucleophilic acyl substitution. Amide ion is the strongest base and the poorest leaving group; amides are the least reactive toward nucleophilic acyl substitution.
- 22. 18-24 Water and Acid Chlorides • Low-molecular-weight acid chlorides react rapidly with water. • Higher molecular-weight acid chlorides are less soluble in water and react less readily. CH3CCl O H2O CH3COH O HCl++ Acetyl chloride
- 23. 18-25 Water and Anhydrides • Low-molecular-weight anhydrides react readily with water to give two molecules of carboxylic acid. • Higher-molecular-weight anhydrides also react with water, but less readily. CH3COCCH3 O O H2O CH3COH O HOCCH3 O ++ Acetic anhydride
- 24. 18-26 Mechanism- Anhydrides • Step 1: Addition of H2O to give a TCAI. (Addition) O CH3 -C- O-C- CH3 H H O-H O O HH CH3 -C- O-C- CH3 H H O-H CH3 -C- O-C- CH3 O O H H H- O-H H + + + Tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate + OO Acid makes carbonyl better electrophile.
- 25. 18-27 Mechanism- Anhydrides • Step 2: Protonation and collapse of the TCAI. (Elimination) O CH3 -C-O-C-CH3 O H O H H + O H H CH3 C O O O C O CH3 H H O H H + CH3 C O O O C CH3 O H H H H H+ H + O Acid sets up better leaving group.
- 26. 18-28 Water and Esters Esters are hydrolyzed only slowly, even in boiling water. • Hydrolysis becomes more rapid if they are heated with either aqueous acid or base. Hydrolysis in aqueous acid is the reverse of Fischer esterification. • acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl oxygen and increases its electrophilic character toward attack by water (a weak nucleophile) to form a tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate. • Collapse of this intermediate gives the carboxylic acid and alcohol.
- 27. 18-29 Mechanism: Acid/H2O - Esters (1o and 2o alkoxy) Acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis. R OCH3 C O H2 O H+ OH C R OCH3 OH H+ R OH C O CH3 OH+ + Tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediateAcid makes carbonyl Better electrophile. Acid sets up leaving group.
- 28. 18-30 Mechanism: Reaction with Acid/H2O – Esters (3o alkoxy) alcohol water But wait!!!!!!!
- 29. 18-31 Reaction with Base/H2O - Esters Saponification: The hydrolysis of an esters in aqueous base. • Each mole of ester hydrolyzed requires 1 mole of base • For this reason, ester hydrolysis in aqueous base is said to be base promoted. O RCOCH3 NaOH H2 O O RCO - Na + CH3OH++
- 30. 18-32 Mechanism of Reaction with Base/H2O – Esters • Step 1: Attack of hydroxide ion (a nucleophile) on the carbonyl carbon (an electrophile). (Addition) • Step 2: Collapse of the TCAI. (Elimination) • Step 3: Proton transfer to the alkoxide ion; this step is irreversible and drives saponification to completion. R- C-OCH3 O OH R- C O OH OCH3 R- C O O H R- C O O HOCH3 (1) + (2) (3) + +OCH3
- 31. 18-33 Acidic Reaction with H2O - Amides Hydrolysis of an amide in aqueous acid requires one mole of acid per mole of amide. • Reaction is driven to completion by the acid-base reaction between the amine or ammonia and the acid. 2-Phenylbutanoic acid2-Phenylbutanamide ++ + heat H2 O HCl H2 O NH4 + Cl - Ph NH2 O Ph OH O
- 32. 18-34 Basic Reaction with H2O - Amides Hydrolysis of an amide in aqueous base requires one mole of base per mole of amide. • Reaction is driven to completion by the irreversible formation of the carboxylate salt. CH3 CNH O NaOH H2O CH3 CO- Na+ O H2N AnilineSodium acetate N-Phenylethanamide (N-Phenylacetamide, Acetanilide) ++ heat
- 33. 18-35 Mechanism: Acidic H2O - Amides • Step1: Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen gives a resonance-stabilized cation intermediate. R C O NH2 OH H H O C NH2R H O C NH2R H C O NH2R H H2 O Resonance-stabilized cation intermediate + + + + + +
- 34. 18-36 Acidic H2O - Amides • Step 2: Addition of water (a nucleophile) to the carbonyl carbon (an electrophile) followed by proton transfer gives a TCAI. • Step 3: Collapse of the TCAI and proton transfer. (Elimination) R C OH C OHRNH3 H C O NH3 + R OH NH4 + ++ O + O H + + O H H C OH NH2R O H H C OH NH3 + R O + C OH NH2R H proton transfer from O to N
- 35. 18-37 Mechanism: Reaction with Basic H2O - Amides Amide hydroxide ion Dianion!
- 36. 18-38 Acidic H2O and Nitriles The cyano group is hydrolyzed in aqueous acid to a carboxyl group and ammonium ion. • Protonation of the cyano nitrogen gives a cation that reacts with water to give an imidic acid. • Keto-enol tautomerism gives the amide. Ph CH2C N 2H2O H2 SO4 H2O Ph CH2COH O NH4 + HSO4 - Ammonium hydrogen sulfate Phenylacetic acid Phenylacetonitrile + heat ++ R-C N H2 O H + NH OH R-C R-C-NH2 O An imidic acid (enol of an amide) + An amide Acid + Ammonium ion
- 37. 18-39 Basic H2O and Nitriles • Hydrolysis of a cyano group in aqueous base gives a carboxylic anion and ammonia; acidification converts the carboxylic anion to the carboxylic acid. CH3( CH2) 9C N NaOH, H2O O CH3( CH2) 9COH CH3( CH2)9 CO - Na + O HCl H2 O NaCl NH3 NH4 Cl Sodium undecanoateUndecanenitrile + heat Undecanoic acid + +
- 38. 18-40 Synthesis: Reaction with H2O - Nitriles • Hydrolysis of nitriles is a valuable route to carboxylic acids. CHO HCN, KCN CN OH H2 SO4 , H2 O COOH OH heat Benzaldehyde Benzaldehyde cyanohydrin (Mandelonitrile) (racemic) 2-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (Mandelic acid) (racemic) ethanol, water CH3( CH2 ) 8 CH2 Cl KCN H2 SO4 , H2 O CH3 ( CH2 ) 9COH heatethanol, water O CH3 ( CH2 ) 9C N 1-Chlorodecane Undecanenitrile Undecanoic acid
- 39. 18-41 RCR' NH Synthesis: Grignards + Nitriles ->ketone 1 Grignard reagents add to carbon-nitrogen triple bonds in the same way that they add to carbon- oxygen double bonds. The product of the reaction is an imine. RC N R'MgX RCR' NMgX H2O diethyl ether
- 40. 18-42 Synthesis: Grignards + Nitriles ->ketone 2 RC N R'MgX RCR' NMgX H2O RCR' NH diethyl ether RCR' O H3O+ Imines hydrolyzed to ketones.
- 41. 18-43 Reaction of Alcohols and Acid Halides Acid halides react with alcohols to give esters. • Acid halides are so reactive toward even weak nucleophiles such as alcohols that no catalyst is necessary. • Where the alcohol or resulting ester is sensitive to HCl, reaction is carried out in the presence of a 3° amine to neutralize the acid. Butanoyl chloride Cyclohexyl butanoate + Cyclohexanol HO HClCl O + O O
- 42. 18-44 Reaction with Alcohols, Sulfonic Esters • Sulfonic acid esters are prepared by the reaction of an alkane- or arenesulfonyl chloride with an alcohol or phenol. • The key point here is that OH- (a poor leaving group) is transformed into a sulfonic ester (a good leaving group) with retention of configuration at the chiral center. (R)-2-Octanol p-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (Tosyl chloride) (R)-2-Octyl p-toluenesulfonate [(R)-2-Octyl tosylate] OH + TsCl pyridine OTs
- 43. 18-45 Reaction of Alcohols and Acid Anhydrides Acid anhydrides react with alcohols to give one mole of ester and one mole of a carboxylic acid. • Cyclic anhydrides react with alcohols to give one ester group and one carboxyl group. (sec-Butyl hydrogen phthalate 2-Butanol (sec-Butyl alcohol) + Phthalic anhydride O O O O OHHO O O Acetic acidEthyl acetateEthanolAcetic anhydride ++CH3 COCCH3 HOCH2 CH3 CH3 COCH2 CH3 CH3 COH O O OO
- 44. 18-46 Reaction of Alcohols and Esters Esters react with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst in an equilibrium reaction called transesterification. Butyl propenoate (Butyl acrylate) (bp 147°C) 1-Butanol (bp 117°C) Methyl propenoate (Methyl acrylate) (bp 81°C) + + HCl CH3 OH Methanol (bp 65°C) OCH3 O HO O O
- 45. 18-47 Reaction of Ammonia, etc. and Acid Halides Acid halides react with ammonia, 1° amines, and 2° amines to form amides. • Two moles of the amine are required per mole of acid chloride. Cl O 2NH3 NH2 O NH4 + Cl - + + Hexanoyl chloride Ammonia Hexanamide Ammonium chloride
- 46. 18-48 Reaction of Ammonia, etc. and Anhydrides. Acid anhydrides react with ammonia, and 1° and 2° amines to form amides. • Two moles of ammonia or amine are required. CH3 COCCH3 O O 2NH3 CH3 CNH2 O CH3 CO- NH4 + O + + Acetic anhydride Ammonia Acetamide Ammonium acetate
- 47. 18-49 Ammonia, etc. and Esters Esters react with ammonia and with 1° and 2° amines to form amides. • Esters are less reactive than either acid halides or acid anhydrides. Amides do not react with ammonia or with 1° or 2° amines. Ph OEt O NH3 Ph NH2 O Et OH PhenylacetamideEthyl phenylacetate + + Ethanol
- 48. 18-50 Acid Chlorides with Salts Acid chlorides react with salts of carboxylic acids to give anhydrides. • Most commonly used are sodium or potassium salts. + +CH3 CCl - OC CH3 COC Na+ Cl -Na + O O O O Acetyl chloride Sodium benzoate Acetic benzoic anhydride
- 49. 18-51 Interconversions of Acid Derivatives
- 50. 18-52 Grignard and an Ester. Look for two kinds of reactions. R' OEt O R-Mg-X R' OEt O R R' R O R-Mg-X R' R OMgX R R' R OH R But where does an ester come from? R'COCl EtOH Acid chloride R'CO2H SOCl2 Perhaps this carboxylic acid comes from the oxidation of a primary alcohol or reaction of a Grignard with CO2. Substitution Addition Any alcohol will do here.
- 51. 18-53 Grignard Reagents and Formic Esters • Treating a formic ester with two moles of Grignard reagent followed by hydrolysis in aqueous acid gives a 2° alcohol. HCOCH3 O 2RMgX H2O, HCl HC-R R OH CH3 OH+ magnesium alkoxide salt A 2° alcoholAn ester of formic acid +
- 52. 18-54 Reactions with RLi Organolithium compounds are even more powerful nucleophiles than Grignard reagents. RCOCH3 1 . 2 R' Li 2 . H2 O, HCl R- C-R' O R' OH + CH3 OH
- 53. 18-55 Gilman Reagents Acid chlorides at -78°C react with Gilman reagents to give ketones. 1 . ( CH3 ) 2 CuLi, ether, -78°C 2 . H2 O Pentanoyl chloride 2-Hexanone Cl O O Gilman Reagents do not react with acid anhydrides, esters, amides or nitriles under these conditions. Selective reaction.
- 54. 18-56 Synthesis: Reduction - Esters by LiAlH4 Most reductions of carbonyl compounds use hydride reducing agents. • Esters are reduced by LiAlH4 to two alcohols. • The alcohol derived from the carbonyl group is primary. Methanol2-Phenyl-1- propanol (racemic) Methyl 2-phenyl- propanoate (racemic) +1 . LiAlH4 , et her 2 . H2 O, HCl CH3 OHPh OCH3 O Ph OH
- 55. 18-57 Mechanism: Reduction - Esters by LiAlH4 Reduction occurs in three steps plus workup: • Steps 1 and 2 reduce the ester to an aldehyde. • Step 3: Work-up gives a 1° alcohol derived from the carbonyl group. A 1° alcohol R C H O + H (3) R C H O H (4) R C H OH H A tetrahedral carbonyl addition intermediate (1) R C OR' O + H R C OR' O H R C H O (2) OR'+
- 56. 18-58 Synthesis: Selective Reduction by NaBH4 NaBH4 reduces aldehydes and ketones. It does not normally reduce esters. LiAlH4 reduces all. Selective reduction is often possible by the proper choice of reducing agents and experimental conditions. OEt O O NaBH4 EtOH OEt OH O (racemic)
- 57. 18-59 Synthesis: Reduction - Esters by DIBAlH -> Aldehyde Diisobutylaluminum hydride (DIBAlH) at -78°C selectively reduces an ester to an aldehyde. • At -78°C, the TCAI does not collapse and it is not until hydrolysis in aqueous acid that the carbonyl group of the aldehyde is liberated. Hexanal Methyl hexanoate + 1 . DIBALH, toluene, -78°C 2 . H2 O, HCl CH3 OH OCH3 O H O
- 58. 18-60 Synthesis: Reduction - Amides by LiAlH4 LiAlH4 reduction of an amide gives a 1°, 2°, or 3° amine, depending on the degree of substitution of the amide. NH2 O 1. LiAlH4 2. H2O 1. LiAlH4 2. H2O NMe2 O NMe2 NH2 Octanamide 1-Octanamine N,N-Dimethylbenzamide N,N-Dimethylbenzylamine
- 59. 18-61 Synthesis: Reduction - Nitriles by LiAlH4 The cyano group of a nitrile is reduced by LiAlH4 to a 1° amine. 6-Octenenitrile 6-Octen-1-amine CH3 CH= CH( CH2 ) 4 C 1 . LiAlH4 2 . H2 O CH3 CH= CH( CH2 ) 4 CH2 NH2 N Can use catalytic hydrogenation also.
- 60. 18-62 Interconversions Problem: Show reagents and experimental conditions to bring about each reaction. Ph OH O OMe O Ph Ph OH Ph Cl O Ph NH2 Ph NH2 O Phenylacetic acid (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h)