Genetics model 2012 fieldspart 2
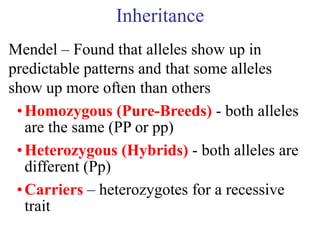
- 1. Inheritance Mendel – Found that alleles show up in predictable patterns and that some alleles show up more often than others • Homozygous (Pure-Breeds) - both alleles are the same (PP or pp) • Heterozygous (Hybrids) - both alleles are different (Pp) • Carriers – heterozygotes for a recessive trait
- 2. Homozygous Pure-Breed Crosses result in: 100% chance dominant phenotype
- 3. Heterozygous Hybrid Crosses result in: 75% chance dominant phenotype 25% chance recessive phenotype
- 4. Compare What makes the difference between a 100% chance of the dominant phenotype and only 17% chance of the dominant phenotype ? Pure-Breed Crosses result in: Hybrid Crosses result in: 100% chance dominant phenotype 75% chance dominant phenotype 25% chance recessive phenotype
- 5. Generations Parents: P1 generation First Generation: First Filial (F1) Second Generation: Second Filial (F2) Third Generation: Third Filial (F3)
- 6. Chance of Inheritance 100% chance 75% chance 75% chance 0% chance
- 7. Alleles can be tracked through multiple generations and probabilities determined Parents: P1 generation First Generation: First Filial (F1) 100% chance dominant phenotype Second Generation: Second Filial (F2) 75% chance dominant phenotype Third Generation: Third Filial (F3) 63% chance dominant phenotype
- 8. Inheritance Alleles can be tracked through multiple generations and probabilities determined Parents: P1 generation First Generation: First Filial (F1) 100% chance dominant phenotype Second Generation: Second Filial (F2) 75% chance dominant phenotype Third Generation: Third Filial (F3) 63% chance dominant phenotype 100% chance 75% chance 75% chance 0% chance
- 9. Practice • Video on making punnett squares • In your notebook complete the Probability (Long vs Short Big Toe) Lab.
- 10. Summary of Mendel’s Principles Gregor Mendel’s work forms the basis of modern genetics: • Genes are passed from parent to offspring • Some forms of genes (alleles) are dominant while others are recessive • Genes randomly segregate (independent assortment) when gametes are formed • The alleles for different genes usually segregate independently of one another Linked genes (genes that occur very close to one another on a chromosome) are the exception Write these 4 ideas from Mendel in your notebook
- 12. DNA Chromosomes • From Chromosome to DNA • How DNA is packaged animation • Meiosis is how DNA is copied and sepereted to make gametes (sperm and egg) • Complete cornell notes for the Meiosis video and glue onto page ___ of your notebook – What is the purpose of Meiosis and Mitosis?
- 13. • Complete the lab “Why don’t we look like our siblings” and glue in your notebook
- 14. Solving Punnett Squares If a round pea plant (AA) is crossed with a wrinkled pea plant (aa), what percent of the offspring will be: • Round? Solve these • Wrinkled? If two heterozygous round pea in your plants are crossed, what percent of the offspring will be: notebook. • Round? • Wrinkled? If a heterozygous round pea plant is crossed with a homozygous wrinkled pea plant, what percent of the offspring will be: • Round? • Wrinkled?
