FTEC 492 Poster
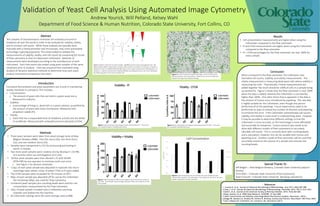
- 1. Validation of Yeast Cell Analysis Using Automated Image Cytometry Andrew Yourick, Will Pelland, Kelsey Wahl Department of Food Science & Human Nutrition, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO Abstract Test samples of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are routinely procured in breweries all over the world in order to be analyzed for viability, vitality, and to conduct cell counts. While these analyses are typically done manually with a hemocytometer and microscope, new, more automated technology is gaining popularity. This study looked to validate the measurements of viability, vitality, and cell counts by comparing the results of flow cytometry to that of a Nexcelom Cellometer. Methods of measurement were developed according to the manufacturer of each instrument. Each instrument was tested using yeast samples of the same treatment prior to analysis. Data was acquired then evaluated using Analysis of Variance statistical methods to determine how each yeast analysis instrument compared to the other. Introduction Consistent fermentation and yeast parameters are crucial in maintaining quality standards in a brewery. This Includes: • Concentration: o The amount of yeast cells that are held in a given yeast slurry. Measured in cells/mL. • Viability: o A percentage of living vs. dead cells in a yeast solution, quantified by the amount of yeast with intact membranes. Measured with propidium iodide (PI). • Vitality: o Yeast that has a measurable level of metabolic activity and the ability to proliferate. Measured with carboxyfluorescein diacetate (CFDA). Special Thanks To: Jeff Biegert – New Belgium Brewery, Colorado State University (adjunct faculty) Chris Allen – Colorado State University (Flow Cytometry) Katie Fromuth –Colorado State University (Brewing Laboratory) References 1. Laverty D, et al. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology. June 2013; 40(6):581-588. 2.Chan L, et al. Journal Of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology. November 2012; 39(11):1615-1623. 3.Saldi S, et al. Journal of the American Society of Brewing Chemists. 2014; 72(4):253-260. 4.Boyd, Andrew, et al. FEMS Yeast Research. ELSEVIER, 10 July 2002. 5.Yeast Concentration and Viability using Image-Based Fluorescence Analysis. Nexcelcom, (2013). 6.Briggs DE, Boulton CA, Brookes PA, Stevens R. Brewing: Science And Practice. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2004. 7.User’s Manual for Cellometer, X2. Lawrence, MA. Nexcelcom (2013) Results • Cell concentration measurements are higher when using the Cellometer compared to the flow cytometer. • PI and CFDA measurements are higher when using the Cellometer compared to the flow cytometer • PI + CFDA percentages for the flow cytometer are near 100% for every sample Methods • Three yeast samples were taken from yeast storage tanks at New Belgium Brewery (NBB). One thin slurry (S4), one thick slurry (S2), and one medium slurry (S3). • Samples were transported to CSU for processing and testing in sterile 1L bottles. • Two more yeast samples were created, one by diluting 4:1 S4:PBS (S1) and the other via centrifugation of S2 (S5). • All five yeast samples were then diluted 1:25 with 50mM EDTA+PBS by one operator to minimize multi-user error. • See Figure 1 for dilution schematic. • 110µL of each yeast sample was aliquoted in triplicate into micro- centrifuge tubes where 110µL of either CFDA or PI were added. • The CFDA samples were incubated for 45 minutes at 30°C. • 40µL of each sample was aliquoted off for use by the Cellometer, the remaining 180µL was used for Flow Cytometry. • Unstained yeast samples plus counting beads were used for cell concentration measurement by the Flow Cytometer. • 20µL of dyed sample is loaded onto a Cellometer counting chamber and loaded into the machine. • All Cellometer settings were the same settings used at NBB. Conclusion When compared to the flow cytometer, the Cellometer over- estimated cell counts, viability, and vitality measurements. The vitality measurement is measuring dead yeast cells where viability is measuring live cells. Theoretically, if these measurements are added together the result should be 100% of cells in a sample being accounted for. Figure 5 shows that the flow cytometer is near 100% when the data is added; whereas the Cellometer is consistently higher than 100%. One other factor that is apparent in the data is the amount of human error introduced by pipetting. The raw data is highly variable for the Cellometer, even though one person performed all of the pipetting. Future experiments need to be performed on ways to reduce the number of dilutions and pipetting to minimize this error. If the Cellometer overestimates cell counts, viability, and vitality it could result in underpitching yeast. However, it may be possible to determine different settings so that the Cellometer is more accurate, as this technology is more affordable and accessible for breweries. Future research also needs to be done with different models of flow cytometery to accurately calculate cell counts. This is currently done with counting beads and a calculation, however, this can be variable with human and pipetting error. Another model of flow cytometer will be used that accurately measures the volume of a sample and removes the counting beads. Figure 3 Graph showing the percentage of yeast cells positive for PI. These cells are considered dead or metabolically inactive. Figure 4 Graph showing the percentage of yeast cells positive for CFDA. These cells are considered metabolically active. Figure 5 Graph showing the additive percentage of yeast cells positive for both PI and CFDA. Theoretically, the percentages should be 100%, accounting for all cells in the sample. Figure 6 Graph showing the cell concentrations for each sample and yeast measurement machine. The Cellometer is much higher for cell counts for every sample compared to the flow cytometer. Figure 2 Picture of Cellometer bright field image. Green circled cells are being counted for cell concentrations. Yellow circles are not counted and indicate cells larger than indicated settings.