Human Reproductive System Guide
- 2. Human Reproductive • Sexual Reproductive. • Male gamete fuses with female gamete to form a zygote
- 3. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female
- 4. Thumbnail.
- 5. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVARIES • Two ovaries contain ova (eggs). Ova = female gametes • Women have these cells in their bodies from birth, whereas men produce new sperm continually = meaning once the ova are finished, the female can no longer reproduce
- 6. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVARIES • Two ovaries contain ova (eggs). Ova = female gametes • Women have these cells in their bodies from birth, whereas men produce new sperm continually = meaning once the ova are finished, the female can no longer reproduce
- 8. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • OVIDUCTS or FALLOPIAN TUBES • From each ovary is an oviduct/fallopian tube. • The oviduct is lined with ciliated cells. Every month, an ovum (egg) develops and becomes mature, and is released from an ovary. The cilia move the ovum along the oviduct and into the uterus.
- 10. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • UTERUS or WOMB • The uterus is a muscular bag with a soft lining. • It is where a baby develops until its birth. • The cervix is a ring of muscle at the lower end of the uterus. It keeps the baby in place while the woman is pregnant.
- 12. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Female • VAGINA • The vagina is a muscular tube that leads from the cervix to the outside of the woman's body. The bladder opening, urethra, it is separate from the vagina. It passes urine out of the body from the bladder.
- 14. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male
- 16. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male • SPERM DUCT and GLANDS • The sperm pass through the sperm ducts, and mix with fluids produced by glands. • The fluids provide the sperm cells with nutrients. This mixture is called semen.
- 18. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Male • SPERM DUCT and GLANDS • The sperm pass through the sperm ducts, and mix with fluids produced by glands. • The fluids provide the sperm cells with nutrients. This mixture is called semen.
- 20. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Sperm Production • Sperm develop in the testis, by meiosis. • From puberty, sperm is produced continuously until death. • QUESTION? • Why are the testes on the outside of the body? • Sperm production is sensitive to heat. Too hot and cells will not develop.
- 21. The structure and functions of the male and female human reproductive systems • Egg Production • Girl is already born with all her eggs. At puberty, some begin to mature. (one at a time) • Ovulation = when the egg is mature, it will burst from the ovary into the oviduct. • PUBERTY = "stage of development during which sexual maturity is reached"
- 22. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation is the fusion of the nucleus of a male gamete with the nucleus of a female gamete, producing a new cell called a zygote. This then matures into an embryo.
- 24. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • The egg is released from the ovary and moves toward the oviduct. • A sperm has been ejaculated into the vagina and is travelling up the cervix. (Using their tails to swim)
- 25. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • The egg and sperm meet at the oviduct and the process of fertilisation begins. Only the head of the one sperm enters the egg. After entry, the egg membrane becomes impenetrable to other sperm
- 27. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Fertilisation • Now a zygote has formed. • The zygote moves slowly down the oviducts. Dividing by mitosis, to form an embryo. • NB. Cilia in oviduct "sweep" the embryo along the tube. (peristalsis) • EMBRYO = an immature organism before all the organs have formed • This embryo is fed from yolk of the egg.
- 28. Fertilization and development of the embryo • Implantation • After several hours, the embryo reaches the uterus • It sinks into the spongy lining of the wall.
- 30. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • After fertilisation, the newly-formed zygote divides repeatedly to form a ball of cells called an embryo. This becomes implanted in the wall of the uterus. • After 11 weeks of development, the embryo is called a fetus. The amniotic sac produces amniotic fluid, which surrounds and protects the developing embryo.
- 32. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • A placenta, connected by an umbilical cord, develops from the embryo. The placenta anchors the embryo in the uterus. • Umbilical cord:- • nutrients and oxygen to move from the mother to the embryo • waste materials and carbon dioxide to move from the embryo to the mother • There is no connection between the circulatory systems of the embryo and its mother, so their blood doesn’t mix. • (Separated by the placenta wall) • These materials pass from one to the other by diffusion. (wall is thin)
- 34. The roles of the placenta • The Placenta • As the fetus grows, so does the placenta • At birth the placenta is a flat disc 12cm x 3cm
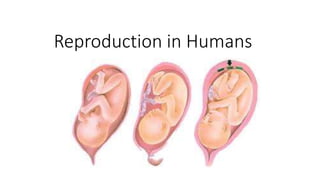
- 36. The roles of the placenta • Development of the embryo/fetus • Zygote Embryo Fetus • At fertilisation Simple ball of cells Cells develop into different types (identical cells) (10-11 Weeks, all organs in place) (6 Weeks, organs begin to form) (8 Weeks, muscles move) (10-38 Weeks, continues to develop) (38 Weeks, ready to be born)
- 38. The roles of the placenta • BIRTH • Birth begins with strong muscle contractions in uterus wall. Stretching the cervix open. • Amniotic sac breaks When cervix is wide enough, muscles push the baby down through the cervix and out of the vagina The baby is still attached by the umbilical cord and placenta. Placenta no longer needed (baby can breath for itself) The placenta detaches from the uterus wall and passes through the vagina (afterbirth) Umbilical cord is cut, painless because there are no nerves. Stump forms the baby's navel A few weeks before birth the fetus usually turns over, so head is next to cervix
- 39. The roles of the placenta • BIRTH • Birth begins with strong muscle contractions in uterus wall. Stretching the cervix open. • Amniotic sac breaks When cervix is wide enough, muscles push the baby down through the cervix and out of the vagina The baby is still attached by the umbilical cord and placenta. Placenta no longer needed (baby can breath for itself) The placenta detaches from the uterus wall and passes through the vagina (afterbirth) Umbilical cord is cut, painless because there are no nerves. Stump forms the baby's navel A few weeks before birth the fetus usually turns over, so head is next to cervix
- 40. • 1 Which statement about sex cells is correct? • Sperm are male gametes • Ova are male gametes • Sperm are female gametes • 2 In reproduction, what is fertilisation? • When a male and female gamete join • When a farmer puts manure on farmland • When plants drop seeds onto the ground QUESTIONS
- 41. • 3 What is a zygote? • A cell formed when two embryos join, which will develop into a gamete • A cell formed when two gametes join, which will develop into an embryo • A cell formed when two gametes join, which will develop into a gland • 4 Which of the following is not a part of the male reproductive system? • Penis • Testes • Uterus QUESTIONS
- 42. • 5 Where are the female sex cells contained? • In the uterus • In the ovaries • In the ova • 6 What is ovulation? • The release of a mature egg cell • The loss of the lining of the uterus • The joining of a male sex cell and a female sex cell QUESTIONS
- 43. • 7 Which way does blood normally pass across the placenta? • From the mother to the foetus • From the foetus to the mother • Blood does not pass across the placenta QUESTIONS