Exam 2 review presentation 1 -middle east
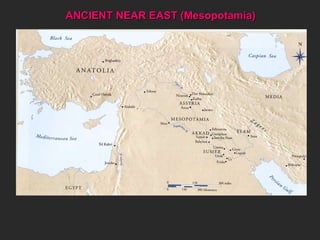
- 1. ANCIENT NEAR EAST (Mesopotamia)
- 2. ZIGGURAT: Elevated temple base Sumer: White Temple, Uruk (Warka), Iraq
- 3. Sumer: Tell Asmar Figures VOTIVE FIGURES: Figures which pray in perpetuity on your behalf TELL ASMAR: in modern-day Iraq
- 4. Akkadians: Victory Stele of Naram Sin STELE (pl. “stelae): tombstone- shaped marker which had a variety of uses, including marking boundaries, commemorating important events, and making proclamations (including listing bodies of laws)
- 6. CODE OF HUMMURABI (Babylonians) LAWS Extends rod and ring: signifies authority
- 7. CODE OF HAMMURABI --Earliest-known example of a ruler proclaiming publicly to his people an entire body of laws. --Laws arranged in orderly groups, so that all men could easily read and know what was required of them. --Carved upon a black stone monument, (it is a STELE) eight feet high. --Begins and ends with addresses to the gods: a law code was in those days regarded as a subject for prayer; the prayers here include curses towards those who neglect or destroy the law. --Found in 1901, not in Babylon, but in a city in the mountains of Iran, to which a later conqueror must have taken it.
- 8. CODE OF HAMMURABI LAWS COVER ALL ASPECTS OF BABYLONIAN LIFE (CIVIL, CRIMINAL, SOCIAL, & DOMESTIC MATTERS) SOME EXAMPLES: --If a man puts out the eye of another man, his eye shall in turn be put out (“an eye for an eye”). --If a person steals property from a temple, both he and the person receiving the stolen goods will be put to death. --If a man kills another’s slave, he must pay a fine of 1/3 of a mina. --If a man rents a boat and it is in turn wrecked, he must replace the boat with another. --If a married woman dies without bearing male heirs (sons), her dowry shall be repaid to her father; if she has male heirs, it will belong to them. --If a woman is caught in adultery both she and her partner will be tied up and thrown in the water.
- 9. CODE OF HUMMURABI (Babylonians) CUNEIFORM CUNEIFORM: Written language of the Ancient Near East
- 10. CUNEIFORM: --Earliest known system of writing (developed in 3000s BC) --Initially developed for the purpose of accountancy (keeping agricultural records) --initially pictographic—originally the marks were intended as simple pictures representing objects (a bull, for example), but over time evolve into an abstract system of marks --paper was not yet known; the marks were incised onto clay tablets using a wedge-shaped stylus (hence the wedge-shaped character of the marks)
- 11. CITADEL of SARGON II at KHORSABAD (DUR SHARRUKIN) Other important citadels: CITADEL of ASSURNASIRPAL II at KAHLU (NIMRUD, IRAQ) CITADEL of ASSURBANIPAL at NINEVEH (KUYUNJIK, IRAQ) Assyrians: CITADELS (Original LAMASSU from Khorsabad; discovered by Botta in 1840s)
- 12. Assyrian citadels: LION HUNTING SCENES
- 13. SEALS Discovered at Tell Asmar, Iraq Worshipper with three gods (c.2000 BC)
- 14. SEALS --A “seal” is an object of hard material (stone, bone, ivory, metal, wood, or hardened clay) which is carved with a design which leaves an impression when pressed into clay or wax --The clay or wax object onto which a seal is impressed is called a “ sealing” --“Glyptic” refers to the art of seals
- 15. SEALS --Used for several thousands of years in the Middle East --Uses included marking property, ratify accounts and transactions, protect goods against theft, secure restricted areas, and indicate that authenticity of documents and objects
- 16. SEALS Button-shaped seal (Iran; c.5000 BC) Seal in the shape of a fox and modern impression (Iraq?; c.4000 BC)
- 17. SEALS Round sealing showing lion attacking bulls; originally placed over two ropes tied into a knot (Uruk: c.3200 BC)
- 18. SEALS Sealing of animals, originally placed on a woven basket (Iraq; c.4000 BC)
- 19. SEALS Sealed clay ball containing tokens which indicate the contents of a consignment; in the event of a dispute upon the consignment’s arrival, the ball would be broken and the tokens checked to reveal the initial contents which had been shipped.
- 20. SEALS “ Cylinder seals” Goddesses present an adherent to the king (Babylon; c.2100 BC)
- 21. SEALS “ Cylinder seals” Worshipper with three gods (Tell Asmar, Iraq; c.2000 BC)
- 22. Assyrian seals: LION HUNTING Seal of the palace administration, Nineveh, 600s BC
- 23. --Constructed on a raised platform, 40’ high, 1500’ long, 900 feet wide --All structures uniformly aligned, parallel to the platform along a roughly north-south axis --Major construction phases under 3 kings: Darius (began construction in 518 BC; built the platform and Triple Portal), Xerxes (completed the Apadana; built the Gateway of All Lands), and Artaxerxes I (finished the Throne Hall) Persians: PERSEPOLIS
- 24. Coins from ancient Lydia CROESUS: --Lydian king famed for his wealth; mints coins --Rules at Sardis (Turkey) --Tremendous gold deposits in and around the River Pactolus --Taken by Persian King Cyrus
- 25. COINS --begins in Near East (Lydia) in 7 th century BC --standard weights of precious metals, stamped with a seal to designate value --initially stamped on only one side Early coin from the reign of Croesus (Lydian king) Stamped on one side: stamped under pressure on back (reverse) so that image seen correctly on front (obverse) Bull and lion
- 26. Early coin from the reign of Croesus (Lydian king) Stamped on one side: stamped under pressure on back (reverse) so that image seen correctly on front (obverse) Bull and lion Stamp seals
- 27. DOUBLE-SIDED COINS --dies carved with design placed on punch and anvil --blank coin placed between --punch struck with a mallet to transfer designs to metal blank