JEE Main Mock Test - Physics
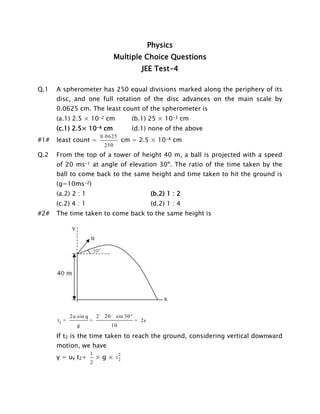
- 1. Physics Multiple Choice Questions JEE Test-4 Q.1 A spherometer has 250 equal divisions marked along the periphery of its disc, and one full rotation of the disc advances on the main scale by 0.0625 cm. The least count of the spherometer is (a.1) 2.5 × 10-2 cm (c.1) 2.5× 10-4 cm #1# (b.1) 25 × 10-3 cm (d.1) none of the above least count = 0.0625 cm = 2.5 × 10-4 cm 250 Q.2 From the top of a tower of height 40 m, a ball is projected with a speed of 20 ms-1 at angle of elevation 30º. The ratio of the time taken by the ball to come back to the same height and time taken to hit the ground is (g=10ms-2) (a.2) 2 : 1 (c.2) 4 : 1 #2# (b.2) 1 : 2 (d.2) 1 : 4 The time taken to come back to the same height is t1 = 2u sin q = 2 ´ 20 ´ sin 30 ° g = 2s 10 If t2 is the time taken to reach the ground, considering vertical downward motion, we have y = uy t2+ 1 2 × g × t2 2
- 2. 40 = -(20 sin 30º) t2+ 40 = -10 1 2 × 10 × t 2 2 t2+5 t 2 2 Or t 2 -2 t2 – 8 = 0 2 On solving t2 = 4s t1 2 = t2 Q.3 1 = 4 2 A particle moves in x – y plane according to equation x = 4t2+5t+16 and 6y = 5t The acceleration of the particle must be (a.3) 8m/ sec2 (c.3) 12m/ sec2 #3# (b.3) 14m/ sec2 (d.3) none of these x = 4t2 + 5t + 16; y = 5t dx vx = dt dv x ax = = 8; ay = dt a = Q.4 = 8t + 5 ; v y = 2 2 ax + ay = dv y dy = 5 dt = 0 dt 2 8 + 0 = 8m / s 2 A dynamometer D is attached to two bodies of masses M = 6 kg and m=4kg. Forces F = 20 N and f = 10N are applied to the masses as shown, The dyanometer reads (a.4) 6 N (c.4) 20 N #4# (b.4) 10 N (d.4) 14 N If a is acceleration of the system, then a= net force total m ass = 20 - 10 = 1ms - 2 6+ 4 It is along the direction of r F . If R is reading of the dynamometer, then R+Ma=F R = F – Ma = 20 - 6 × 1 = 14 N
- 3. Q.5 Sand falls on to a conveyor belt at a constant rate of 2kg/s. If the belt is moving at 0.1 m/s, then the extra force required to maintain speed of the belt is (a.5) 2N (c.5) 0.2 N #5# (b.5) 20 N (d.5) 10 N dm Here, = 2 kg / s dt u=0.1 m/s Extra force required = u ´ dm =0.1× 2 = 0.2 N dt Q.6 A body of mass m is accelerated uniformly from rest to a speed ν in a time T. The instantaneous power delivered to the body as a function of time is given by (a.6) mv T (c.6) #6# 2 2 1 mv .t (b.6) 2 T 2 2 T2 .t (d.6) 2 Acceleration, a = v and F = m a = T 2 mv .t 2 1 mv 2 2 T2 .t mv T Velocity acquired, V = at = v t T Instantaneous power, P=FxV= mv T Q.7 ´ v T t= mv T 2 2 t A rigid body rotates about a fixed axis with variable angular velocity equal to (α-βt) at time t, where α and β are constants. The angle through which it rotates before it comes to rest is (a.7) a 2 a 2 - b 2b #7# 2 - b 2 a (d.7) a (a - b ) 2b (c.7) 2 (b.7) 2a 2
- 4. dq w= = a - bt dt d q = ( a - b t )d t w h en w = 0, t = a b q t ò d q = ò (a q= 0 t = ò 0 t a dt - 0 Q.8 - b t )d t ò b td t 0 Select the proper graph between the gravitational potential (Vg) due to hollow sphere and distance (r) from its centre. (a.8) (c.8) #8# (b.8) (d.8) Gravitational potential at a point outside the sphere V g = - GM r But Vg is same at a point inside the hollow sphere as on the surface of sphere. Hence graph (c) is correct. Q.9 A hollow steel pipe, with inner and outer diameter 8 cm and 10 cm respectively and length 3 m support a roof. Its length increases by 0.1 mm due to load. The magnitude of load is (Y for steel is 2 × 1011Nm-2) (a.9) 3.76 × 103N (b.9) 188 N (c.9) 37.6 N (d.9) 1.88 × 104 N
- 5. #9# F= Y (A 2 - A 1 ) l 2 = L L 2 ´ 10 so F = 2 Y p (r2 - r1 ) l 11 2 2 ´ (22 / 7 ) ´ (5 - 4 ) ´ 10 - 4 ´ 10 - 4 3 4 = 1.88 ´ 10 N Q.10 A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of side L at a depth y from the top and the other is a circular hole of radius R at a depth 4y from the top. When the tank is completely filled with water, the quantities of water flowing out per second from both holes are the same. Then R is equal to (a.10) L (c.10) L/ (b.10) 2πL (d.10) L/2π 2p #10# Since volume is same in both cases AV = Constant 2 L ´ 2 2gy = p R ´ or R = L / 2g ´ 4 y 2p Q.11 In the P-V diagram shown in fig. ABC is a semicircle. The work done in the process ABC is V(m3) (a.11) zero (b.11) p J 2 (c.11) 4J (d.11) - p J 2 #11# In the part AB, volume of the gas is decreasing, and in the part BC, volume of the gas is increasing. Therefore, WAB is negative and WBC is positive. As |WBC| > |WAB|, therefore, net work done is positive. Wnet = area of semicircle ABC = 1 2 2 pr = 1 2 2 p (1) = p 2 joule
- 6. Q.12 Two gram of helium is enclosed in a vessel at NTP. How much heat should be given to it to double the pressure. Specific heat of He is 3 J/gK. (a.12) 800 J (b.12) 819 J (c.12) 1638 J (d.12) 1600 J #12# In vessel, volume is constant ∴ ∆Q = n CVdT Now, n = 1 m ole 2 CV = 3×4=12 J/mole K P2 At constant volume, = P1 T2 T1 To double the pressure, temp. of gas has to be doubled i.e. if T1 = 273K T2=546K ∴ ∆ T=T2-T1 = 546 – 273 = 273 K From (i) ∆Q = 1 ×12×273 = 1638 K. 2 Q.13 An electron tube was sealed off during manufacture at a pressure of 1.2 ×10-7 mm of mercury at 27ºC. Its volume is 100 cm3. The number of molecules that remain in the tube is (g=10m/s2) (a.13) 3.86 ×1011 (b.13) 2 × 1016 (c.13) 3 × 1015 (d.13) 5 × 1011 #13# Here, P=1.2 × 10-7 mm of Hg =1.2 × 10-7 × 10-3 × (13.6×103) ×10N/m2 Gas constant, R = PV = (1.2 ´ 13.6 ´ 10 - 6 ) ´ (100 ´ 10 - 6 ) 300 T = 1.2 × 13.6 × 10-12 N o. of m olecules = 6.023 ´ 10 23 ´ 1.2 ´ 13.6 ´ 10 - 12 8.31 = 3.86 × 1011 Q.14 A string of mass 0.2 kg/m has length ℓ = 0.6m. It is fixed at both ends and stretched such that it has a tension of 80 N. The string vibrates in three segments with amplitude = 0.5 cm. The velocity of transverse wave is (a.14) 1.57 m/s (b.14) 3.14 m/s (c.14) 9.42 m/s (d.14) 6.28 m/s
- 7. #14# As the string is vibrating in three segments, therefore, l = 3l i.e. l = 2l 2 = 3 T As V = V = m n= V l = 2(0.6) = 0.4 m 3 80 = 20 m / s 0.2 20 = 50 H z 0.4 ædy ö A m plitude of particle velocity = ç ÷ = (a m ax ) w = a m ax (2 p n ) ç ÷ ç dt ÷ è øm ax = (0.5 ´ 10 - 2 ) ´ 2 p ´ 50 = 1.57 m / s Q.15 One plate of a capacitor is connected to a spring as shown in fig. Area of both the plates is A. In steady state, separation between the plates is 0.8 d (spring was unstretched and the distance between the plates was d when the capacitor was uncharged). The force constant of the spring is approximately (a.15) 4 Î 0 AE d (c.15) 3 2 Î 0 AE d 2 (b.15) 6Î 0 E Ad 2 2 (d.15) 3 Î 0 AE 2d 2 3 3 #15# In equilibrium, electrostatic force of attraction between the plates = restoring force in the string
- 8. 2 q 2Î = kx A 0 (C E ) 2Î 2 = k (d - 0.8d ) = 0.2 kd A 0 2 C E k= 2Î A (0.2d ) 0 N ow C = 2 Î 0 A 0.8d Î k= 2 0 A 0.64d 2 2 E 2Î 0 2 A (0.2d ) = 4Î 0 d AE 2 3 Q.16 There are two concentric spheres of radius a and b respectively. If the space between them is filled with medium of resistivity ρ, then the resistance of the intergap between the two spheres will be (a.16) (c.16) r æ1 1 ö ç - ÷ ÷ ç è ø 4p ç b a ÷ (b.16) r æ1 1 ö ÷ ç ç 2 - 2÷ ÷ è 4p ç a b ø (d.16) r 4 p (b + a ) r æ1 1 ö ÷ ç ÷ ç è ø 4p ç a b÷ #16# Consider a concentric spherical shell of radius x and thickness dx as shown in fig. Its resistance, dR is dR = r dx 4p x 2 ∴ Total resistance, R = r 4p b ò a dx x 2 = r é1 1 ù ê ú 4 p êa bú ë û Q.17 An electron whose e/m is 1.76×1011 C/kg eneter a region where there is a uniform magnetic field of induction 2 × 10-3 tesla with a velocity of 3 × 106 m/s in a direction making an angle of 45º with the field. The pitch of its helical path in the region is (a.17) 5.36 cm (b.17) 8.4 cm
- 9. (c.17) 1.2 cm (d.17) 3.8 cm #17# When particle is projected at an angle θ other then 90º with the magnetic field, the velocity of electron has two rectangular components (i) v sin θ perpendicular to field (ii) v cos θ along the field. Here v sin θ provides circular motion while v sin θ provides motion along the magnetic field. Centripetal force, m ( v sin q) = Bq r i.e. r = v sin q m Bq 2p r T im e period , T = = 2p m v sin q Bq Pitch of helix, h= v cos θ × T = v cos θ × 2πm / (Bq) 6 h= 3 ´ 10 ´ cos 45 ´ 2 ´ 3.14 11 1.76 ´ 10 ´ 2 ´ 10 - 3 h = 3.8 cm u r $ k Q.18 The magnetic field in a certain region is given by B = ( 4 0i - 1 8 $ ) g au ss .How much flux passes through a 5.0 cm2 area loop in this region, if the loop lies flat on the xy plane. (a.18) 0 (b.18) 900 n Wb (c.18) 9 Wb (d.18) -900 n Wb #18# As loop is in xy plane, only z component of magnetic field is effective B=-18 gauss = -18 × 10-4 T A = 5 × 10-4 m2 Φ = BA cos 0º = -18 × 10-4 × 5 ×10-4 = - 90 × 10-8 Wb=-900 × 10-9 Wb =-900 n Wb Q.19 In the circuit shown in fig. switch S is closed at time t = 0. The charge which passes through the battery in one time constant is
- 10. EL (a.19) eR (c.19) (b.19) 2 eL ER 2 æL ö (d.19) E ç ÷ ç ÷ ÷ eR E çR ø è L #19# In LR circuit, the growing current at time t is given by I=I0[1-e-t/τ] E Where I 0 = L and T = R R ∴ Charge passed through the battery in one time constant is T q= T ò Idt = ò I 0 (1 0 - t /T ) dt 0 éI e - t / T q = I0 T - ê 0 ê ê- 1 / T ë = I 0 T + I 0 T[e - 1 = I0 T - I0 T + q= e I0 T ùT ú ú ú0 û - 1] I0 T e (E / R )(L / R ) = e = e EL eR 2 Q.20 If the time taken in exciting an electron is 10-2μs, then the uncertainty in the frequency of emitted photon will be (a.20) 1.6 × 105 Hz (b.20) 1.6 × 107 Hz (c.20) 1.6 × 109 Hz (d.20) 1.6 × 1011 Hz #20# As, ∆E=h∆ν and DE = h h = Dt 2p D t h hD n = 2p D t Dn = 1 2p D t = 1 6.28 ´ 10 - 8 = 1.6 ´ 7 10 H z
- 11. Q.21 Light of wavelength 6000Å is incident on a single slit. The first minimum of the diffraction pattern is obtained at 4 mm from the centre. The screen is at a distance of 2m from the slit. The slit width will be (a.21) 0.15 mm (b.21) 0.2 mm (c.21) 0.3 mm (d.21) 0.1 mm #21# From a sin θ= nλ a x = nl a= nl D D = 1´ 6000 ´ 10 4 ´ 10 x - 10 ´ 2 - 3 = 3 × 10-4 m = 0.3 mm Q.22 The energy of a photon is equal to the kinetic energy of a proton. The energy of a photon is E. Let λ1 be the de-Broglie wavelength of the proton and λ2 be the wavelength of the photon. The ratio λ1/λ2 is proportional to (a.22) E0 (b.22) E-2 (c.22) E-1 (d.22) E1/2 #22# For proton , E = 1 2 mn = 2 or p = (m n ) 2 = 2m p 2 2m 2mE D e - B roglie w avelength l 1 = h = p l 1 l h 2 = 2mE h/ 2mE hc / E = E 2c or l 1 l 2 µ E Q.23 Radius of wavelength λ are incident on hydrogen atoms in the ground state. A fraction of these radiations is absorbed by these atoms. There are different wavelengths in the emission spectrum of excited atoms. One of the values of λ will be (a.23) 1211 Å (b.23) 912 Å (c.23) 950 Å (d.23) 6208 Å #23# No. of wavelengths in emission spectrum
- 12. n (n - 1) N = = 10 2 2 n - n - 20 = 0 n = 5 (- 4is not possible) æ1 1 = Rç ç 2 2 ç1 l è 5 1 25 l = 25 = 24 R ö ÷ = 24 R ÷ ÷ ÷ 25 ø 24 ´ 1.097 ´ 10 7 = 950 Å Q.24 If a hydrogen atom at rest emits a photon of wavelength λ, the recoil speed of the atom of mass m is h (a.24) (b.24) ml l (c.24) mh l (d.24) mhλ mH #24# From de-Broglie wave equation, l = h h or p = p This is the momentum associated with photon emitted. l From the law of conservation of linear momentum, momentum of recoil atom = p = h l i.e. mv = h l v= h ml Q.25 An AND gate (a.25) is a universal gate (b.25) is equivalent to a series switching circuit (c.25) is impliments logic addition (d.25) is equivalent to a parallel switching circuit. #25# For AND gate; we get output only if A = 1 and B = 1 i.e. AND gate is equivalent to a series switching circuit. Q.26 The value of current in the following diagram will be
- 13. (a.26) 10 amp (b.26) 10-2 amp (c.26) 0 amp (d.26) 0.025 amp #26# Here p-n junction is forward biased with voltage = 5 – 3 = 2V. ∴ current I = 2 1 = 200 = 10 - 2 A 100 Q.27 The carrier frequency generated by a tank circuit containing 1 nF capacitor and 10 microhentry inductor is (a.27) 159.2 Hz (b.27) 1592 Hz (c.27) 1592 kHz (d.27) 15920 Hz #27# C=1nF = 10-9 F, L=10μH = 10-5 H 1 n= 2p 1 = LC 2 p 10 - 5 = ´ 10 - 9 10 7 2p = 1.592 × 106 Hz = 1592 kHZ Q.28 A travelling microscope focused directly on an ink dot reads 2.758cm. A glass slab is placed on the dot. The microscope is focused on the dot and its scale reading is 3.398 cm. The microscope is now focused on the surface of the glass slab and it reads 4.680 cm. What is refractive index of material of the slab? (a.28) 1.5 (b.28) 3.398 (c.28) 1.6 (d.28) 2.758 #28# Here, position of object O : R1 = 2.758cm Position of image I : R2 = 3.398 cm Position of top surface, S ; R3 = 4.680 cm m= real depth (O S) apparent depth (IS) = R 3 - R1 = R3 - R2 = 1.922 4.680 - 2.758 4.680 - 3.398 = 1.5 1.282 Q.29 Two liquids are at temps. 20ºC and 40ºC. When same mass of both of them is mixed, the temperature of the mixture is 32ºC. What is the ratio of their specific heats ? (a.29) 3/2 (b.29) 1/3 (c.29) 2/3 (d.29) 2/5
- 14. #29# Heat gained by one = Heat lost by the other C1 × m (32-20) = C2 × m (40-32) C1 8 = C2 = 12 2 3 Q.30 For a given sonometer wire under given tension, first resonance length with a fork of frequency 256 is 20 cm. If fork of frequency 512 is used, the first resonance length would be (a.30) 20 cm (b.30) 10 cm (c.30) 40 cm (d.30) 30 cm #30# As n1 = l2 l1 = l2 20 n2 256 512 l2 = 256´ 20 512 = 1 0 cm
