Episiotomy
- 2. Definition: It is an intrapartum incision of the perineum to widen the introitus.
- 4. Benefits: •Prevention of perineal lacerations by anatomical incision and repair of the episiotomy. •Prevention of prolonged and overstretch of the perineum which predisposes to prolapse and stress incontinence. •Minimizing compression and decompression of the head which causes intracranial haemorrhage.
- 5. Indications: Maternal: • Nearly in all primiparas. • Old perineal scar about to rupture. • Prolonged second stage due to rigid perineum. • Prior to most instrumental vaginal delivery as forceps and vacuum. • Vulval oedema.
- 6. Foetal • Large sized baby. • Preterm baby. • Direct occipito-posterior. • Breech delivery.
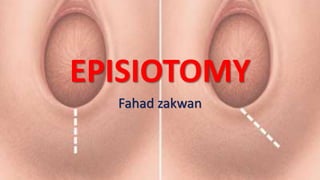
- 7. TYPES
- 9. Median episiotomy • A midline incision down to, but not, including the external anal sphincter. Advantages: • It is the easiest to perform and to repair. • Less blood loss. • Less pain and discomfort in the pueperium. • Less dyspareunia later on. • Better end-result cosmetic appearance.
- 10. Disadvantages: •Its inadvertent extension will injure the external anal sphincter and rectum. •This can be prevented by extending the incision by the scissors in a J-shaped manner to avoid the external sphincter.
- 11. Mediolateral episiotomy: •The incision extends from the midline of the forchette mediolaterally at 5 or 7 o’clock towards the direction of the ischial tuberosity. Advantages: •Extension to the anal sphincter is less common so it is more suitable for instrumental delivery and in short perineum.
- 12. Disadvantages: •Difficult to perform and to repair. •More blood loss. •More pain and discomfort in the puerperium. •More dyspareunia later on. •Less end-result cosmetic appearance.
- 13. Procedure •Anaesthesia: Local infiltration, pudendal nerve block, epidural, spinal or general anaesthesia can be used. •Timing: when the introitus is distended by the presenting part or the cup of the ventouse with a visible diameter not less than 3-4 cm, and done at the maximum of a uterine contraction. If forceps will be used episiotomy is done just before its application.
- 14. •Incision: The index and middle fingers of one hand is introduced between the presenting part and the proposed site of perineal incision to protect the presenting part and support the tissues that will be incised. The incision is usually 3-5 cm length. including the posterior vaginal wall, forchette, perineal muscles and perineal skin.
- 15. •Repair: Cut gut O, Dexon or vicryl 2/0 may be used to close the posterior vaginal wall by continuous sutures where the first stitch should be above the apex of the vaginal incision, then the muscles with interrupted sutures and lastly the skin with interrupted or subcuticular sutures.
- 16. Postnatal care: •A non- steroidal anti-inflammatory agent as diclofenac is used as an analgesic for the first 72 hours. •Local antiseptic lotion and antibiotic powder or spray is used for 7 days.
