Me307 machine elements formula sheet Erdi Karaçal Mechanical Engineer University of Gaziantep
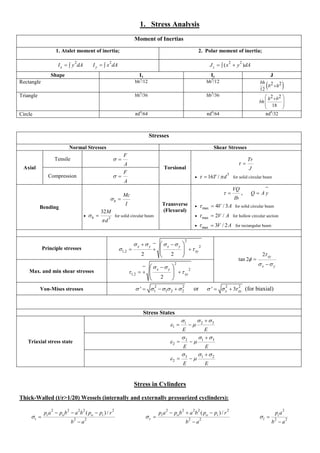
- 1. 1. Stress Analysis Moment of Inertias 1. Atalet moment of inertia; 2. Polar moment of inertia; 2 x I y dA 2 y I x dA 2 2 ( ) z J x y dA Shape Ix Iy J Rectangle bh3/12 hb3/12 2 2 12 bh b h Triangle bh3/36 hb3/36 2 2 18 h b bh Circle πd4/64 πd4/64 πd4/32 Stresses Normal Stresses Shear Stresses Axial Tensile F A Torsional Tr J 3 Compression 16T / d for solid circular beam F A Bending b Mc I 3 32 b M d for solid circular beam Transverse (Flexural) VQ Ib , Q A y max 4V / 3A for solid circular beam max 2V / A for hollow circular section max 3V / 2A for rectangular beam Principle stresses 2 2 1,2 2 2 x y x y xy 2 tan 2 xy x y Max. and min shear stresses 2 2 1,2 2 x y xy Von-Mises stresses 2 2 1 1 2 2 ' or 2 2 ' 3 x xy (for biaxial) Stress States Triaxial stress state 1 2 3 1 E E 2 1 3 2 E E 3 1 2 2 E E Stress in Cylinders Thick-Walled (t/r>1/20) Wessels (internally and externally pressurized cyclinders): 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ( ) / i o o i t p a p b a b p p r b a 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ( ) / i o o i r p a p b a b p p r b a 2 2 2 i l p a b a
- 2. If the external pressure is zero (po=0); 2 2 2 2 2 1 i t a p b b a r 2 2 2 2 2 1 i r a p b b a r r=a r pi 2 2 t i 2 2 b a p b a r=b 0 r 2 2 2 2 t i a p b a If the internal pressure is zero (pi=0); 2 2 2 2 2 1 t o b a p b a r 2 2 2 2 2 1 r o b a p b a r r=a 0 r 2 2 2 2 t o b p b a r=b r o p 2 2 t o 2 2 b a p b a a=inside radius of the cylinder b=outside radius of the cylinder pi=internal pressure po=external pressure Thin-Walled Wessels(t/r<1/20): 2 i t pd t 4 i l pd t Curved Members In Flexure: A r dA ( ) My Ae r y o o o Mc Aer , i i i Mc Aer Press and Shrink Fit: 2 2 it 2 2 b a p b a 2 2 ot 2 2 c b p c b 2 2 o 2 2 o o bp c b E c b 2 2 i 2 2 i i bp b a E b a 2 2 2 2 o i 2 2 o 2 2 i o i bp c b bp b a E c b E b a 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ; interface pressure 2 o i E c b b a if E E E = p = b b c a
- 3. 2. Deflection Analysis F k y , k=spring constant T GJ k l ,k=Torsional spring rate for tension or compression loading AE k l Castigliano’s Theorem: Strain Energy Axial Load 2 2 F L U AE Direct Shear Force 2 2 F L U AG Torsional Load 2 2 T L U GJ Bending Moment 2 2 M U dx EI Flexural Shear 2 2 CF U dx GA , C is constant Buckling Consideration: Slenderness ratio= l k , I k A 1/2 1 l 2 EC k Sy 2 2 1 Critical Unit Load = Euler Column / cr l l P C E k k A l k ; 2 2 P cr C EI l 2 2 1 1 Critital Unit Load Johnson's Column 2 cr y y = l l P S l = S k k A CE k 1. Both ends are rounded-simply supported C=1 2. Both ends are fixed C=4 3. One end fixed, one end rounded and guided C=2 4. One end fixed, one end free C=1/4 U Total energy F Force on the deflection point Angular deflection U y F Tl GJ
- 4. 3.Design For Static Strength Ductile Materials 1. Max. Normal Stress Theory (MNST): If, 1 2 3 1 y S n 3. Distortion Energy Theory If, 1 2 3 2 2 2 1 2 2 3 3 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ' 2 For baxial stress state; 2 2 ' 3 x xy 1 y S n 2. Max. Shear Stress Theory (MSST): Yield strength in shear (Ssy)=Sy/2 1 3 max 2 , for biaxial stress state; max 1 2 2 4 2 x xy max sy S n Brittle Materials 1. Max. Normal Stress Theory (MNST): 3. The Modified Mohr Theory (MMT) If, 1 2 3 1 ut S n or 3 uc S n If, 1 2 3 3 1 3 1 uc uc ut ut S S S S S 3 3 S n 2. The Column Mohr Theory (CMT) or Internal Friction Theory (IFT): 3 1 3 1 uc uc ut S S S S 3 3 S n
- 5. 5. Design for Fatigue Strength Endurance limit for test specimen (Se’); For ductile materials: Se’=0.5 Sut if Sut<1400 MPa Se’=700 MPa if Sut 1400 MPa For irons: Se’=0.4 Sut if Sut<400 MPa Se’=160 MPa if Sut 400 MPa For Aliminiums: Se’=0.4 Sut if Sut<330 MPa Se’=130 MPa if Sut 330 MPa For copper alloys: Se’ 0.4 Sut if Sut<280 MPa Se’ 100 MPa if Sut 280 MPa Se = ka kb kc kd ke Se’ Sf=10c Nb u e 1 0.8S b log 3 S 2 u e 0.8S c log S ka= surface factor, ka=aSut b Surface Finish Factor a Factor b Ground 1.58 -0.065 Machined or Cold Drawn 4.51 -0.265 Hot Rolled 57.7 -0.718 As Forged 272 -0.995 kb= size factor; kb=1 if d 8 mm and kb= 1.189d-0.097 if 8 mm<d 250 mm for bending & torsional loading. For non-rotating element, 0.097 b eq k 1.189d deq=0.37d For pure axial loading, kb=1 and Se’=0.45Sut For combined loading, =1.11 if Sut 1520 MPa and =1 if Sut 1520 MPa for ductile materials. kc=reliability factor kd=temperature effects, kd=1 if T 3500 and kd=0.5 if 3500<T 5000 ke=stress concentration factor, ke=1/Kf Kf=1+q(Kt-1) Kt=geometric stress concentration factor, q=notch sensitivity. Modified Goodman Soderberg Infinite Life Finite Life Infinite Life Finite Life a m e u 1 n = σ σ + S S a m f u 1 n = σ σ + S S a m e y 1 n = σ σ + S S a m f y 1 n = σ σ + S S Fa=(Fmax-Fmin)/2 Fm=(Fmax+Fmin)/2
- 6. 6. Tolerances and Fits TF=Cmax-Cmin dL=DU-c Cmax=DU-dL Cmin=DL-dU TF=Imax+Cmax dU=dL+TS Imax=dU-DL Imin=dL-Du TF=Imax-Imin dU=DL+Imax TS=dU-dL TH=DU-DL TF=TH+TS 7. Design of Power Screws m m R m Fd L d T 2 d L m m L m Fd d L T 2 d L Or considering tan ; m R Fd T tan 2 m R Fd T tan 2 If the friction between the stationary member and the collar of the screw is taken into consideration; m c c R Fd d F T tan 2 2 m c c R Fd d F T tan 2 2 o R R T FL T 2 T when collar friction is negligible, we obtain as, tan tan If tan or m L d then screw is self locking. Bearing Stresses b 2 2 r 4pF h d d b m Fp d th p t 2 Shear Stresses For Screw Thread For Nut Thread s r 2F d h n 2F dh Bending Stresses The maximum bending stress, m 6F d Np N=h/p
- 7. Tensile or Compressive stresses x t F A 2 t t d A 4 r m t d d d 2 Combined Stresses R xy 3 t 16T d Based on distortion energy theory; R xy 3 t 16T d 2 2 ' x 3xy y S n ' Based on maximum shear stres theory; 2 2 max x xy 1 4 2 sy max S n 8. Design of Bolted Joints Fe=Feb+Fep Feb=CFe Fep=(1-C)Fe b b m k C = k k Fb=Fi+CFe Fm=Fi-(1-C)Fe b b b A E k L m 1 2 n 1 1 1 1 .......... k k k k i b b F k i m m F k Shigley and Mishke approach; For cone angle of 0 30 , i i i i 1.813E d k 1.15L 0.5d ln 5 1.15L 2.5d m 1 2 n 1 1 1 1 .......... k k k k If L1=L2=L/2 and materials are same, m 1.813Ed k 2.885L 2.5d 2ln 0.577L 2.5d
- 8. For cone angle of 0 45 , i i i i E d k 5 2L 0.5d ln 2L 2.5d If L1=L2=L/2 and materials are same, m Ed k L 0.5d 2ln 5 L 2.5d Wileman approach; (Bid/L) m i k EdA e Where Ai and Bi are constants related to the material. For Steel Ai=0.78715 and Bi=0.62873, for Aliminium Ai=0.79670 and Bi=0.63816, for Gray cast iron Ai=0.77871 and Bi=0.61616. Filiz approach; 1 d B 5 L m eq 2 1 k E d e 2 1 B 1 2 eq 1 2 E E E E E 2 1 0.1d B L 8 1 1 2 L B 1 L Static loading; b y t F S A or b p t F S A p y S 0.85S mF 0 e i p t e 1C nF F S A CnF n=load factor of safety Critical load= i ce F F 1 C Dynamic Loading: e a t CnF 2A i m a t F A s a m e u 1 n S S t u e u i s e A S CnF S F 1 n 2 S Fi=the maximum value of preload for there is no fatigue failure. Limitations: p i p 0.6F F 0.9F where p t p F A S e ut imax t ut e cF n S F A S 1 2N S e e i t p F cF (1 c) F A S N N b 3.5d c 10d b 180 c N
- 9. 9. Design of Riveted Joints Shearing of Rivets: F A , F=Force on each rivet 2 d A 4 Secondary Shear Force i i N 2 i 1 Mr F '' r Bearing (compression) Failure: F A , A=td, t=thickness of the plate Plate Tension Failure: F A , A w Nd t w=width of plate N=number of rivets on the selected cross section Primary Shear Force N i 1 F F' A 10. Design of Welded Joints Primary Shear Stress F ' A u J 0.707hJ Secondary Shear Stress Mr '' J u I 0.707hI Bending Stress Mc I
- 10. Table 9-3 Minimum weld-metal properties AWS electrode Number n Tensile Strength MPa Yield Strength MPa Percent Elongation E60xx 420 340 17-25 E70xx 480 390 22 E80xx 530 460 19 E90xx 620 530 14-17 E100xx 690 600 13-16 E120xx 830 740 14 Table 9-5 Fatigue-strength reduction factors Type of Weld Kf Reinforced butt weld 1.2 Toe of transverse fillet weld 1.5 End of parallel fillet weld 2.7 T-butt joint with sharp corners 2.0
- 11. Table 9-1 Torsional Properties of Fillet Welds* Weld Throat Area Location of G Unit Polar Moment of Inertia *G is centroid of weld group; h is weld size; plane of torque couple is in the plane of the paper; all welds are of the same size.
- 12. Table 9-2 Bending Properties of Fillet Welds* Weld Throat Area Location of G Unit Moment of Inertia *Iu, unit moment of inertia, is taken about a horizontal axis through G, the centroid of the weld group; h is weld size; the plane of the bending couple is normal to the paper; all welds are of the same size
- 13. Table A3-8 Stress concentration factors for round shaft with shoulder fillet in tension d r D . o= F/A, where A= d2/4 D/d =1,02 D/d =1,05 D/d =1,1 D/d=1,5 r/d Kt Kt Kt Kt 0,025 1,800 - - - 0,028 1,728 - 2,200 - 0,031 1,678 2,000 2,125 - 0,037 1,610 1,868 2,020 - 0,044 1,550 1,778 1,938 2,522 0,050 1,508 1,714 1,866 2,400 0,062 1,452 1,626 1,766 2,235 0,075 1,408 1,550 1,684 2,086 0,088 1,370 1,502 1,624 1,970 0,100 1,336 1,457 1,568 1,893 0,125 1,286 1,400 1,496 1,760 0,150 1,254 1,364 1,452 1,662 0,175 1,230 1,340 1,400 1,600 0,200 1,220 1,314 1,372 1,546 0,250 1,216 1,292 1,342 1,508 0,275 1,200 1,270 1,325 1,480 0,300 1,200 1,250 1,296 1,452 * Adopted from Ref. [12]
- 14. Table A3-9 Stress concentration factors for round shaft with shoulder fillet in torsion d r D T T . o= Tc/J, where c=d/2 and J=d4/32 D/d =1,09 D/d =1,20 D/d =1,33 D/d =2,0 r/d Kt Kt Kt Kt 0,009 - - - - 0,012 1,800 2,300 - 2,600 0,030 1,566 2,040 2,144 2,288 0,025 1,472 1,894 2,020 2,122 0,033 1,384 1,761 1,878 1,966 0,042 1,322 1,644 1,755 1,828 0,050 1,283 1,576 1,677 1,750 0,062 1,244 1,500 1,600 1,644 0,075 1,206 1,434 1,516 1,572 0,087 1,184 1,378 1,458 1,510 0,100 1,166 1,342 1,412 1,466 0,125 1,144 1,275 1,344 1,400 0,150 1,122 1,220 1,294 1,344 0,200 1,110 1,160 1,220 1,266 0,250 1,100 1,130 1,178 1,222 0,300 1,100 1,120 1,160 1,200 * Adopted from Ref. [12]
- 15. Table A3-10 Stress Concentration factors for round shaft with shoulder fillet in bending d r M D M . o= Mc/I, where c=d/2 and I=d4/64 D/d =1,02 D/d =1,05 D/d =1,1 D/d =1,5 D/d =3 r/d Kt Kt Kt Kt Kt 0,012 2,290 2,553 2,700 - - 0,017 2,120 2,378 2,500 3,000 - 0,021 2,000 2,240 2,366 2,774 3,000 0,025 1,926 2,134 2,260 2,600 2,862 0,036 1,760 1,936 2,046 2,310 2,600 0,050 1,644 1,782 1,865 2,060 2,310 0,062 1,574 1,700 1,750 1,925 2,140 0,075 1,518 1,628 1,688 1,800 1,986 0,087 1,472 1,563 1,630 1,728 1,880 0,100 1,440 1,534 1,580 1,660 1,804 0,125 1,380 1,468 1,500 1,584 1,684 0,150 1,330 1,412 1,450 1,510 1,584 0,175 1,297 1,358 1,400 1,450 1,510 0,200 1,264 1,336 1,360 1,400 1,457 0,225 1,242 1,308 - - 1,410 0,250 1,225 1,286 - - 1,374 0,275 1,210 1,264 - - 1,340 0,300 1,200 1,242 - - 1,320 * Adopted from Ref. [12]