Epidemiological Studies
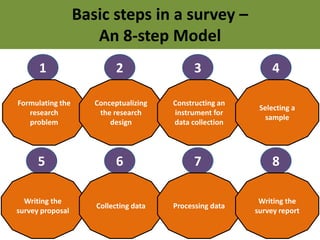
- 1. Basic steps in a survey – An 8-step Model 1 Formulating the research problem 2 Conceptualizing the research design 3 Constructing an instrument for data collection 4 Selecting a sample 5 Writing the survey proposal 6 Collecting data 7 Processing data 8 Writing the survey report
- 2. 2 Conceptualizing the research design
- 4. Observational Studies • A DESCRIPTIVE STUDY is limited to a description of the occurrence of a disease in a population and is often the first step in an epidemiological investigation. • An ANALYTICAL STUDY goes further by analyzing relationship between health status and other variables.
- 6. Some Examples of Descriptive Studies • Case Report • Case Series • Surveys Pure descriptive studies make no attempt to analyze the links between outcome and exposure
- 8. Ecological Studies • In an ecological study, the units of analysis are groups of people rather than individuals.
- 11. Cross-sectional studies • Because they measure the prevalence of a disease, they are sometimes also called ‘prevalence studies’. • Exposure and effect (outcome) are measured at the same time.
- 12. Uses of cross-sectional studies • Prevalence • Disease outbreaks • Assessing healthcare needs of populations. • Trends in diseases (repeated c/s studies) • Risk factors for diseases (e.g., NCDs)
- 13. Advantages and Disadvantages • Easy and relatively inexpensive • Less time consuming • The temporal relationship between exposure and effect is difficult to establish.
- 15. Key Features • The exposure experience of a group of people who have the disease [CASES] is compared to the exposure experience of a similar (matched) group who do not have the disease [CONTROLS] • Suitable for rare diseases or diseases with long latency periods • The study proceeds backwards from “EFFECT to CAUSE’
- 16. Basic Design
- 17. • Selection of cases • Selection of controls • Measurement of exposure • Analysis Steps
- 18. Selection of Cases • Define a ‘case’ Hospital General population • Sources of cases • ‘Incident’ cases ‘Prevalent cases’??? Temporality Disease severity (Those who are exposed survive longer)
- 19. Selection of Controls • Free from disease • As similar to the cases (matched) as possible, except for the absence of disease under study • Sources of controls • General population • Relatives/Friends/Neighbours • Hospital controls • How many controls per case? • One to four
- 20. “MATCHING” is the process of selecting controls in a case-control study so that the controls are similar to the cases with regard to certain key characteristics-such as age, sex and race. Group matching (Frequency matching) Individual matching (Pair matching)
- 21. Measurement of exposure • Definition and criteria • Done in the same way for both cases and controls • How to measure exposures? – Interviews/Questionnaires – Past records (Hospital, Employment) – Laboratory measurements
- 22. Analysis • Find exposure rate in cases • Find exposure rate in controls • Calculate “Odds Ratio”
- 23. Exposure Disease Yes No Yes a b No c d Total a+c b+d Odds Ratio=ad/bc
- 24. Use of Oral Contraceptive Thromboembolism Yes No Yes 26 10 No 32 106 Total 58 116 Exposure rate among cases=(26/58)x100=45% Exposure rate among controls=(10/116)x100=9% Odds ratio= (26x106)/(10x32)=2756/320=8.6
- 25. How to interpret the OR? People who use oral contraceptives have an 8.6 times higher risk of developing thromboembolism compared to those who do not use oral contraceptives
- 26. Cigarette smoking Lung cancer Yes No Yes 85 160 No 15 240 Total 100 400 Odds Ratio=(85x240)/(160x15)=8.5
- 27. Q. An investigator selected 40 cases of gastric carcinoma and an equal number of controls matched for age, sex and socioeconomic status. It was found that among cases 30 had an 5 evidence of H pylori infection and among controls 15 had an evidence of H pylori infection. Is there an evidence of association between H pylori infection and gastric carcinoma?
- 29. COHORT STUDIES
- 30. Key Features • The study proceeds from “CAUSE to EFFECT” • At the start of the study, all participants are free from disease. • A group of people who are ‘exposed’ to some factor and another ‘not-exposed’ group are followed up for a certain time. The disease rate (incidence of disease) among ‘exposed’ is compared to the disease rate among the ‘not-exposed’ group.
- 31. Basic Design
- 32. • Selection of study subjects • Obtaining data on exposure • Follow-up • Analysis Steps
- 33. Selection of Study Subjects • General population • Special groups – Occupation group – Professional group • Radiologists • Nurses • Doctors • Teachers, etc. Free from study disease
- 34. Obtaining data on exposure Cohort Exposed Not-exposed 1 2 Exposed Cohort Not-Exposed Cohort 3 Low Exposure Exposed Cohort Medium Exposure High Exposure
- 35. Follow-up • The follow-up procedures should be similar for both the exposed and the non-exposed groups. • Clear, and valid definitions for disease status.
- 36. Analysis • Find disease incidence rate in exposed • Find disease incidence rate in non-exposed • Calculate “Relative Risk” (Risk Ratio)
- 37. Exposure Disease Total Yes No Yes a b a+b No c d c+d Incidence rate among exposed=(a/a+b)*10x Incidence rate among non-exposed=(c/c+d)*10x Relative Risk = (a/a+b) (c/c+d)
- 38. Exposure to prolonged heat stress Kidney disease Total Yes No Yes 67 4458 4525 No 39 5443 5482 Incidence rate among exposed= 14.8 Incidence rate among non-exposed= 7.1 Relative Risk= 14.8/7.1 = 2.1
- 39. How to interpret the RR? People exposed to prolonged heat stress have a 2.1 times higher risk of developing kidney disease compared to those who are not exposed to prolonged heat stress
- 40. THREE types of Cohort studies • Prospective • Retrospective (Historical) • Retrospective-Prospective (Ambispective)
- 41. Retrospective cohort studies Study starts 2014 1990 Data about oral contraceptive intake in a cohort of women How many of the women have thromboembolic disease, exposed versus not-exposed
- 42. Case-control studies start with outcome/disease Cohort studies start with exposure Case-control studies compare exposure rates among cases and controls Cohort studies compare disease rates among exposed and not-exposed
- 43. Case control Cohort Advantages Excellent way to study rare diseases with long latency Better for studying rare exposures Relatively quick Provides complete data on cases, stages Relatively inexpensive Allows study of more than one effect of exposure Requires relatively few study subjects Can calculate and compare rates in exposed and unexposed Can often use existing records Choice of factors available for study Can study many possible causes of a disease Quality control of data
- 44. Case control Cohort Disadvantages Relies on recall or existing records about past exposure Need to study large numbers Difficult or impossible to validate data May take many years Control of extraneous factors incomplete Circumstances may change during study Difficult to select suitable comparison group Expensive Cannot calculate rates Control of extraneous factors may be incomplete Cannot study mechanism of disease Rarely possible to study mechanism of disease
- 48. • Intervention or experimentation involves attempting to change a variable in one or more groups of people. • The effects of an intervention are measured by comparing the outcome in the experimental group with that in a control group. • Ethical considerations • Informed consent
- 50. A randomized controlled trial is an epidemiological experiment designed to study the effects of a particular intervention, usually a treatment for a specific disease (clinical trial). Subjects in the study population are randomly allocated to intervention and control groups, and the results are assessed by comparing outcomes.
- 51. “Randomization” is a statistical procedure wherein patients are allocated randomly to either the intervention group or the control group. The purpose of randomization is to ensure that the patients in the two groups are similar and hence comparable.
- 52. FIELD TRIALS
- 53. Field trials, in contrast to clinical trials, involve people who are healthy. Data collection takes place “in the field,” usually among people in the general population
- 55. COMMUNITY TRIALS
- 56. Treatment groups are communities, rather than individuals. This is particularly appropriate for diseases that are influenced by social conditions, and for which prevention efforts target group behavior.
- 57. ERRORS IN EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDIES
- 58. RANDOM ERROR SYSTEMATIC ERROR
- 59. RANDOM ERROR • When a value of the sample measurement diverges-due to chance alone-from that of the true population value. • Random error is “random”; therefore cannot be predicted.
- 60. • THREE major sources of random error – Individual biological variation – Sampling error • Increase the size of the sample – Measurement error • Stringent protocols • Systematic quality control measures
- 61. SYSTEMATIC ERROR • Also called “BIAS” • Systematic deviation of results or inferences from truth. • Bias is defined as ‘any systematic error in the design, conduct or analysis of a study that results in a mistaken estimate of an exposures effect on the risk of disease’.
- 62. TWO major types of bias SELECTION BIAS INFORMATION BIAS
- 63. SELECTION BIAS • A systematic difference between the characteristics of the people selected for a study and the characteristics of those who are not. • Examples – Bias due to non-response – Exclusion bias – Berkson’s bias (Berksonian bias)
- 64. • Bias due to non-response – Those who volunteer to take part in a study are different from those who don’t • Exclusion bias – Different eligibility criteria for cases and controls •Berkson’s bias or Berksonian bias
- 65. • Berkson’s bias (Berksonian bias) –When both exposure and disease under study affect selection. This occurs when the combination of exposure and disease under study increases the chance of admission to hospital, leading to a higher exposure rate among hospital cases as compared to hospital controls. Thus it causes hospital cases and controls in a case-control study to be systematically different from one another.
- 66. INFORMATION BIAS • A flaw in measuring exposure or outcome variables that results in different accuracy of information between comparison groups. • This usually arises when the way of obtaining information about exposure or outcome is inadequate and hence may lead to incorrect information about exposure or outcome.
- 67. Examples of Information bias • Misclassification bias – Wrongly classify exposure or outcome • Recall bias – Differential recall about exposure among cases and controls. Case are more likely to remember exposure as compared to controls • Reporting bias – Cases may be reluctant to report exposure
- 68. • Surveillance bias – If exposed group is monitored more closely compared to the unexposed group • Interviewer bias – Knowledge about exposure status may consciously or subconsciously influence the interviewers measurements biased. Observer bias is a related bias. • Single-blinding • Double-blinding • Triple blinding
- 69. CONFOUNDING
- 70. • In a study of whether factor A is a cause of disease B, we say that a third factor, factor X is a confounder if the following are true: – Factor X is a known risk factor for disease B – Factor X is associated with factor A, but is not a result of factor A
- 74. Approaches to handling confounding • In designing and carrying out the study – Matching – Exclusion • In the analysis of data – Stratification – Adjustment
