The cell in action
•Télécharger en tant que PPT, PDF•
2 j'aime•6,007 vues
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
Biology 11 and 12: Cell modifications and specialization

Biology 11 and 12: Cell modifications and specialization
Dacota_blue K12: Science 7: Quarter 1: Module 1 matter

Dacota_blue K12: Science 7: Quarter 1: Module 1 matter
En vedette
En vedette (20)
Mdp 511 2012 organizations in development - session 1

Mdp 511 2012 organizations in development - session 1
Similaire à The cell in action
Similaire à The cell in action (20)
10. Transport System in Organisms E-learning - Diffusion & Osmosis

10. Transport System in Organisms E-learning - Diffusion & Osmosis
2.2.1.2 functions of the cell membrane UEC Senior 1 Biology 独中高一生物 

2.2.1.2 functions of the cell membrane UEC Senior 1 Biology 独中高一生物
Plus de jdrinks
Plus de jdrinks (20)
Dernier
Dernier (20)
08448380779 Call Girls In Friends Colony Women Seeking Men

08448380779 Call Girls In Friends Colony Women Seeking Men
Boost PC performance: How more available memory can improve productivity

Boost PC performance: How more available memory can improve productivity
Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...

Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...
Tech Trends Report 2024 Future Today Institute.pdf

Tech Trends Report 2024 Future Today Institute.pdf
Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)

Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Handwritten Text Recognition for manuscripts and early printed texts

Handwritten Text Recognition for manuscripts and early printed texts
08448380779 Call Girls In Greater Kailash - I Women Seeking Men

08448380779 Call Girls In Greater Kailash - I Women Seeking Men
[2024]Digital Global Overview Report 2024 Meltwater.pdf![[2024]Digital Global Overview Report 2024 Meltwater.pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![[2024]Digital Global Overview Report 2024 Meltwater.pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
[2024]Digital Global Overview Report 2024 Meltwater.pdf
Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff

Strategize a Smooth Tenant-to-tenant Migration and Copilot Takeoff
08448380779 Call Girls In Diplomatic Enclave Women Seeking Men

08448380779 Call Girls In Diplomatic Enclave Women Seeking Men
From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation

From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation
Workshop - Best of Both Worlds_ Combine KG and Vector search for enhanced R...

Workshop - Best of Both Worlds_ Combine KG and Vector search for enhanced R...
The cell in action
- 1. The Cell in Action
- 2. Section 1: Exchange with the Environment A cell must be able to obtain food and raw materials and get rid of wastes. What is diffusion? Diffusion = the movement of particles from regions of higher density to regions of lower density ∗ Cells do not need to use energy for diffusion
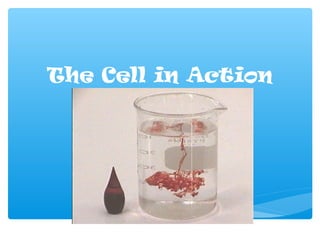
- 3. Diffusion of Ink in Water ∗ The particles of the dye of the ink slowly diffuse through the water
- 4. Diffusion of Water ∗ The cells of organisms are surrounded by and filled with fluids that are made mostly of water ∗ Osmosis = the diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane ∗ “semi permeable” means that some things, but not all, can get through
- 5. Osmosis, continued ∗ Pure water has highest concentration of water molecules ∗ When you mix something with water, you lower the concentration of water molecules. ∗ During osmosis, water particles move to where they are less concentrated
- 7. Salt would cause water molecules to travel out of the cell membrane. Water loss equals dead slugs!
- 8. The Cell and Osmosis ∗ Osmosis is important to cell functions ∗ Example: red blood cells are surrounded by plasma, which is made up of water, salt, sugars, and other particles. The concentration of these particles is kept in balance by osmosis!
- 9. ∗ Osmosis also occurs in plant cells Example: when a wilted plant is watered, osmosis makes the plant firm again
- 10. Osmosis in Plant Cells
- 11. Comprehension Question: ∗Why would red blood cells burst if you placed them in pure water?
- 12. Answer: ∗ Red blood cells would burst in pure water because water particles move from outside, where particles are dense, to the inside of the cell, where particles are less dense. This movement of water would cause red blood cells to fill up and burst!
- 14. SORRY! Knowledge does not diffuse from the pages of the textbook to your brain!
- 15. Moving Small Particles ∗ Small particles, like sugar, cross the cell membrane through channels, which are made up of proteins
- 16. Passive Transport ∗ Passive transport = the movement of substances across the cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell ∗ During passive transport, particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration ∗ Examples of passive transport : osmosis and diffusion
- 18. Active Transport ∗ Active transport = the movement of substances across the cell membrane that requires the cell to use energy ∗ Examples of active transport: endocytosis and exocytosis ∗ involves the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration
- 19. Endocytosis: ∗ Endocytosis = the process by which a cell membrane surrounds a particle and encloses the particle in a vesicle to bring the particle into the cell ENDO = IN and GO
- 20. Steps of Endocytosis: 1. The cell comes into contact with a particle 2. The cell membrane begins to wrap around the particle 3. Once the particle is completely surrounded, a vesicle pinches off 4. Endocytosis = “within the cell”
- 22. Exocytosis: ∗ Exocytosis = the process in which a cell releases a particle by enclosing the particle in a vesicle that then moves to the cell surface and fuses with the cell membrane EXO = EXIT THE CELL
- 24. Steps of Exocytosis ∗ Large particles that leave the cell must be packaged in vesicles. ∗ Vesicle travels to the cell membrane and fuses with it. ∗ Cell releases the particle to the outside of the cell ∗ Exocytosis = “outside the cell”
- 26. Let’s Review: 1. What part of the cell do materials pass through to get into and out of the cell? 2. What is osmosis? 3. What are 2 examples of passive transport? 4. Large particles enter the cell by_________ and leave by ______________.
- 27. Answers: 1. Cell membrane 1. The diffusion of water through the semi- permeable cell membrane 1. Diffusion and osmosis 1. Endocytosis, exocytosis