Lecture6 analogdigitalsignals
•Télécharger en tant que DOC, PDF•
0 j'aime•532 vues
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
IB Physics Standing Waves Flippingphysics by Nothingnerdy

IB Physics Standing Waves Flippingphysics by Nothingnerdy
En vedette (8)
Similaire à Lecture6 analogdigitalsignals
Similaire à Lecture6 analogdigitalsignals (20)
DCN 5th ed. slides ch03 Introduction to Physical Layer.pdf

DCN 5th ed. slides ch03 Introduction to Physical Layer.pdf
Computer Networks 04 Data and Signal Fundamentals.pptx

Computer Networks 04 Data and Signal Fundamentals.pptx
Ch3Data communication and networking by neha g. kurale

Ch3Data communication and networking by neha g. kurale
Plus de H K
Plus de H K (20)
Dernier
💉💊+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHABI}}+971581248768
+971581248768 Mtp-Kit (500MG) Prices » Dubai [(+971581248768**)] Abortion Pills For Sale In Dubai, UAE, Mifepristone and Misoprostol Tablets Available In Dubai, UAE CONTACT DR.Maya Whatsapp +971581248768 We Have Abortion Pills / Cytotec Tablets /Mifegest Kit Available in Dubai, Sharjah, Abudhabi, Ajman, Alain, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah, Umm Al Quwain, UAE, Buy cytotec in Dubai +971581248768''''Abortion Pills near me DUBAI | ABU DHABI|UAE. Price of Misoprostol, Cytotec” +971581248768' Dr.DEEM ''BUY ABORTION PILLS MIFEGEST KIT, MISOPROTONE, CYTOTEC PILLS IN DUBAI, ABU DHABI,UAE'' Contact me now via What's App…… abortion Pills Cytotec also available Oman Qatar Doha Saudi Arabia Bahrain Above all, Cytotec Abortion Pills are Available In Dubai / UAE, you will be very happy to do abortion in Dubai we are providing cytotec 200mg abortion pill in Dubai, UAE. Medication abortion offers an alternative to Surgical Abortion for women in the early weeks of pregnancy. We only offer abortion pills from 1 week-6 Months. We then advise you to use surgery if its beyond 6 months. Our Abu Dhabi, Ajman, Al Ain, Dubai, Fujairah, Ras Al Khaimah (RAK), Sharjah, Umm Al Quwain (UAQ) United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic provides the safest and most advanced techniques for providing non-surgical, medical and surgical abortion methods for early through late second trimester, including the Abortion By Pill Procedure (RU 486, Mifeprex, Mifepristone, early options French Abortion Pill), Tamoxifen, Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Clinic performs Same Day Abortion Procedure using medications that are taken on the first day of the office visit and will cause the abortion to occur generally within 4 to 6 hours (as early as 30 minutes) for patients who are 3 to 12 weeks pregnant. When Mifepristone and Misoprostol are used, 50% of patients complete in 4 to 6 hours; 75% to 80% in 12 hours; and 90% in 24 hours. We use a regimen that allows for completion without the need for surgery 99% of the time. All advanced second trimester and late term pregnancies at our Tampa clinic (17 to 24 weeks or greater) can be completed within 24 hours or less 99% of the time without the need surgery. The procedure is completed with minimal to no complications. Our Women's Health Center located in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, uses the latest medications for medical abortions (RU-486, Mifeprex, Mifegyne, Mifepristone, early options French abortion pill), Methotrexate and Cytotec (Misoprostol). The safety standards of our Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates Abortion Doctors remain unparalleled. They consistently maintain the lowest complication rates throughout the nation. Our Physicians and staff are always available to answer questions and care for women in one of the most difficult times in their lives. The decision to have an abortion at the Abortion Cl+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...?#DUbAI#??##{{(☎️+971_581248768%)**%*]'#abortion pills for sale in dubai@
Dernier (20)
Navi Mumbai Call Girls 🥰 8617370543 Service Offer VIP Hot Model

Navi Mumbai Call Girls 🥰 8617370543 Service Offer VIP Hot Model
Exploring the Future Potential of AI-Enabled Smartphone Processors

Exploring the Future Potential of AI-Enabled Smartphone Processors
EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY GRADE 11 QUARTER 2 REVIEWER

EMPOWERMENT TECHNOLOGY GRADE 11 QUARTER 2 REVIEWER
Apidays New York 2024 - Accelerating FinTech Innovation by Vasa Krishnan, Fin...

Apidays New York 2024 - Accelerating FinTech Innovation by Vasa Krishnan, Fin...
Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business

Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business
+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...

+971581248768>> SAFE AND ORIGINAL ABORTION PILLS FOR SALE IN DUBAI AND ABUDHA...
Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...

Mastering MySQL Database Architecture: Deep Dive into MySQL Shell and MySQL R...
Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...

Strategies for Unlocking Knowledge Management in Microsoft 365 in the Copilot...
Web Form Automation for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions Apri...

Web Form Automation for Bonterra Impact Management (fka Social Solutions Apri...
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...

Connector Corner: Accelerate revenue generation using UiPath API-centric busi...
Automating Google Workspace (GWS) & more with Apps Script

Automating Google Workspace (GWS) & more with Apps Script
ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges

ICT role in 21st century education and its challenges
Lecture6 analogdigitalsignals
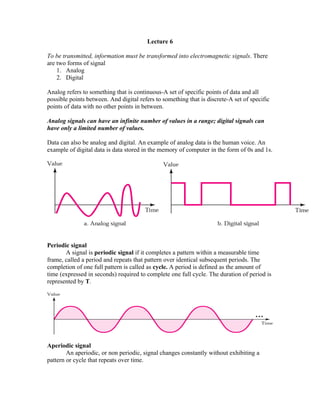
- 1. Lecture 6 To be transmitted, information must be transformed into electromagnetic signals. There are two forms of signal 1. Analog 2. Digital Analog refers to something that is continuous-A set of specific points of data and all possible points between. And digital refers to something that is discrete-A set of specific points of data with no other points in between. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values in a range; digital signals can have only a limited number of values. Data can also be analog and digital. An example of analog data is the human voice. An example of digital data is data stored in the memory of computer in the form of 0s and 1s. Periodic signal A signal is periodic signal if it completes a pattern within a measurable time frame, called a period and repeats that pattern over identical subsequent periods. The completion of one full pattern is called as cycle. A period is defined as the amount of time (expressed in seconds) required to complete one full cycle. The duration of period is represented by T. Aperiodic signal An aperiodic, or non periodic, signal changes constantly without exhibiting a pattern or cycle that repeats over time.
- 2. In data communication, we commonly use periodic analog signals and aperiodic digital signals There are three attributes of analog signals or three properties: 1. Amplitude 2. Frequency 3. Phase Amplitude of a signal is the value of the signal at any point on the wave. It is equal to the vertical distance from a given point on the wave form to the horizontal axis. In other words amplitude refers to the height of the signal. Frequency of a signal is the number of cycles per second. T=1/f. Frequency is denoted by f and its units are Hz or KHz. Frequency and period are inverses of each other. Frequency is the rate of change with respect to time. Change in a short span of time means high frequency. Change over a long span of time means low frequency. If a signal does not change at all, its frequency is zero. If a signal changes instantaneously, its frequency is infinite.
- 3. Phase of a signal describes the position of the waveform relative to time zero. If we think of the wave that can be shifted backward or forward along the time axis, phase describes the amount of that shift.
- 4. Frequency Domain Plot and Time Domain Plot A sine wave is comprehensively defined by its amplitude, frequency and phase. We have been showing a sine wave using a frequency domain plot. The time domain plot shows changes in signal amplitude with respect to time (it is amplitude versus time plot). Phase and frequency are not explicitly measured on a time domain plot.
- 5. A single-frequency sine wave is not useful in data communications; we need to change one or more of its characteristics to make it useful. Why? Answer to this will be discussed later on. When we change one or more characteristics of a single-frequency signal, it becomes a composite signal made of many frequencies. According to Fourier analysis, any composite signal can be represented as a combination of simple sine waves with different frequencies, phases, and amplitudes. The waveform below represents a composite signal consisting of three frequencies, each frequency being represented with a different color. Bandwidth: The bandwidth of a signal is the width of the frequency spectrum. In other words, bandwidth can be calculated by subtracting the lowest frequency from the highest frequency.
- 6. Q) If a periodic signal is decomposed into five sine waves with frequencies of 100, 300, 500, 700, and 900 Hz, what is the bandwidth? Draw the spectrum, assuming all components have maximum amplitude of 10 V. Answer: B = fh – fl = 900 - 100 = 800 Hz The spectrum has only five spikes, at 100, 300, 500, 700, and 900 Q) A signal has a bandwidth of 20 Hz. The highest frequency is 60 Hz. What is the lowest frequency? Draw the spectrum if the signal contains all integral frequencies of the same amplitude. Answer: B = fh – fl 20 = 60 - fl fl = 60 - 20 = 40 Hz Q) A signal has a spectrum with frequencies between 1000 and 2000 Hz (bandwidth of 1000 Hz). A medium can pass frequencies from 3000 to 4000 Hz (a bandwidth of 1000 Hz). Can this signal faithfully pass through this medium? Answer: The answer is definitely no. Although the signal can have the same bandwidth (1000 Hz), the range does not overlap. The medium can only pass the frequencies between 3000 and 4000 Hz; the signal is totally lost.
