2.5 Cell division Mitosis
•Télécharger en tant que PPT, PDF•
1 j'aime•1,433 vues
Signaler
Partager
Signaler
Partager
Recommandé
Contenu connexe
Tendances
Tendances (20)
Dna replication and enzymes involved in dna replication

Dna replication and enzymes involved in dna replication
En vedette
ABSTRACT
This PhD. thesis examines links between Māori deficit statistics, Māori experiences of historical intergenerational trauma or HIT, and colonisation. The thesis draws upon Western critical theory combined with Indigenous methodologies that employ Māori epistemologies or ways of knowing to make sense of historical discourses that have traditionally impeded Māori wellbeing and development. Indigenous methodologies such as Pūrākau theory are employed in this thesis to peel back layers of narratives that are sometimes intergenerational, to expose contributing factors to Māori deficit statistics. These theories interpret underlying themes and key factors in HIT. In essence the study examines Māori experiences; Māori concepts and oral traditions relevant to HIT. Essentially four research questions are posed. "What are Māori experiences of historical intergenerational trauma?" "What were the political, socio- economic implications for Māori both pre and post signing of Te Tiriti o Waitangi?" "What significance does locating self in this research have in terms of contextualising Māori experiences of historical intergenerational trauma?" And finally "What are Māori strategies that respond to this phenomenon?"
These research questions frame the thesis from a position that distinguishes Māori experiences of this phenomenon, from the distinctive lived experiences of other Indigenous cultures across the globe. The research questions also investigate the political, socio- economic environment both pre and post Te Tiriti o Waitangi. This gives a macro view that draws attention to Māori success in international trade and economic development pre Treaty [Te Tiriti o Waitangi]. The thesis then examines how Māori became subjugated to intergenerational positions of impoverishment, and displacement through war, and legislative policies of the New Zealand Settler Government who coveted Māori land, assets, raw materials and resources post Te Tiriti o Waitangi. Locating self in research offers a micro view contextualising how historical events may impact at a personal level. It also draws attention to how those impacts have the potential for manifesting deficit outcomes. The final frame is solution focused, and draws attention to strategies that respond to Māori experiences of historical intergenerational trauma.
Transforming Māori Experiences of Historical Intergenerational Trauma Phd th...

Transforming Māori Experiences of Historical Intergenerational Trauma Phd th...Dr Rawiri Waretini-Karena
En vedette (20)
Poowhiri Poutama Framework Session 4 Whakaratarata

Poowhiri Poutama Framework Session 4 Whakaratarata
A basic structure for layering a masters or doctoral thesis

A basic structure for layering a masters or doctoral thesis
Transforming Māori Experiences of Historical Intergenerational Trauma Phd th...

Transforming Māori Experiences of Historical Intergenerational Trauma Phd th...
Similaire à 2.5 Cell division Mitosis
Similaire à 2.5 Cell division Mitosis (20)
Mitosis- with an animated explanation of the concept 

Mitosis- with an animated explanation of the concept
Plus de Patricia Lopez
Plus de Patricia Lopez (17)
2.5 Cell division Mitosis
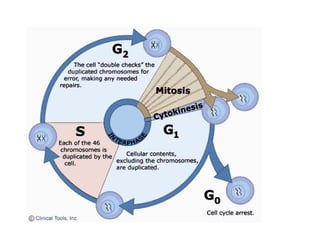
- 4. INTERPHASE G1 phase . Metabolic changes prepare the cell for division. At a certain point - the restriction point - the cell is committed to division and moves into the S phase. S phase . DNA synthesis replicates the genetic material. Each chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids. G2 phase . Metabolic changes assemble the cytoplasmic materials necessary for mitosis and cytokinesis. M phase . A nuclear division (mitosis) followed by a cell division (cytokinesis). The period between mitotic divisions - that is, G1, S and G2 - is known as interphase
- 7. Prophase
- 8. Prophase Prophase occupies over half of mitosis. The nuclear membrane breaks down to form a number of small vesicles and the nucleolus disintegrates. A structure known as the centrosome duplicates itself to form two daughter centrosomes that migrate to opposite ends of the cell. The centrosomes organise the production of microtubules that form the spindle fibres that constitute the mitotic spindle . The chromosomes condense into compact structures. Each replicated chromosome can now be seen to consist of two identical chromatids (or sister chromatids ) held together by a structure known as the centromere .
- 10. METAPHASE
- 12. ANAPHASE
- 14. TELOPHASE
- 16. CYTOKINESIS The final cellular division to form two new cells. In plants a cell plate forms along the line of the metaphase plate; in animals there is a constriction of the cytoplasm. The cell then enters interphase - the interval between mitotic divisions
