Bio F4 Cell Organel
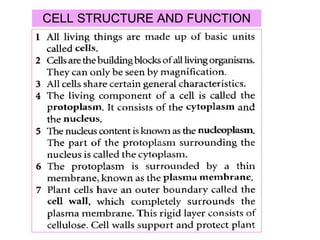
- 1. CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
- 2. CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
- 4. PLANT CELL 1. What organelles can be seen under the light microscope and electron microscope? If examined under light microscope If examined by electron microscope Cell wall vacuole Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Chloroplast Rough endoplasmic reticulum Ribosome Nucleus Nuclear membrane Cell membrane Tonoplast Mitochondrion Golgi body Nucleolus Cell wall Vacuole Chloroplast Cell membrane Nucleus
- 6. STRUCTURE OF A TYPICAL PLANT CELL ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF A PLANT CELL A TYPICAL PLANT CELL Mitochond rion Tonoplast Nucleus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Plasma membrane Cell wall Golgi body Vesicle Chloroplast Cytoplasm Vacuole Cell wall
- 8. STRUCTURE OF A TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL Centriol Plasma membrane Mitochondrion Vesicle (containing secretions) A TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ELECTRON MICROGRAPH OF AN ANIMAL CELL Nucleus Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Golgi body
- 9. CELL ORGANELLES Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus lysosome mitochondrion chloroplast Cell wall Smooth ER vacuole
- 14. PROTEIN TRANSPORT IN CELL NUCLEUS Rough endoplasmic reticulum Plasma membrane (Secretory) vesicle e Transport vesicle Golgi body cytoplasm Excretion of substances produced in cell Protein like enzymes are synthesized in ribosomes. Then they are transported in the lumen of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). At one end, the RER , having the proteins buds off forming transport vesicle. Transport vesicle moves to Golgi body, unites with it and forms part of the Golgi body. In that way the proteins / enzymes are contained in the Golgi body where it is further processed, modified and finally packed off as secretory vesicle. The secretory vesicle containing secretions moves to plasma membrane, unite with it and thereby eliminates the secretions.
- 15. FUNCTION OF ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
- 17. CELL MEMBRANE- THE FLUID MOSAIC HYPOTHESIS O 2 , CO 2 Glukosa ion (Membentuk tapak penerima dengan protein pembawa) The lipid molecules are moving to make the bilayer fluid in nature. Cholesterol in the membrane helps to make the ‘lipid fluid’ more viscous in the cell membranel Allows small, nonpolar and fat soluble molecules to pass through it eg. water, fatty acid, gas The carrier and channel proteins help to move polar/ charged and bigger molecules through the membrane eg. ions, glukose, amino acid Explain the fluid – mosaic hypothesis of the cell membrane. polysaccharides Channel in protein molecule Phospholipid bilayer Protein molecules scattered throughout and moving in / outside the menbrane forming mosaic structure External of the cell Internal of the cell cytoplasm protein cholesterol Carbohydrate(sugar) Channel protein
- 18. CELL MEMBRANE cytoplasm Plasma membrane based on fluid – mosaic hypothesis
- 20. EXTENSIVE DISTRIBUTION OF SOME CELL ORGANELLES
- 21. EXTENSIVE DISTRIBUTION OF CELL ORGANELLS
- 22. DIFFERENT CONCENTRATION / FREQUENCY OF ORGANELLES IN BODY CELL Why are there many mitochondria found in a sperm cell ? Name other cells in animal that possess a large number of mitochondria. Give example of cells that contain a large number of the following organelles . Explain why. a) Chloroplast b) Golgi body c) Ribosome Mitochondrion Nucleus Mitochondrion Mitochondria in a sperm cell Electron Micrograph of a sperm cell showing mitochondria in a neck region of the cell. head neck tail
- 23. CELL ORGANELLES Nucleus Cell membrane Mitochondrion Chloroplast Rough endoplasmic reticulum Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Ribosome structure function It contains 1.………… and 2……………… surrounded by 3…………….………………… Chromosomes consists of DNA that carries 5.………………… for the inheritance. It controlls 23…………… of cell Consists of membrane system which is very much folded in the cytoplasm. It contains 6. …..………. on the outer surface. Its function is 7…………………….. ………………………. It is located on the surface of RER . Its function is in the synthesis of 8…………………… in cell. It has the same structure as RER but contains no 9…………….. on the surface. The function of SER is 10..……………………… …. ……. The Fluid Mosaic Hypothesis Bilayer of 11………………….. which is mobile and contains 12…………………molecules scattered throughout in it. It is a 13…………. …. layered structure containing grana (that contains 14……….……) and 15……..………… (which contains 16……… .) for photosynthesis Receives 17 ..….. ......like enzymes, 18…………………, packing them to form 19….……… It is bounded by two layers of 20…………… The inner membrane is folded in the foem of stacks. Mitochondrion is considered as 21………… of a cell because its function is to generate energy for cell metabolism. Active cells like 22…………. contains a lot of mitochondrion 24 …….. Reaction takes place in the stroma Light reaction takes place in the 25…………
- 24. CELL STRUCTURE AND ORGANELLES mitochondrion Nucleus H J A G C B D F E K
- 25. INVESTIGATING CELL STRUCTURE Task : Design an experiment to investigate the structure and shape of the onion epidermal cell by refering to the steps shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 1. Write down the hypothesis of the experiment. 2. Suggest the technique used in the experiment. 3. How are you going to record the results? 4. What is the purpose of using iodine drop in the experiment ? Water droplet Scale leaf of onion scalpel Epidermis of onion Forceps Epidermal tissue Water droplet Mounting needle Cover slip slide iodine droplet Filter paper
- 28. PENYEDIAAN SLAID SEL PIPI MANUSIA Differentiate between plant and animal cell. What is the purpose of using blue methylene solution in the exp.? dropper Distilled water Glass slide Tooth pick Mounting needle Cover slip Methylene blue Filter paper
- 31. CELL ORGANISATION Binary fission in Amoeba sp. Cell organisation in multicellular organism
- 34. VARIETY OF CELLS
- 35. EPITHELIAL TISSUE SPECIALISED CELL Egg cell ( ovum ) is being fertilised by the sperms. Only a single sperm is capable of penetrating the ovum. Epithelial cells in the renal tubules ( of kidney) lumen Epithelial cells form a layer of epithelial tissue in lining of the renal tubules.
- 36. HUMAN CELLS AND FUNCTION
- 37. SPECIALISED CELLS Cross section of a dicot. leaf showing various cell types in the leaf. Nerve cell ( neurone) White blood cells- agranulosite CARDIAC MUCLE Skletal muscle Differentiate between an afferent neurone and an efferent neurone Describe the organisation of cells in a leaf. MUSCLE TISSUE SMOOTH MUSCLE Describe the location and function of each muscle type. Describe the structure and roles of each type of blood cells Impulse Granulosite Red blood cell BLOOD
- 38. TYPES OF EPITHELIAL TISSUES
- 40. CONNECTIVE TISSUES Darah Rawan
- 43. ORGANS AND THEIR FUNCTION
- 44. ORGANS FUNCTION
- 45. ORGANS FUNCTION
- 46. ORGANS FUNCTION
- 48. PEMBAHAGIAN SEL MITOSIS A B C
- 50. ORGANS AND SYSTEMS IN PLANTS
- 51. PLANT CELLS p Q R S T U ……………… 1 …………… ....2 ……………… 3 ......................4 …………… ....5
- 56. HOMEOSTASIS What? Maintainance of a relatively constant internal environment Internal environment The physical and chemical factors that affect the physiology and metabolism of the body pH temperature Osmotic pressure Glucose concentration comprises Blood plasma Tissue / interstitial fluid Why it must be kept constant? An organism may have greater environmntal freedom and greater geographycal range Salt concentration or salinity Their living is not very much restricted by temperature Water supply Saline conditions And therefore better access to food water shelter Constant environment means Constant or small changes in the internal environment i.e within the tolerance of the body How it is achieved ? negative feedback mechanism What are the consequences if there is no homeostasis or negative feedback mechanism? through A mechanism that slows down a process when there is overproduction of a substance and speeds up the process when there is underproduction of the substance. normal normal Above normal Below normal increasing decreasing Negative feedback Negative feedback Chemical or nervous coordination or There is a positive feedback , instead Positive feedback tends to deviate further the process from normal and finally will destroy or cause harmful effect to the system. Chemical / hormonal nervous examples Regulation of blood glucose by insulin and glucagon Regulation of body temperature during cold and hot days. Blood pressure Enable body cells to function optimally
- 58. TEMPERATURE REGULATION Erector muscles relax, hairs on on skin tend to fall down/ lowered, thus trapping thin layer of air for less insulation of body heat. Erector muscles contract, hairs on skin is raised and traps thick layer of air for insulating body heat
- 61. REGULATION OF BODY TEMPERATURE
- 63. THE PANCREAS 1. Explain the function of pancreas as an endocrine organ as well as exocrine organ. 2. Name hormones and hydrolytic enzymes produced by pancreas. 3. How are those hormones and enzymes from pancreas are transported to their target organs?
- 65. REGULATION OF BLOOD OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE (regulation of breathing)