Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Pathogenesis, Clinical Features & Management
- 1. NOOR AFIFAH BT ABD RAHMAN AZIZAH BT MAJID MOHD NAQIB B BAJURI DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS
- 2. Definition • Deep vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in one of the deep veins of the body, usually in the leg
- 3. • 2 types of VT – Superficial • Occur in tortuous dilated varicose vein ; pregnancy – Deep • may be referred to as proximal DVT or distal DVT. • Occasionally, DVT also occurs in the veins of the upper extremities. • DVT can occur spontaneously without known underlying cause (idiopathic thrombosis) or after provoking events, such as trauma, surgery or acute illness (provoked thrombosis).
- 4. EPIDEMIOLOGY • Untreated Proximal DVT – 30-50% risk PE – 12-15% mortality • Untreated Proximal DVT – 30-50% risk PE – 12-15% mortality • Treated DVT – <8% risk PE – Mortality <2%
- 5. RISK FACTORS • Principal Risk Factors – Immobilization – Trauma – Surgery – Infection – Post-partum period • Other Factors – Age – Obesity – Malignancy – Previous VTE – Varicose Veins – Dehydration – smoking – Hormonal Therapy
- 6. SFJ SPJ
- 7. ETIOLOGY • DVT usually originates in the lower extremity venous level ,starting at the calf vein level and progressing proximally to involve popliteal ,femoral ,or iliac system. .80 -90 % pulmonary emboli originates here .
- 8. Virchow triad • More than 100 years ago, Virchow described a triad of factors of • venous stasis, • endothelial damage, and • hypercoagulable state
- 9. DVT: Pathogenesis Clinical features Azizah Binti Majid 027653
- 10. More than 100 years ago, Virchow described a triad of factors of venous stasis, endothelial damage, and hypercoagulable state Virchow triad
- 13. • deficiencies of protein ‘S, • ’ protein ‘C,’ and • antithrombin III.Inherited disorders of coagulation • nephrotic syndrome results in urinary loss of antithrombin III, this diagnosis should be considered in children presenting with thromboembolic disease • Antiphospholipid antibodies accelerate coagulation and include the lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies. Acquired disorders of coagulation
- 14. The nidus for a clot is often an intimal defect RBC, WBC, Platelets, and Fibrin adhere (stick together) to form a clot (thrombus.) The thrombus enlarges as blood products accumulate forming a large clot that occludes the vein lumen. When a clot forms on an intimal defect, the coagulation cascade promotes clot growth proximally. Thrombus can extend from the superficial veins into the deep system from which it can embolize to the lungs. Clinical Pathophysiology
- 15. Two different types of thrombus can form: • Arterial thrombus (white thrombus) • Venous thrombus (red thrombus) Arterial and venous thrombi differ in composition and appearance. Arterial thrombi are typically composed mainly of platelet aggregates, giving the appearance of ‘white thrombi’. Venous thrombi largely consist of fibrin and red blood cells so are known as ‘red thrombi’. Cont…
- 16. Opposing the coagulation cascade is the endogenous fibrinolytic system. After the clot organizes or dissolves, most veins will recanalize in several weeks. Residual clots retract as fibroblasts and capillary development lead to intimal thickening. Venous hypertension and residual clot may destroy valves, leading to the postphlebitic syndrome- a state characterized by edema,pain, and skin discoloration most often as a complication of DVT- which develops within 5- 10 years Cont…
- 17. Edema, sclerosis, and ulceration characterize this syndrome, which develops in 40-80% of patients with DVT. patients also can suffer exacerbations of swelling and pain, probably as a result of venous dilatation and hypertension Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a serious complication of DVT. Many episodes of pulmonary embolism go unrecognized, and at least 40% of patients with DVT have clinically silent PE. Cont…
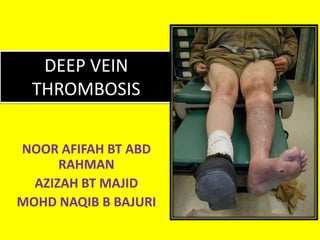
- 18. Clinical feature of DVT and PE DVT • Swelling of the leg • Pain or tenderness in the leg; the pain is usually in 1 leg and may only be present when standing or walking • Skin that is warm to the touch in the leg • Red or discolored skin • Swelling with pitting oedema • Swelling below knee in distal deep vein thrombosis and up to groin in proximal deep vein thrombosis • Superficial venous dilatation • Cyanosis can occur with severe obstruction • Positive Homan’s Sign-pain on forced dorsiflexion of the foot when the leg is raised • Low Grade Fever • Unequal Leg Measurements??? • Pallor- Phlegmasia Alba Dolens • Cyanosis-Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens PE • Unexplained shortness of breath • Chest pain and/or palpitations • Anxiety and/or sweating • Hemoptysis • Fever • Fatigue and/or fainting • tachycardia (common), • tachypnea • Massive Emboli- Shock, Pallor, Severe Dyspnea, Crushing Chest Pain Not all people with DVT have signs or symptoms If the inferior vena cava is involved – lower extremities edematous and cyanotic If the superior vena cava is involved – upper extremities, back, neck and face show signs
- 19. • Phlegmasia Alba Dolens • known as milk leg or white leg) • deep vein thrombosis that progresses to total occlusion of the deep venous system. • sudden (acute) process. • The leg, then, must rely on the superficial venous system for drainage • Phlegmasia Cerulea Dolens • painful blue edema, • occlusion of the superficial venous system, thereby preventing all venous outflow from the extremity • Sudden occurrence - edematous cyanotic painful leg. • May result in gangrene and high risk for massive pulmonary embolism
- 20. PE • From the thrombi originating in the deep venous system of the lower extremities • Rarely, they may originate in the pelvic, renal, or upper extremity veins and the right heart chambers. • Large thrombi lodge at the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery or the lobar branches, accumulate and may cause haemodynamic compromise. • Smaller thrombi continue distally, occluding smaller vessels in the lung periphery. These are more likely to produce pleuritic chest pain by initiating an inflammatory response adjacent to the parietal pleura. • Most pulmonary emboli are multiple, and the lower lobes are involved more commonly than the upper lobes
- 21. The Wells clinical prediction guide incorporates risk factors, clinical signs, and the presence or absence of alternative diagnoses
- 22. Investigation
- 23. • D-dimer measurement • Duplex ultrasound examination after raised D-dimer • Filling defects in flow and a lack of compressibility indicate the presence of a thrombosis
- 24. • Ascending venography (rarely) • Pulmonary embolism is diagnosed by ventilation–perfusion scanning shows mismatched defects • Computerised tomographic (CT) scanning of the pulmonary arteries, which can show filling defects in pulmonary arteries • Pulmonary angiography (rarely)
- 25. Management
- 26. • low molecular weight heparin • Warfarin – started at a dose of 10 mg on day one, 10 mg on day two and 5 mg on day three • Thrombolysis – Iliac vein thrombosis – tissue plasminogen activator administered directly into thrombus via popliteal vein or by direct puncture in groin • stent grafting for iliac vein compression syndrome • Thrombectomy (rarely)
- 27. • pulmonary emboli – Anticoagulation – severe right heart strain & shortness of breath need for fibrinolytic treatment
