HPV Infection Classification, Transmission, Replication Cycle
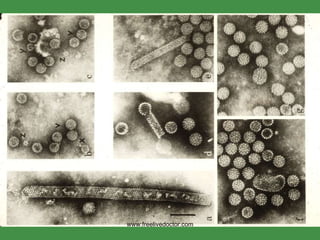
- 5. HPV and skin warts www.freelivedoctor.com
- 7. Clinical genital tract and mucosal HPV’s www.freelivedoctor.com
- 9. HPV16 genome Genomic map of HPV-16. The genome is a double-stranded circular DNA molecule of 7904 base pairs. Transcription occurs in a clockwise manner; the only transcriptional promoter presently mapped for HPV-16 is designated P97. The open reading frames deduced from the DNA sequence are designed E1 to E7, L1, and L2 and are indicated outside of the circular genome. AE and AL represent the early and late polyadenylation sites. The viral long control region (LCR) contains transcriptional and replication regulatory elements. www.freelivedoctor.com
- 10. Papilloma virus gene function www.freelivedoctor.com
- 11. Papillomavirus replication and differentiation of the epidermis Differentiation of normal cutaneous squamous epithelium and papillomaviral activities in productively infected benign lesions. The various epithelial strata and the host-differentiation, stage-specific, gene-expression profile are indicated in the left and center panels. www.freelivedoctor.com
- 12. Replication cycle of a papillomavirus. To establish a wart or papilloma, the virus must infect a basal epithelial cell. Our knowledge is limited about the initial steps in the replication cycle such as attachment (1), uptake (2), endocytosis (3), and transport to the nucleus and uncoating of the viral DNA (4). Early-region transcription (5), translation of the early proteins (6), and steady-state viral DNA replication (7) all occur in the basal cell and in the infected suprabasal epithelial cell. Events in the viral life cycle leading to the production of virion particles occur in the differentiated keratinocyte: vegetative viral DNA replication (8), transcription of the late region (9), production of the capsid proteins L1 and L2 (10), assembly of the virion particles (11), nuclear breakdown (12), and release of virus (13). (From Fields Virology, 4th ed, Knipe & Howley, eds, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2001, Fig. 65-6.) Papillomavirus replication www.freelivedoctor.com
- 14. Cervical HPV infection Natural history of cervical HPV infection. Approximate number of US cases of the different categories of infeciton. Most subclinical infections and low-grade dysplasias regress spontaneously. Even high-grade dysplasia has some potential to regress spontaneously. Infection with HPV-16 or HPV-18 represents a minority of the subclinical infections and low-grade dysplasias, whereas they represent most of the high grade dysplasias and invasive cancers. www.freelivedoctor.com
- 15. Progression from benign cervical condylomatous liesion to invasive carcinoma. Infection by oncogenic HPV types, especially HPV16, may directly cause a benign condylomatous lesion, low-grade dysplasia, or sometimes even an early high-grade lesion. Carcinoma in situ rarely occurs until several years after infection. It results from the combined effects of HPV genes, particularly those encoding E6 and E7, usually after integration of the viral DNA into the host DNA and a series of genetic and epigenetic changes in cellular genes. HSIL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion, LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. HPV and cervical dysplasia www.freelivedoctor.com
- 16. Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. A: Histologic section showing koilocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm and parakeratosis (H&E, *234). B: The darkly stained nuclei contain papillomavirus capsid antigen. [Immunoperoxidase stained with genus-specific antiserum (H&E, *234)]. C: Cervical smear. The squamous epithelial cells are rounded. They occur in clumps and display koilocytic changes (Papanicolaou stain; H&E *375). D: Cervical smear. The darkly stained nuclei contain papilloamavirus capsid antigen. (Immunoperoxidase staind with genus-specific antiserum; H&E, *750). Cervical dysplasia www.freelivedoctor.com
- 17. Papanicolaou stain of the exfoliated cervicovaginal squamous epithelial cells showing the perinuclear cytoplasmic vacuolization, termed koilocytosis (vacuolated cytoplasm), which is characteristic of human papillomavirus infection. Papillomavirus cytology www.freelivedoctor.com
- 18. Correlation between HPV type, integration, and histology www.freelivedoctor.com