Group 3 measures of central tendency and variation - (mean, median, mode, range standard deviation and variance)
- 1. Group 3
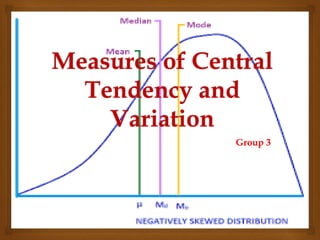
- 2. Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Central tendency: indicates where the center of the distribution tends to be (88% grade) (compact, disperse) Measures of central tendency answers whether the scores are generally high or general low.
- 3. Measures of Central Tendency and Variation Average Height is 6’4” Average Height is 5’4”
- 4. Use of Central Tendency Simplification: one number Prediction: Predict other scores Chairs, Classrooms, Books, School needs. Determining which off central tendency to use depends on: Scale of measurement Nominal, Ordinal, interval, Ratio (NOIR) Shape of Distribution Skew Kurtosis Average Children: 2.3
- 5. Prepared by : Mrs. Analie M. Sunga
- 7. Median is what divides the scores in the distribution into two equal parts. Fifty percent (50%) lies below the median value and 50% lies above the median value. It is also known as the middle score or the 50th percentile. MEDIAN
- 8. The median is a single value from the data set that measures the central item in the data. This single value is the middlemost or most central item in the set of scores. Half of the scores lie above this point and other half lie below it. MEDIAN
- 9. MEDIAN OF UNGROUPED DATA 1. Arrange the scores(from lowest to highest or highest to lowest). 2. If the data has odd numbered items, the median is middle item of the array. However, if it has even number of items, the median is the average of the two middle items. MEDIAN
- 10. X (score) 19 17 16 15 10 5 2 Example 1: Find the media score of 7 students in an English class.
- 11. x(score) 30 19 17 16 15 10 5 2 Example 2: Find the media score of 8 students in an English class. x= 16 +15 2 x= 15.5
- 12. MEDIAN OF GROUPED DATA FORMULA: 𝑥 = 𝐿B + 𝑛 2 − 𝑐𝑓< 𝑓𝑚 × c.i MEDIAN 𝒙 = median value MC = median class is a category containing 𝑛 2 LB = lower boundary of the median class (MC) cf< = cumulative frequency before the median class if the scores are arranged from lowest to highest value Fm = frequency of the median class c.i = size of the class interval n= number of scores
- 13. 1. Complete the table for <cf. 2. Get 𝑛 2 of the scores in the distribution so that you can identify MC. 3. Determine LB, cfp, fm and c.i. 4. Solve the median using the formula. Steps in Solving Median for Grouped Data
- 14. X F <cf 10-14 5 5 15-19 2 7 20-24 3 10 25-29 5 15 30-34 2 17 35-39 9 26 40-44 6 32 45-49 3 35 50-54 5 40 n=40 Example: Scores of 40 students in a science class consist of 60 items and they are tabulated below. The highest score is 54 and the lowest score is 10.
- 15. 𝑛 2 = 40 2 = 20 (The category containing 𝑛 2 is 35-39) LB= 34.5 (Lower Limit of the MC = 35) Cf<= 17 fm=9 c.I = 5 𝑥 = 𝐿B + 𝑛 2 − 𝑐𝑓< 𝑓𝑚 × c.i = 34.5 + 20 − 17 9 × 5 = 34.5 + 15 9 𝑥 = 36.17 𝑥 = 𝐿B + 𝑛 2 − 𝑐𝑓< 𝑓𝑚 × c.i
- 17. Mode or Modal Score is the measure of central tendency that identifies the category or score that occurs the most frequently within the distribution of data
- 18. Classification of Mode Unimodal- is a distribution of scores that consist of only one mode. Bimodal- is a distribution of scores that consists of two modes. Trimodal- is a distribution of scores that consist of three modes or multimodal a distribution of scores that consists of more than two modes.
- 19. Example: Score of 10 students in Section A,B and C ( Ungrouped Data) A B C 25 25 25 24 24 25 24 24 25 20 20 22 20 18 21 20 18 21 16 17 21 12 10 18 10 9 18 7 7 18
- 20. Sample (Grouped Data) x f 10-14 5 15-19 2 20-24 3 25-29 5 30-34 2 35-39 9 40-44 6 45-49 3 50-54 5 N=40 Scores of 40 students in a students in a science class consist of 60 items and they are tabulated below:
- 21. Terms Lb= Lower boundary of the modal class Modal Class (MC)= is a category containing the highest frequency D1= difference between the frequency of the modal class and the frequency above it, when the scores are arranged from lowest to highest.
- 22. D2= difference between the frequency of the modal class and the frequency below it, when the scores are arranged from lowest to highest. C.i size of class interval = LB + d1 d1 + d2 𝑥 𝐶. 𝑖X̂
- 23. Range It is the difference between the lowest and highest values. Example: In 4,6,9,3,7 the lowest value is 3, and the highest is 9. Solution: 9 - 3 = 6
- 24. Standard deviation It is a number used to tell how measurements for a group are spread out from the average (mean) or expected value. Low standard deviation means that most of the numbers are close to the average. High standard deviation means that the numbers are more spread out .
- 25. Standard deviation for ungrouped data SD= Standard deviation ∑= sum of X= each value in the data set X= mean of all values in the data set n= number of value in the data set
- 26. How to Calculate the Standard Deviation for Ungrouped Data 1.Find the Mean. 2.Calculate the difference between each score and the mean. 3.Square the difference between each score and the mean.
- 27. How to Calculate the Standard Deviation for Ungrouped Data 4.Add up all the squares of the difference between each score and the mean. 5.Divide the obtained sum by n – 1. 6.Extract the positive square root of the obtained quotient.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31. How to Calculate the Standard Deviation for Grouped Data 1.Calculate the mean. 2.Get the deviations by finding the difference of each midpoint from the mean. 3.Square the deviations and find its summation. 4.Substitute in the formula.
- 32. Find the standard deviation 100 99 106 86 104 113 103 98 105 95 79 101 92 103 91 124 89 100 105 87 110 122 95 118 96 104 108 84 113 99 93 109 102 106 80 116 90 111 101 115 110 109 78 88 107 114 75 127 102 72
- 33. How to get class intervals Class Limits/ Interval Range= Highest – Lowest = 127- 72 = 55
- 34. How to get number of class Number of Class= ( Range ÷ Class Size) + 1 = (55 ÷ 5 ) + 1 = 12 Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74
- 35. How to get midpoint Midpoint(X)= (upper limit +lower limit) ÷ 2 = (125 + 129) ÷ 2 = 127 Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72
- 36. Frequency Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequency 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50
- 37. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequency 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035
- 38. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequency 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035
- 39. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequency 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35
- 40. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequenc y 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035 X 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 Mp- X 76.6 5 71.6 5 66.6 5 61.6 5 56.6 5 51.6 546. 65 41.6 5 36.6
- 41. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequenc y 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035 X 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 (mp- x)² 587.22 5133.7 2 4442.2 2 3800.7 2 2667.7 2 2176.2 2 1734.7 2 1343.7 2 1001.7 Mp- X 76.6 5 71.6 5 66.6 5 61.6 5 56.6 5 51.6 546. 65 41.6 5 36.6
- 42. Class Limits/ Interval 125- 129 120- 124 115- 119 110-114 105- 109 100- 104 95- 99 90- 94 85-89 80-84 75- 79 70- 74 Midpoint 127 122 117 112 107 102 97 92 87 82 77 72 Frequenc y 1 2 3 6 8 10 6 4 4 2 3 1 N= 50 fX 127 244 351 672 856 1020 582 368 348 164 231 72 ∑fX= 5035 X 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 50.35 (mp- x)² 587.22 5133.7 2 4442.2 2 3800.7 2 2667.7 2 2176.2 2 1734.7 2 1343.7 2 1001.7 Mp- X 76.6 5 71.6 5 66.6 5 61.6 5 56.6 5 51.6 546. 65 41.6 5 36.6
- 43. (mp- x)² 587.22 5133.7 2 4442.2 2 3800.7 2 2667.7 2 2176.2 2 1734.7 2 1343.7 2 1001.7 F(mp-x) ² 5875.22 10267.45 13326.67 22804.34 25673.78 26677.23 13057.34 6938.89 5372.89 2003.44 2130.67 468.72 ∑f(mp-x) ² = 134596.6 SD= √134596.6 50-2 = √ 134596.6 49 = √2746.86 = 52.41
- 44. Variance is the square of the standard deviation. It is a measure of how dispersed or spread out the set is, something that the “average” (mean or median) is not designed to do.
- 46. How to Calculate the Variance for Ungrouped Data 1.Find the Mean. 2.Calculate the difference between each score and the mean. 3.Square the difference between each score and the mean. 4.Add up all the squares of the difference between each score and the mean. 5.Divide the obtained sum by n – 1
- 51. How to Calculate the Variance for Grouped Data 1.Calculate the mean. 2. Get the deviations by finding the difference of each midpoint from the mean. 3.Square the deviations and find its summation. 4.Substitute in the formula.
- 52. Find the variance s²= √134596.6 50-2 s² = √ 134596.6 49 s² = 2746.86
- 53. Jonathan Profeta Analie Sunga Reymart Tabelisma Valerio, Pammelle Group 3