3122008 tlc
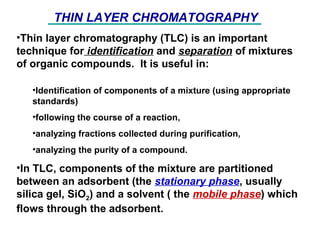
- 1. •Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is an important technique for identification and separation of mixtures of organic compounds. It is useful in: •Identification of components of a mixture (using appropriate standards) •following the course of a reaction, •analyzing fractions collected during purification, •analyzing the purity of a compound. •In TLC, components of the mixture are partitioned between an adsorbent (the stationary phase, usually silica gel, SiO2) and a solvent ( the mobile phase) which flows through the adsorbent. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
- 2. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY In TLC, a plastic, glass or aluminum sheet is coated with a thin layer of silica gel. A very small amount of a solution of the substance to be analyzed is applied in a small spot with a capillary tube, ~1cm from the bottom of the TLC plate The TLC is developed in a chamber which contains the developing solvent (the mobile phase). A truncated filter paper placed in the chamber serves to saturate the chamber with mobile phase. A B CU D A B CU filter paper D
- 3. As the mobile phase rises up the TLC plate by capillary action, the components dissolve in the solvent and move up the TLC plate. Individual components move up at different rates, depending on intermolecular forces between the component and the silica gel stationary phase and the component and the mobile phase. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY The stationary phase is SiO2 and is very “polar”. It is capable of strong dipole-dipole and H-bond donating and accepting interactions with the “analytes” (the components being analyzed). More polar analytes interact more strongly with the stationary phase in move very slowly up the TLC plate. By comparison, the mobile phase is relatively nonpolar and is capable of interacting with analytes by stronger London forces, as well as by dipole- dipole and H-bonding. More nonpolar analytes interact less strongly with the polar silica gel and more strongly with the less polar mobile phase and move higher up the TLC plate. http://www.instructables.com/id/EW1YDCYF4REC0IU/
- 4. Once the solvent is within ~1-2 cm of the top of the TLC sheet, the TLC is removed from the developing chamber and the farthest extent of the solvent (the solvent front) is marked with a pencil. The solvent is allowed to evaporate from the TLC sheet in the hood. The spots are visualized using a UV lamp. A fluorescent compound, usually Manganese- activated Zinc Silicate, is added to the adsorbent that allows the visualization of spots under a blacklight (UV254). The adsorbent layer will fluoresce light green by itself, but spots of analyte quench this fluorescence and appear as a dark spot. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY http://orgchem.colorado.edu/hndbksupport/TLC/TLCprocedure.html
- 5. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY - Visualization As the chemicals being separated may be colorless, several methods exist to visualize the spots: • Visualization of spots under a UV254 lamp. The adsorbent layer will thus fluoresce light green by itself, but spots of analyte quench this fluorescence. • Iodine vapors are a general unspecific color. • Specific color reagents exist into which the TLC plate is dipped or which are sprayed onto the plate. • Once visible, the Rf value of each spot can be determined Chromatogram of 10 essential oils, Stained with vanillin reagent.
- 6. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Calculation of Rf’s The Rf is defined as the distance the center of the spot moved divided by the distance the solvent front moved (both measured from the origin) A B CU x xx x Solvent Front Origen Distance solvent migrated = 5.0 cm Distance A migrated = 3.0 cm Distance B migrated = 2.0 cm Distance C migrated = 0.8 cm 0.8 cm 3.0 cm Rf (A) = Rf (B) = Rf (C) = Rf (U1) = Rf (U2) = 2.0 cm 5.0 cm = 0.40 = 0.60 = 0.16 = 0.60 = 0.16 3.0 cm 5.0 cm 0.8 cm 5.0 cm 3.0 cm 5.0 cm 0.8 cm 5.0 cm D x Rf (D) = = 0.804.0 cm 5.0 cm 4.0 cm
- 7. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Calculation of Rf’s The Rf is defined as the distance the center of the spot moved divided by the distance the solvent front moved (both measured from the origin) A B CU x xx x Solvent Front Origen Distance solvent migrated = 5.0 cm Distance A migrated = 3.0 cm Distance B migrated = 2.0 cm Distance C migrated = 0.8 cm 0.8 cm 3.0 cm Rf (A) = Rf (B) = Rf (C) = Rf (U1) = Rf (U2) = 2.0 cm 5.0 cm = 0.40 = 0.60 = 0.16 = 0.60 = 0.16 3.0 cm 5.0 cm 0.8 cm 5.0 cm 3.0 cm 5.0 cm 0.8 cm 5.0 cm D x Rf (D) = = 0.804.0 cm 5.0 cm 4.0 cm
- 8. Rf values can be used to aid in the identification of a substance by comparison to standards. The Rf value is not a physical constant, and comparison should be made only between spots on the same sheet, run at the same time. Two substances that have the same Rf value may be identical; those with different Rf values are not identical. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY – Rf’s
- 9. Absorption of Solutes The adsorption strength of compounds increases with increasing polarity of functional groups, as shown below: -CH=CH2, -X, -OR, -CHO, -CO2R, -NR2, -NH2, -OH, -CONR2, -CO2H. (weakly adsorbed) (strongly adsorbed) (nonpolar) (more polar) THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY – Rf’s Elution Strength of Mobile Phase (ε) Elution strength is generally considered to be equivalent to polarity. A solvents elution strength depends on Intermolecular Forces between the solvent and the analytes and between the solvent and the stationary phase. A more polar (or more strongly eluting solvent) will move all of the analytes to a greater extent, than a less polar, weakly elution solvent. For example, the elution strength of hexane is very low; ε = 0.01. the elution strength of ethyl acetate is higher; ε = 0.45 the elution strength of ethanol is even higher; ε = 0.68
- 10. Solvent MF MW Bp ( o C) Density (g/mL) Hazards* Dipole Elution Stength (ε) Hexane CH3(CH2)4CH3 C6H14 86.17 68.7 0.659 Flammable Toxic 0.08 0.01 Toluene C6H5CH3 C7H8 92.13 110.6 0.867 Flammable Toxic 0.31 0.22 Diethyl ether CH3CH2OCH2CH3 C4H10O 74.12 34.6 0.713 Flammable Toxic, CNS Depressant 1.15 0.29 Dichloromethane CH2Cl2 CH2Cl2 84.94 39.8 1.326 Toxic, Irritant Cancer suspect 1.14 0.32 Ethyl Acetate CH3CO2CH2CH3 C4H8O2 88.10 77.1 0.901 Flammable Irritant 1.88 0.45 Acetone CH3COCH3 C3H6O 58.08 56.3 0.790 Flammable Irritant 2.69 0.43 Butanone CH3CH2COCH3 C4H8O 72.10 80.1 0.805 Flammable Irritant 2.76 0.39 1-Butanol CH3CH2CH2CH2OH C4H10O 74.12 117.7 0.810 Flammable Irritant 1.75 0.47 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH C3H8O 60.09 82.3 0.785 Flammable Irritant 1.66 0.63 Ethanol CH3CH2OH C2H6O 46.07 78.5 0.789 Flammable Irritant 1.70 0.68 Methanol CH3OH CH4O 32.04 64.7 0.791 Flammable Toxic 1.7 0.73 Water HOH H2O 18.02 100.0 0.998 1.87 >1 Solvent Properties and Elution Strengths
- 11. Elution Strength of Mixed Solvents The elution strength of the mixture is assumed to be the weighted average of the elution strengths of the components: εo net = εo A (mole % A) + εo B (mole % B) where: mole % A = (moles A) / (moles A + moles B) Thus, to determine the εo net of a solvent mixture, the molar ratio of the solvents must first be calculated. For example, the εo net of a solvent mixture prepared from 1.0 mL of ethyl acetate plus 9.0 mL of hexanes is calculated as shown below: εo net = εo EtOAc [(moles EtOAc)/(moles EtOAc+moles hexane)] + εo hexane [(moles hexane)/(moles EtOAc+moles hexane)] where: moles EtOAc = [(volume EtOAc) (density EtOAc)] / [molecular weight of EtOAc] thus: εo net = {0.45[(1.0mLEtOAc)(0.902g/mL)/(88.11g/mole)]+0.01[(9.0mLhexane) (0.659g/mL)/86.18g/mole)]} {(1.0 mLEtOAc)(0.902g/mL)/88.11g/mole) + (9.0 mLhexane)(0.659g/mL)/86.18g/mole)} and εo net = 0.067
- 12. Resolution The separation between two analytes on a chromatogram can be expressed as the resolution, Rs and can be determined using the following equation: Rs = (distance between center of spots) (average diameter of spots) In TLC, if the Rs value is greater than 1.0, the analytes are considered to be resolved. x x
- 13. Improving Resolution: For two closely migrating components, optimum resolutions are usually obtained when the Rf’s of both compounds are between 0.2 and 0.5 * To Improve Rs, change the elution strength of the solvent to optimize Rf’s • change εo net (= in capacity factor), all compounds will be effected similarly. • Alter the composition of the solvent system so that the components affinity for the mobile phase vs. the solid phase are differentially changed (= change in selectivity). • Changing the chemical nature of the solvent system, such as changing a hydrogen bonding solvent to a solvent which cannot hydrogen bond to the analyte, is often the most effective. ** Improve Rs by decreasing the diameter of the analyte spots. This can be achieved by applying smaller and less concentrated spots. http://orgchem.colorado.edu/hndbksupport/ TLC/TLCprocedure.html
- 14. Optimize Rf’s
- 15. TLC – Stationary Phases www.vwr.com
- 16. www.vwr.com
- 18. TLC - Optimizing for column chromatography Optimum: 0.2 < Rf < 0.5