Learning theorymatrix
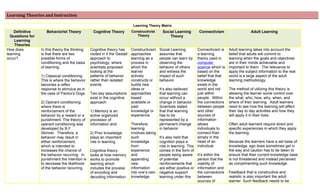
- 1. Learning Theories and Instruction Learning Theory Matrix Definitive Behaviorist Theory Cognitive Theory Constructivist Social Learning Connectivism Adult Learning Questions for Theory Theory Learning Theories How does In this theory the thinking Cognitive theory has Constructivism Social Learning Connectivism is Adult learning takes into account the learning is that there are two rooted in it the Gestalt approaches assumes that a learning belief that adults will commit to occur? possible forms of approach to learning as a people can learn by theory used in learning when the goals and objectives conditioning and the basis psychology, where process in observing the computer are in their minds achievable and of learning: scientists proposed which the behavior of others science which is important to them. The relevance to looking at the learner and witness the based on the apply the subject information to the real 1) Classical conditioning: patterns of behavior actively impact of such belief that that world is a large aspect of the adult This is where the behavior rather than isolated constructs or behavior. knowledge learning methodology. becomes a reflex events. builds new exists in the response to stimulus as in ideas or It’s also believed world and not The method of utilizing this theory is the case of Pavlov's Dogs. Two key assumptions approaches that learning can just within allowing the learner some control over exist in the cognitive based occur without a people. Within the what, who, how, why, when, and 2) Operant conditioning approach: available or change in behavior. the connections where of their learning. Adult learners where there is past Scientists stated between people need to see how the learning will affect reinforcement of the 1) Memory is an knowledge or that that learning and other their day to day activities and how they behavior by a reward or a active organized experience. has to be sources of will apply it in their lives. punishment. The theory of processor of represented by a information operant conditioning was information and; Therefore, permanent change allows Often adult learners require direct and developed by B.F. learning in behavior. individuals to specific experiences in which they apply Skinner. Therefore, a 2) Prior knowledge involves taking connect than the learning. behavior may result in plays an important such It’s also held that simply in the either reinforcement, role in learning. knowledge cognition plays a head of an Because the learners have a set base of which is intended to from role in learning. This individual. knowledge, ego does sometimes get in increases the chance of Cognitive theory experience comes in the form of the way and caution has to be taken to the behavior recurring. In looks at how memory and people being aware It’s within the ensure that their current knowledge base punishment the intention is works to promote appending of potential person that the is not threatened and instead perceived to decrease the likelihood learning which new reinforcements that viability of as complimenting such knowledge. of the behavior recurring. includes the process information are either positive or information and of encoding and into one’s own negative support the connections Feedback that is constructive and decoding information. knowledge. learning under this between realistic is also important the adult sources of learner. Such feedback needs to be
- 2. Learning Theories and Instruction structured and specific in order to be In theory. knowledge and meaningful. Constructivist connecting them learning, together as part Adults also need to participate in group learning is of integrating activities during the learning to move more personal the information them beyond understanding. Such group in that the into knowledge activities provide an opportunity to share process acts as the and reflect upon their learning resides within basis of experiences. the individual connectivism. and is unique to different Called "a people due to learning theory the diverse for the digital availability of age", knowledge Connectivism and has been used experience. to explain the effect technology has had on how people live, how they communicate, and how they learn (Siemens, 1995). What factors This theory believes that A major factor is Constructivist Factors that Several factors The influences to adult learning include influence behaviors can be related to how an theories influence such will affect the social relationships and the ability for learning? described scientifically individual processes propose that learning include the learning in adults to make new associations and without any impact on information. Similar knowledge is setting and connectivism develop new relationships as part of their emotions or physiological to whether the learner being actively circumstances in learning theory. learning experience. influences. This very visualizes an activity, constructed by which learning is The type and
- 3. Learning Theories and Instruction scientific approach analyzes the the individual taking place. The availability of the The perspective of the learner during contends that the results of variables to the task and knowing is people involved information in adult learning as to the value of the learning will remain or knowledge an adaptive also have influence which to network information and how it will complement consistent among different influence such process, which to include their will impact the their current knowledge or improve their subjects without variation learning organizes the existing direction and own circumstances influence how and based upon individual (http://web.cortland.e individual’s relationships and context of the whether the information will be preferences or responses. du/andersmd/learning own view. connections with learning incorporated in to the learners /cognitive.htm). One of the each other. outcome (Smith, knowledge. main beliefs of There is also the 2009). the expectations of Personal advancement, the ability to see constructivist each person as to It’s from the how the learning will help the learner theory is that what the variety of ways achieve a higher status in a job, secure people develop information offers of learning professional advancement, and stay and build can influence the through practice, ahead of competitors are also influence understanding effectiveness of personal the motivation and perspective of the from their own social learning. network, and learning resulting in the direct impact of personal and completion of the learning experience. subjective Lastly, the types of tasks affect and experiences. models are also an act as significant Lastly, cognitive interest (Harper & Learners bring influence. Whether factors that Meyer, 1998) or to learn for the sake of their own past the source of the influence learning or seek knowledge is an perspectives in information is a learning. additional dimension to how adult order to person, a machine learning takes place. connect what or media can also The concept is to be be considered to be includes the learned and types of social belief that what is already learning and learning is a known. influence the continual outcome of the process that learning situation lasts a lifetime (http://theelearning and has become coach.com/elearnin a part of daily g2-0/social-media- life. and-learning/) . Technology is also an influence to
- 4. Learning Theories and Instruction connectives learning theory. The type, development, and changes in the use of technology are changing how we make these connections and offer a wider variety of learning opportunities through connections. It’s from this form of learning that the importance of knowing and how to find the needed knowledge is becoming equally important (Siemens, 2005). What is the role of This theory subscribes to Cognitive theory Memory as it Memory is believed Prior knowledge Within the adult memory different facets memory? the premise that learning involves applies to this to be cognitive remixed to affect the significant of whether builds up over time from a understanding how theory states function under this current context. information is retained or not. The adult series of consistent and many pieces of that memory theory and is The connection often has attained a means in which to similar experiences. This information can be retention will believed that the between what learn how to learn and therefore be repeated method solidifies retained in short-term take place as ability to use information is aware of the necessity of remembering the information into memory before long as there symbols in learning offered and what
- 5. Learning Theories and Instruction knowledge and becomes information loss exists a and remembering is absorbed is and how to remember. Also, the social part of the person’s natural occurs, then how to connection is a key element to determined by element of remembering whether it is tendencies and behaviors transfer that memory between attaining and retain the cognitive names, working information, or data (Spence, 1937). into long-term pieces of the information. For process of facilitates the adult’s process of memory memory. The information. future use. It is the sorting and (http://www.infed.org/biblio/b- application of This concept is belief that humans connecting the learn.htm) cognitive theory in derived by don’t just respond new information this application is to connecting to stimuli, but to the existing develop learning so what is already interpret it which (Kim & Gil, that this transfer of known to what contributes towards 2007). memory takes place new learning (Bandura, (Chandler, & Sweller, information 1977). 1991). does to compliment or expand upon that original information. How does Involves generalization Transfer takes place By applying Occurs during the Connecting to Transfer of learning for adults is not transfer occur? from one stimulus to when a learner the information process of and adding automatic and must be facilitated. another (Skinner, 1953). connects the new into new observation and nodes and Coaching and other kinds of follow-up information to known problems and resulting growing the support are needed to help adult learners information. scenarios. application of the network. transfer learning into daily practice so information. that it is sustained. The pivotal role that making connections between past experiences and current problems plays in supporting transfer of learning is a centerpiece of common elements theory of transfer (Butterfield & Nelson, 1989). What types of The approaches include Methods include: Learning Methods include: Approaches Methods may include: learning are best tutorials, drill and practice, approaches include: explained by this behavioral simulations, -Debates include: -On the job training -Problem-Solving theory? and programmed -Role Playing -Tutorial Groups -Hands-on -Case Reviews instruction. An approach -Panels -Interviewing -Interviewing training -Debates that combines all these -Brainstorming -Conferencing -Conferencing -Compare & -Role Playing teaching strategies into -Peer Partner -Problem -Case Studies Contrast -Panels
- 6. Learning Theories and Instruction one "system" is called an -Learning Solving -Reflective -Panels -Brainstorming "integrated learning -Discussion -Case Studies Discussion -Brainstorming -Discussion system" -Laboratory Groups -Field Trips -Peer Partner -Structured Controversy (http://viking.coe.uh.edu/~i -Think, Pair, Share (http://olc.spsd. -Conducting Learning -Interviewing chen/ebook/et- -Cooperative sk.ca/de/pd/inst Experiments -Discussion -Conferencing it/behavior.htm) Learning Groups r/categ.html) -Simulations -Laboratory -Inquiry -Problem Solving -Games Groups -Reflective Discussion -Structured Overview -Demonstration -Storytelling -Cooperative -Computer Assisted Instruction -Lecture -Role-playing Learning Groups -Journals -Explicit Teaching (http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/d -Problem -Learning Logs -Compare & Contrast e/pd/instr/categ.html) Solving -Reports (http://olc.spsd.sk.ca -Learning Activity Packages -Didactic Questions -Structured /de/pd/instr/categ.ht -Research Projects -Demonstrations - Controversy ml) -Assigned Questions -Guided & Shared - -Interviewing -Learning Centers reading, listening -Conferencing -Narratives -Problem -Conducting Experiments (http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/pd Solving -Simulations /instr/categ.html) -Case Studies -Games -Simulations -Storytelling -Games -Focused Imaging -Storytelling -Field Observations -Role-playing -Role-playing -Model Building (http://olc.spsd.sk Surveys .ca/de/pd/instr/ca teg.html) (http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/pd/instr/categ.html ) How is Computer-based The use of Computer- Training matrix with Training Teleconferenced sessions provided by a technology used instruction and provides demonstration relates based learning machinery facilitator for a specific subject. for learning in rigid introduction of by way of video or on simulation management established to your industry? information for compliance the job training. programs and system tracking of teach purposes. Examples such systems. tasks mastered. machinists. as safety rules, policies, etc. REFERENCES:
- 7. Learning Theories and Instruction Bandura, A. (1977) Social Learning Theory, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J. 1977, p. 59. Butterfield, E. C., & Nelson, G. D. (1989). Theory and practice of teaching for transfer. Educational Technology, Research and Development, 37 (3), 5–38. Chandler, P., Sweller, J. (1991). Cognitive Load Theory and Format of Instruction. Cognition and Instruction, 1991, 8(4), 293-332. Harp, S.F, Mayer, R.E. (1998). How Seductive Details Do Their Damage: A Theory of Cognitive Interest in Science Learning. Journal of Educational Psychology. 1998, Vol. 90, No. 3, 414-434. Retrieved from: http://visuallearningresearch.wiki.educ.msu.edu/file/view/Harp+%26+Mayer+(1998).pdf/50533273/Harp+%26+Mayer+(1998).pdf Kim, J., Gil, Y. (2007). Incorporating Tutoring Principles into Interactive Knowledge Acquisition. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies (IJHCS, 2007). Lieb, S. (1991). Principles of Adult Learning, VISION http://honolulu.hawaii.edu/intranet/committees/FacDevCom/guidebk/teachtip/adults-2.htm Ormrod, J.E. (1999). Human learning (3rd Ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Skinner, B.F. (1953). Science and human behavior. New York: Free Press. Siemens, G. (1995). Connectivism:A Learning Theory for the Digital Age. International Journal of Instructional Technology and Distance Learning. Vol. II, No. 1, Smith, E.R. (2009). Distributed Connectionist Models in Social Psychology. Social and Personality Psychology Compass 3/1 (2009): 64–76, 10.1111/j.1751-9004.2008.00160.x Spence, K.W. (1937). The differential response in animals to stimuli varying within a single dimension. Psychological Review, 44, 430-444.