Survey Training and LQAS
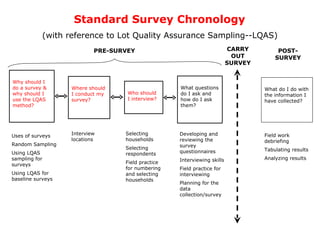
- 1. Standard Survey Chronology (with reference to Lot Quality Assurance Sampling--LQAS) CARRY OUT SURVEY Why should I do a survey & why should I use the LQAS method? Where should I conduct my survey? PRE-SURVEY Who should I interview? What questions do I ask and how do I ask them? Uses of surveys Random Sampling Using LQAS sampling for surveys Using LQAS for baseline surveys Interview locations Selecting households Selecting respondents Field practice for numbering and selecting households Developing and reviewing the survey questionnaires Interviewing skills Field practice for interviewing Planning for the data collection/survey What do I do with the information I have collected? Field work debriefing Tabulating results Analyzing results POST-SURVEY
- 2. Key Concepts: Program Area and Supervision Areas Together, A, B, C, D, and E represent the Program Area A, B, C, D, and E represent 5 Supervision Areas . Why Survey/Why LQAS A B C D E
- 4. Key Concept: Coverage Knowing coverage enables us to... Plan by allowing us to choose priorities. To focus our efforts on improving those knowledge and practices that have low coverage. Over time, repeated measures of coverage show us if our efforts are leading to improvements in coverage. Additionally, knowing the coverage is especially poor in one or more supervision areas helps us choose priorities. We can decide to focus our efforts in those supervision areas with poor coverage. Why Survey/Why LQAS
- 5. What Surveys Can Show You Surveys can help you identify the level of coverage of the program area as a whole, AND if there are: large differences in coverage regarding knowledge and practices among supervision areas little difference in coverage regarding knowledge and practices among supervision areas Why Survey/Why LQAS
- 6. Scenario One Indicator: Percent of women (15-49) who know 2 or more ways to prevent HIV transmission. Scenario Two Scenario Three Why Survey/Why LQAS A = 30 B = 40 C = 80 D = 75 E = 20 A = 85 B = 80 C = 90 D = 85 E = 80 A = 25 B = 20 C = 30 D = 25 E = 20
- 8. Key Concept: Random Sampling Sampling allows you to use the “ few ” to describe the “ whole ” (to generalize from the few to the whole) AND Random sampling is a critical way to improve your ability to generalize in this way (it improves “external validity”) Why Survey/Why LQAS
- 9. Key Concept: Lot Quality Assurance Sampling Indicator: Percent of women (15-49) who know 2 or more ways to prevent HIV transmission. A special type of random sampling that allows us to use small samples to distinguish between supervision areas in relation to coverage--to see if certain areas have much higher or lower coverage than others. LQAS allows us to make comparisons between supervision areas AND estimate overall program coverage. Why Survey/Why LQAS Watch! A = ? B = 80 C = ? D = 75 E = 45
- 11. Why Survey/Why LQAS “ Limits” of LQAS Let’s say we want ALL SAs to achieve the result that at least 50% of all women 15-49 know at least 2 ways to prevent the transmission of HIV. If we take a sample of 19, what is the probability of misclassifying an SA as having achieved the target (using a decision rule of 7) or of NOT having achieved the target for various TRUE population rates? 0% 100% 70% 1% 99% 60% 3% 97% 55% 8% 92% 50% 17% 83% 45% 31% 69% 40% 48% 52% 35% 67% 33% 30% 82% 18% 25% 93% 7% 20% 98% 2% 15% Probability of classifying the SA as not having achieved the target of 50% (based on n=19 with decision rule of 7 or more who know 2 ways) Probability of classifying the SA as having achieved the target of 50% (based on n=19 with decision rule of 7 or more who know 2 ways) True Population Proportion who Know 2 Ways to Prevent HIV Transmission in the SA
- 14. Why Survey/Why LQAS One More Thing… LQAS in Baseline Surveys Generally we think of using LQAS for ongoing monitoring to assess whether we have evidence that we are meeting pre-set targets. However, it can be used at baseline to assess whether certain SAs appear to be “lagging” behind the program area average coverage. Five SAs & One Indicator 1. Add number correct in all SAs: 12+9+16+11+14=62 2. Add all sample sizes 19*5=95 3. Average Coverage Estimate 62/95=65.3% round up to nearest 5%=70% 4. Decision rule for sample of 19 and 70% is 11 One SA & Five Indicators Yes 14 SA E Yes 11 SA D Yes Decision Rule 11 16 SA C No 9 SA B Yes 12 SA A Equal to or Above Average Coverage? Average Coverage Estimate 65.3% Number Correct Indicator: Women who know 2 or more ways to prevent HIV transmission Supervision Areas A, B, C, D and E 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 -- -- 19 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 Average Coverage (for baselines) or Coverage Target (for monitoring/evaluation) n= Yes 3 30% 6 Women who know where to get test Yes 10 65% 13 Men know how HIV transmitted No 6 45% 4 Women know how HIV transmitted Yes 1 20% 4 Men using condoms w/ sex Yes 6 45% 7 Women “using” condoms w/ sex Equal or Above Rule Pgm. Cove-rage Est. Cor-rect out of 19 Indicator
- 15. Standard Survey Chronology (with reference to Lot Quality Assurance Sampling--LQAS) CARRY OUT SURVEY Why should I do a survey & why should I use the LQAS method? Where should I conduct my survey? PRE-SURVEY Who should I interview? What questions do I ask and how do I ask them? Uses of surveys Random Sampling Using LQAS sampling for surveys Using LQAS for baseline surveys Interview locations Selecting households Selecting respondents Field practice for numbering and selecting households Developing and reviewing the survey questionnaires Interviewing skills Field practice for interviewing Planning for the data collection/survey What do I do with the information I have collected? Field work debriefing Tabulating results Analyzing results POST-SURVEY
- 17. Where and With Whom? Programs in Which Participants are “Listed” Let’s go back to our 5 SAs and assume that, in this case, the 5 are “bank” branches of a microfinance institution. In each branch (each SA) lists of clients are maintained. If we are doing an education program with members and want to learn if 50% in branch “A” know 2 ways to prevent HIV transmission we can take a sample of 19 from this branch. To do this we start by assembling a numbered list (in a completely random order--NOT by community for example) of all client names. Next we use some means (random number table or other) to select 19 numbers at random. The numbers must be between 1 and the highest number on the list. We then decide when and how we will interview each client whose name corresponds with the number chosen. A B C D E
- 18. Programs in which Participants are not “Listed” (but for which we know all the communities in which they live and have a general idea of population size in each community) This case is common in community-based programs in which “all” members of a group (women 15-49) in a certain geographic area are intended beneficiaries If we are doing an education program with women 15-49 in an entire program area and want to assess whether 50% of them in SA A (a geographic area) know at least two ways to prevent HIV transmission the approach is a bit more challenging and usually requires “multi-stage”, “systematic” sampling. Here are the general steps (to be repeated in each SA) Step 1. List communities and total population. Step 2. Calculate the cumulative population. Step 3. Calculate the sampling interval. Step 4. Choose a random number. Step 5. Beginning with the random number, use the sampling interval to identify communities for the 19 sets of interviews. This ONLY gives us the communities in which we need to sample! We need another step to identify the actual women we will interview (that is why we call it “multi-stage”) Where and With Whom? A B C D E
- 19. Where and With Whom? Step 1. List communities and total population. Step 2. Calculate the cumulative population. Step 3. Calculate the sampling interval=Total Cumulative Population/Sample Size (2714/19= 114.42 ) Step 4. Choose a random number between 1 and the interval - Step 5. Beginning with the random number, use the sampling interval to identify communities for the 19 sets of interviews. X is the first then X+114.42, etc. Supervision Area A 2174 Total 92 Kilkil 554 Guimbe 216 Jilwa 188 Farry 126 Masrag 253 Nevi 97 Garafa 115 Ishri 381 Santai 152 Pagal Population Name of the Community 2174 2082 1528 1312 1124 998 745 648 533 152 Cumulative Population 2136 1564, 1678, 1793, 1907, 2022 1335, 1450 1221 1106 763, 877, 992 649 534 191, 305, 420 77 Interview Location Number Interview Location
- 22. Where and With Whom? Choosing the “Final” Respondent So, now you have selected the household where to start. Use this table to decide how to proceed… In Guimbe you need to conduct five interviews so once you have completed the first interview go back to the steps for selecting the first household and begin again following the approach that is appropriate to the size of the community. You will repeat this each time you must select a new respondent. Go find the respondent with the help of someone who knows where she is. IF you cannot find the person in the next 30 minutes THEN… Go the next nearest household from the FRONT ENTRANCE to the household you are at and check for an appropriate respondent at this household. Continue this process until you find the type of respondent you are looking for. If two households are equally near, then choose the one with the closest door or flip a coin. The type of respondent you are looking for lives at the household BUT is absent BUT is within 30 minutes of where you are The type of respondent you are looking lives in the household BUT is away/absent at the time of the interview AND is more than 30 minutes away Go the next nearest household from the FRONT ENTRANCE to the household you are at and check for an appropriate respondent at this household. Continue this process until you find the type of respondent you are looking for. If two households are equally near, then choose the one with the closest door or flip a coin. The type of respondent you are looking for does NOT live in the household you selected Interview that person if she consents (see the bottom of the table for what to do next) The type of respondent you are looking for is at the household you selected THEN: IF: