MicroRNA Profiling of Hepatocellular Carcinomas in B6C3F1 Mice Treated with Ginkgo biloba Extract by Gavage for 2 Years
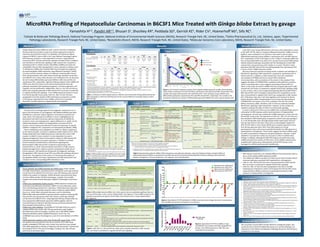
- 1. MicroRNA Profiling of Hepatocellular Carcinomas in B6C3F1 Mice Treated with Ginkgo biloba Extract by gavage 1Cellular & Molecular Pathology Branch, NaPonal Toxicology Program, NaPonal InsPtute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), Research Triangle Park, NC, United States, 2Taisho PharmaceuPcal Co. Ltd., Saitama, Japan, 3Experimental Pathology Laboratories, Research Triangle Park, NC, United States, 4BiostaPsPcs Branch, NIEHS, Research Triangle Park, NC, United States, 5Molecular Genomics Core Laboratory, NIEHS, Research Triangle Park, NC, United States. Abstract Ginkgo biloba Yamashita H1,2, Pandiri AR1,3, Bhusari S1, Shockley KR4, Peddada SD4, Gerrish KE5, Rider CV1, Hoenerhoff MJ1, Sills RC1. leaf extract (GBE) has been used for centuries in tradiPonal Chinese medicine and today is used as an herbal supplement touted for improving neural funcPon and for its anPoxidant and anPcancer effects. Exposure of B6C3F1 mice to GBE in the 2-‐year NaPonal Toxicology Program (NTP) bioassay resulted in a dose-‐dependent increase in hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC). We have previously reported increased and alteraPons in Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling in GBE-‐induced HCC compared to spontaneous HCC in vehicle controls. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-‐ coding RNAs that are ogen dysregulated in various diseases including cancer. To idenPfy key miRNAs that modulate GBE-‐induced hepatocarcinogenesis, we examined global miRNA expression using Affymetrix GeneChip® miRNA 3.0 arrays and two pairwise analyses (n=5/group) comparing GBE-‐induced HCCs and spontaneous HCCs with vehicle control age-‐matched normal livers from B6C3F1 mice. Using a false discovery rate threshold of 5%, we observed 16 and 3 unique differenPally expressed miRNAs in GBE-‐induced HCC and spontaneous HCC, respecPvely. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of the miRNA and mRNA array data from these tumors demonstrated altered molecular pathways associated with hepatocarcinogenesis, cell cycle progression, cell migraPon and cell proliferaPon. AddiPonally, miRs-‐31, 145, 329 and 433-‐3p, which were uniquely expressed in GBE-‐induced HCC, are known or predicted to regulate Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling. In the miRNA expression analysis in livers from the 90-‐day GBE mouse study, miRs-‐411, 300, 127 and 134 were upregulated more than double in GBE-‐treated group compared to vehicle control group, indicaPng that these miRNAs could serve as potenPal biomarkers for GBE exposure or hepatocellular carcinogenesis. It has become increasingly apparent that epigenePc mechanisms are at play in the mechanisms of carcinogenesis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been idenPfied as a new layer of gene regulatory mechanisms (Lujambio and Lowe, 2012). The importance of miRNAs in cancer is highlighted by the observaPon that half of the known aberrant expressions of miRNAs are located in cancer associated genomic regions (Wiklund et al., 2010). On the relaPonship between miRNAs and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in humans, several studies have detected the aberrant expression of specific miRNAs in malignant HCC, compared to normal hepatocyte (Masaki, 2009). There is widespread and unregulated use of GBE as a dietary supplement by the American public, and thus is a significant public health concern. NTP’s Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (GBE) bioassay has indicated that chronic GBE exposure to B6C3F1 mouse resulted in a dose dependent increase in hepatocarcinogenicity. Recent transcriptomic studies on GBE-‐induced HCC indicated dysregulated cancer gene expression. In AddiPon, increased Ctnnb1 mutaPons and alteraPons in Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling were demonstrated in GBE-‐induced HCC compared to spontaneous HCC (Hoenerhoff et al., 2013). Determining the mechanisms of GBE-‐induced hepatocarcinogenicity in rodents may aid in assessing the health risks of human exposure. We hypothesize that genePc and epigenePc pathways dysregulated in GBE-‐induced mouse HCC may reflect key pathways altered in human HCC. The objecPve of this study is to characterize the pamern of dysregulated miRNAs occurring in spontaneous and GBE-‐induced HCC and compare it to the corresponding mRNA alteraPons in HCC. Tissue collec*on and miRNA extrac*on for miRNA array: Ctnnb1 mutaPons Frozen samples from GBE-‐induced HCCs, spontaneous HCCs and vehicle control age-‐matched normal livers from B6C3F1 mice from the 2-‐year NTP bioassay were used for miRNA array analysis (n=5/group). miRNA extracPon was performed using mirVana miRNA IsolaPon Kit (Life technologies, Carlsbad, CA) and RNA integrity was measured with Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). miRNA array hybridiza*on & data analysis: miRNA expression analysis was conducted using Affymetrix GeneChip® miRNA 3.0 Array (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA) following manufacturer’s direcPons. miRNA expression data were normalized across all samples using the robust mulParray analysis (RMA) (Guo et al., 2010). RMA-‐normalized data were used for idenPfying differenPally expressed miRNAs using two pairwise analyses comparing GBE-‐ induced HCCs and spontaneous HCCs with vehicle control age-‐matched normal livers from B6C3F1 mice. Using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA), we have analyzed the differenPally expressed miRNAs together with the corresponding transcriptomic data that we have previously obtained from these samples (Hoenerhoff et al., 2013). miRNA array data valida*on: QuanPtaPve RT-‐PCR (QRT-‐PCR) was used to validate miRNA array results. QRT-‐PCR was performed using TaqMan® MicroRNA Assay (Life technologies, Carlsbad, CA) on ABI PRISM 7900HT Sequence DetecPon System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). snoRNA202 was used as the endogenous control for normalizaPon of miRNA levels. miRNA expression analysis in livers from 90-‐day GBE mouse study: miRNA was isolated and extracted from two 20 μm secPons of formalin-‐fixed, paraffin-‐embedded (FFPE) livers from control mice and from mice treated with 2000 mg/kg GBE for 90 days (n=6/group) with RecoverAll™ Total Nucleic Acid IsolaPon Kit for FFPE (Life technologies, Carlsbad, CA). QRT-‐PCR was performed as described above. In the NTP 2-‐year mouse GBE bioassay, there was a dose dependent increase in HCC (NTP TR 578, Table 1). Using the Affymetrix GeneChip® miRNA 3.0 Array plaoorm, when compared to normal livers, there were 3 and 16 unique differenPally expressed mouse miRNAs in spontaneous HCC and GBE-‐induced HCC, respecPvely, at FDR ≤ 0.05 (Figure 1 and 2, Table 2). Analyzing miRNA and the corresponding mRNA array data in IPA, we have found several differenPally altered molecular pathways associated with HCC development in both GBE-‐ induced HCCs and spontaneous HCCs (Tables 3, 4, and 5). Therefore, these data show that GBE-‐induced HCCs are disPnguishable from spontaneous HCC in terms of their miRNA expression profile. We have previously reported increased Ctnnb1 mutaPons and alteraPons in Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling in GBE-‐induced HCC compared to spontaneous HCC in vehicle controls. In addiPon, in GBE-‐induced HCC, there was cytoplasmic accumulaPon of CTNNB1 and loss of normal CDH1 membrane immunoreacPvity, with accumulaPon of the protein in the cytoplasm that suggests disrupPon of CTNNB1/CDH1 complexes within adherens juncPons, which is associated with a more malignant phenotype (Hoenerhoff et al., 2013). In this study, we found 4 miRNAs that were uniquely expressed in GBE-‐ induced HCC and known or predicted to regulate Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling (Table 5). One of them, miR-‐31 was strongly downregulated (83-‐fold by QRT-‐PCR) in GBE-‐induced HCC with no change in spontaneous HCC compared to normal livers and predicted to regulate Cdk1, which was upregurated in GBE induced HCC. CDK1 plays a key role in cell cycle regulaPon and increases Src kinase acPvity (Roskoski, 2005). PhosphorylaPon by Src kinase disrupts binding of CTNNB1/CDH1 and results in loss of the complexes from the cell surface (Nelson and Nusse, 2004). Therefore, miR-‐31 seems to indirectly modulate Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling in GBE-‐induced HCC. However, further studies are needed to evaluate the effect of miR-‐31 on Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling. In order to determine if there are any miRNAs that could potenPally serve as a biomarker for GBE exposure and/or early biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinogenesis, we have also analyzed the miRNA expression in livers from the 90-‐day GBE mouse study. The expression of miRs-‐411, 300, 127 and 134 more than doubled in GBE-‐treated group compared to vehicle control group (Figure 3). In the 90-‐day GBE study, although hepatocellular hypertrophy and focal necrosis were found in the livers, there were no preneoplasPc hepaPc foci (NTP TR 578, Table 1). Since these miRNAs were uniquely expressed in livers from 90-‐day exposures and in HCCs from GBE exposure or arising spontaneously, they could serve as potenPal biomarkers for GBE exposure or hepatocellular carcinogenesis. These results suggest that these miRNAs might be useful as biomarkers of exposure and apical endpoints. However, further validaPons in prospecPve studies are necessary in order to validate these findings. In addiPon, although this QRT-‐PCR analysis was performed using miRNA extracted from secPons of FFPE livers, all the miRNAs analyzed were amplified with relaPve ease, indicaPng that archival FFPE Pssues can be leveraged for miRNA-‐based biomarker idenPficaPon. Introduc.on Materials and Methods Result Results and Discussion Table 1 Table 1. Incidences of select hepaPc lesions in B6C3F1 mice treated with Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (GBE) by gavage in subchronic (90-‐day) and chronic (2-‐year) NaPonal Toxicology Program studies (NTP TR 578). Figure 1 Figure 1. Normal liver Spontaneous HCC (A) Principal component analysis (PCA) of global miRNA expression profiles demonstrated nearly disPnct clustering of normal liver (blue), spontaneous HCC (green) and GBE-‐induced HCC (red) samples. (B) Using a false discovery rate threshold of 5%, 3 and 16 unique mouse miRNAs were differenPally expressed in spontaneous HCC and GBE-‐induced HCC, respecPvely. The number in the parenthesis indicates the number of differenPally expressed miRNAs from other species besides mice. Conclusions • GBE-‐induced mouse HCCs are markedly different from spontaneous HCCs in terms of their global miRNA expression profile. • The miRNA and mRNA array data from these tumors demonstrated altered molecular pathways associated with hepatocellular carcinogenesis. • miRs-‐31, 145, 329 and 433 that were uniquely expressed in GBE-‐induced HCC are known or predicted to regulate Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling. • miRs-‐411, 300, 127 and 134 were upregulated in the livers from GBE-‐ treated group compared to vehicle control group from 90-‐day GBE mouse study and these miRNAs could serve as potenPal biomarkers for GBE exposure or hepatocellular carcinogenesis. References Acknowledgements We would like to thank DNTP and DIR, NIEHS for funding this project. We would also like to thank the NIEHS Microarray core and the Histology core Laboratory in the Cellular and Molecular Pathology Branch for their technical assistance on this project. Table 2 Table 2. DifferenPally expressed miRNAs and their target genes in spontaneous and GBE-‐induced HCC compared to age-‐matched normal livers. Table 3 ê: Known to decrease the diseases or funcPon and is down-‐regulated in the dataset. é: Known to increase the diseases or funcPon and is up-‐regulated in the dataset. êé: Literature indicates this gene is involved in the diseases or funcPon but does not indicate whether it increases or decreases it. And the gene is down-‐ or up-‐regulated in the dataset. #1 Target genes that showed relaPonship with the respecPve miRNA in IPA analysis (experimentally observed or predicted) and down-‐ or up-‐regulated in GBE-‐induced HCC microarray analysis. Table 3. RepresentaPve altered miRNA-‐mRNA interacPons and molecular pathways. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of target mRNAs of differenPally altered miRNAs in spontaneous and GBE-‐induced HCC demonstrated dysregulated molecular pathways associated with hepatocarcinogenesis, cell cycle progression, cell migraPon and cell proliferaPon. Table 4. DifferenPally altered miRNAs from other species that are staPsPcally significant (but not in mice) and that play a role in human hepatocellular carcinogenesis. These miRNA sequences are typically conserved across species and are likely to be relevant even in mouse hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Table 5 Table 5. miRs-‐329, 31, 145 and 433-‐3p, which were uniquely expressed in GBE-‐induced HCC, are known or predicted to regulate Wnt/Ctnnb1 signaling. Figure 2 Figure 2. QuanPtaPve RT-‐PCR validaPon of miRNA array expression changes observed in spontaneous HCC and GBE-‐induced HCC normalized to normal livers. Figure 3. QuanPtaPve RT-‐PCR of miRNAs in livers from B6C3F1 mice treated with 2000 mg/kg GBE for 90 days. The miRNA expression in GBE livers was normalized to normal livers. 1. Lujambio A, Lowe SW. 2012. The microcosmos of cancer. 482(7385):347-‐55. 2. Wiklund ED, Kjems J, Clark SJ. 2010. EpigenePc architecture and miRNA: reciprocal regulators. Epigenomics. 2(6):823-‐40. 3. Masaki T. 2009. MicroRNA and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 39(8):751-‐2. 4. Hoenerhoff MJ, Pandiri AR, Snyder SA, et al. 2013. Hepatocellular carcinomas in B6C3F1 mice treated with Ginkgo biloba extract for two years differ from spontaneous liver tumors in cancer gene mutaPons and genomic pathways. Toxicol Pathol. 41(6):826-‐41. 5. Guo W, Sarkar SK, Peddada SD. 2010. Controlling false discoveries in mulPdimensional direcPonal decisions, with applicaPons to gene expression data on ordered categories. Biometrics. 66(2):485-‐92. 6. NTP TR 578. 2013. NTP technical report on the toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of Ginkgo Biloba Extract (CAS NO. 90045-‐36-‐6) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1/N mice (Gavage studies) 7. Li J, Fu H, Xu C, et al. 2010. miR-‐183 inhibits TGF-‐beta1-‐induced apoptosis by downregulaPon of PDCD4 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer. 10:354. 8. Ura S, Honda M, Yamashita T, et al. 2009. DifferenPal microRNA expression between hepaPPs B and hepaPPs C leading disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 49(4):1098-‐112. 9. Sun X, He Y, Huang C, Ma TT, et al. 2013. DisPncPve microRNA signature associated of neoplasms with the Wnt/β-‐catenin signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 25(12):2805-‐11. 10. Toffanin S, Hoshida Y, Lachenmayer A, et al. 2011. MicroRNA-‐based classificaPon of hepatocellular carcinoma and oncogenic role of miR-‐517a. Gastroenterology. 2011. 140(5):1618-‐28. 11. Law PT, Ching AK, Chan AW, et al. 2012. MiR-‐145 modulates mulPple components of the insulin-‐like growth factor pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 33(6):1134-‐41. 12. Sachdeva M, Mo YY. 2010. MicroRNA-‐145 suppresses cell invasion and metastasis by directly targePng mucin 1. Cancer Res. 70(1):378-‐87. 13. Kim SJ, Oh JS, Shin JY, et al. 2011. Development of microRNA-‐145 for therapeuPc applicaPon in breast cancer. J Control Release. 155(3):427-‐34. 14. Roskoski R Jr. 2005. Src kinase regulaPon by phosphorylaPon and dephosphorylaPon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331(1):1-‐14. 15. Nelson WJ, Nusse R. 2004. Convergence of Wnt, beta-‐catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303(5663):1483-‐7. (B) a 10 male and female B6C3F1 mice were exposed to 0, 125, 250, 500, 1,000, and 2,000 mg/kg GBE by gavage, once daily, 5 days per week for 90 days. b Severity grade based on 0–4 grading scale (0 = no significant lesion, 1 = minimal, 2 = mild, 3 = moderate, 4 = severe). c 50 male and female B6C3F1 mice were exposed to 0, 200, 600, and 2,000mg/kg GBE by gavage, once daily, 5 days per week for two years. d StaPsPcal analysis not available for metastaPc lesions. Significantly different from controls *p < .05, **p < .01 by the poly-‐3 test. #1 Target genes that showed relaPonship with the respecPve miRNA in IPA analysis (experimentally observed or predicted) and down-‐ or up-‐regulated in GBE-‐induced HCC microarray analysis. #2 No informaPon on the target genes was found in IPA knowledge base on these miRNAs. Figure 3 Table 4 (A) GBE-‐induced HCC
