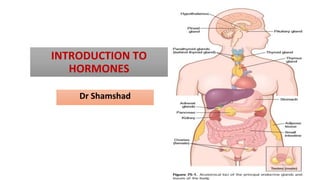
Introduction to hormones
- 2. OBJECTIVES: 1. Classify the hormones according to their chemical structure. 2. Outline the general mechanisms for synthesis & secretion of hormones. 3. Describe the role of hormone binding proteins. 4. Discuss Clearance of hormones from blood. 5. Brief the methods for measurement of hormone concentration in blood.
- 3. Definition: Hormone is a chemical substance secreted by ductless gland into the blood. ⮚ Endocrine hormones are released by glands or specialized cells into the circulating blood & influence the function of target cells at another location in the body. ⮚ Neuroendocrine hormones are secreted by neurons into the circulating blood & influence the function of target cells at another location in the body. Function: To integrate with Neural system of body & thus maintain the homeostasis of the body.
- 5. ⮚1: Proteins and polypeptides: Ant. pituitary hormone( GH,TSH etc.), post. Pituitary(ADH Oxytocin), Pancreas :Insulin& glucagon and parathyroid gland:PTH. ⮚2: Steroids: Adrenal cortex :cortisol & aldosterone, • Ovaries & placenta: estrogen and progesterone, • Testes :testosterone. ⮚3. Derivatives of the amino acid Tyrosine: ⮚Thyroid gland: Thyroxine & triiodothyronine • Adrenal medullae :Epinephrine & norepinephrine. Note: There are no known polysaccharides or nucleic acid hormones.
- 6. Based on distance of target cells 1:Paracrines are secreted by cells into the extracellular fluid and affect neighboring target cells of a different type. 2: Autocrines are secreted by cells into the extracellular fluid and affect the function of the same cells that produced them. 3.Intracrine
- 7. Main functions of Endocrine hormones ⮚ Maintain Internal Homeostasis ⮚ Support Cell Growth ⮚ Coordinate Development ⮚ Coordinate Reproduction ⮚ Facilitate Responses to External Stimuli
- 11. 1.Preprohormone 2.prohormone 3.Active hormone/peptide fragment 5.Released into ECF BY Exocytosis 1.Peptide hormones:
- 13. 2.Hydrophobic /lipophilic hormones :Steroids, derived from cholesterol
- 14. Locations for the different types of hormone receptors: 1. In or on the surface of the cell membrane:The membrane receptors are specific mostly for the water soluable hormones. 2. In the cell cytoplasm: The primary receptors for the different steroid hormones are found mainly in the cytoplasm. 3. In the cell nucleus. The receptors for the thyroid hormones are found in the nucleus .Believed to be located in direct association with one or more of the chromosomes.
- 15. INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING AFTER HORMONE RECEPTOR ACTIVATION ⮚Ion Channel–Linked Receptors: NT like Ach & NE combine with receptors in the postsynaptic membrane. Change the structure of the receptor :open/ close channel for one/ more ions. Alter movement of these ions through the channels.Cause configurational changes on the postsynaptic cells. ⮚G Protein–Linked Hormone Receptors: Many hormones activate receptors that indirectly regulate the activity of target proteins (e.g., enzymes or ion channels) by coupling with groups of cell membrane G proteins. ⮚cAMP is second messenger used by the different hormones. • Few peptide hormones, Ex: ANP cGMP act as second messenger. • Others are 1: Calcium ions & associated calmodulin • 2: Products of membrane phospholipid breakdown.
- 16. Number & Sensitivity of Hormone Receptors Regulation ★ Not constant from day to day or even from minute to minute. Increased hormone concentration and increased binding with its target cell receptors sometimes cause the number of active receptors to decrease. Down-regulation of the receptors can occur as a result of 1)Inactivation of some of the receptor molecules. 2) Inactivation of some of the intracellular protein signaling molecules; 3) Temporary sequestration of the receptor to the inside of the cell, away from the site of action of hormones that interact with cell membrane receptors. 4) Destruction of the receptors by lysosomes after they are internalized; 5) decreased production of the receptors. Receptor downregulation decreases the target tissue’s responsiveness to the
- 17. Some hormones cause up-regulation of receptors and intracellular signaling proteins; The stimulating hormone induces greater than normal formation of receptor or intracellular signaling molecules by the target cell or greater availability of the receptor for interaction with the hormone. When upregulation occurs, the target tissue becomes progressively more sensitive to the stimulating effects of the hormone
- 19. HORMONES THAT ACT MAINLY ON THE GENETIC MACHINERY OF THE CELL Steroid Hormones Increase Protein Synthesis in the target cells. These proteins then function as enzymes, transport proteins, or structural proteins, which in turn provide other functions of the cells. The full action of the steroid hormone is delayed for at least 45 minutes—up to several hours or even days.
- 20. Thyroid Hormones Increase Gene Transcription in the Cell Nucleus Two features of thyroid hormone function in the nucleus are important: 1. They activate the genetic mechanisms for the formation of > 100 types of intracellular proteins. Most of them are enzymes that promote enhanced intracellular metabolic activity in virtually all cells of the body. 2. Once bound to the intranuclear receptors, the thyroid hormones continue to express their control functions for days or even weeks.
- 21. The cell membrane phospholipid second messenger system by which some hormones exert their control of cell function. DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol triphosphate; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol biphosphate.
- 22. ⮚Amine Hormones Are Derived From Tyrosine : Thyroid & adrenal medullary hormones, are formed by the actions of enzymes in the cytoplasmic compartments of the glandular cells.
- 23. ⮚Hormone Secretion After a Stimulus & Duration of Action of Different Hormones. • Hormones, like NE & E , secreted within seconds after the gland is stimulated & may develop full action within another few seconds to minutes. • Hormones, like T4 or GH, require months for full effect. ⮚Concentrations of Hormones in the Circulating Blood and Hormonal Secretion Rates. • The concentrations of hormones required to control most metabolic and endocrine functions are incredibly small. • Ranges: 1 picogram-few mg/ml of blood . ⮚Rate of secretion of the various hormones :Extremely small: μmg or mg/day
- 24. Cyclical Variations Occur in Hormone Release. Superimposed on the negative and positive feedback control of hormone secretion are periodic variations in hormone release that are influenced by seasonal changes, various stages of development and aging, the diurnal (daily) cycle, and sleep.
- 26. FEEDBACK CONTROL OF HORMONE SECRETION Negative Feedback Prevents Overactivity of Hormone Systems Surges of Hormones Can Occur With Positive Feedback. Negative feedback Positivefeedback
- 27. TRANSPORT OF HORMONES IN THE BLOOD I:Water-soluble hormones: dissolve in the plasma and are transported from their sites of synthesis to target tissues, They diffuse out of the capillaries, into the interstitial fluid, and ultimately to target cells. II:Steroid and thyroid hormones: Circulate in the blood as mainly bound to plasma proteins. ➔ < 10 % in the plasma exist free in solution. ➔ Protein bound hormones are biologically inactive cannot easily diffuse across the capillaries and gain access to their target cells ➔Protein bound Hormones serve as reservoirs ➔Replenish the concentration of free hormones when they are bound to target receptors /lost from the circulation. ➔Binding of hormones to plasma proteins greatly slows their clearance from the plasma.
- 28. Clearance of Hormones From the Blood (1) metabolic destruction by the tissues (2) binding with the tissues (3) excretion by the liver into the bile and (4) excretion by the kidneys into the urine. Sometimes degrade at their target cells by enzymatic processes that causes endocytosis of the cell membrane hormone receptor complex. The hormone then metabolized in the cell, and the receptors recycled back. Water soluble remain for short time :Circulate freely in the blood. Degraded by enzymes in the blood & tissues & rapidly excreted by the kidneys & liver. Ex:The half life of angiotensin II circulating in the blood is < 1 min. Hormones bound to plasma proteins :Cleared from the blood at slower rates , remain in the circulation for several hours or even days. Ex:1) The half life of adrenal steroids in the circulation, ranges b/w 20 & 100 min., 2) The half life of the protein bound thyroid hormones b/w 1 to 6 days.
- 29. Factors that increase / decrease the concentration of a hormone in the blood. 1:Rate of hormone secretion into the blood. & 2:Rate of removal of the hormone from the blood. Metabolic clearance rate =Rate of disappearance of hormone from the plasma/Concentration of hormone . • Expressed : Number of ml of plasma cleared of the hormone/ minute.
- 31. Compared to RIA methods ,ELISA methods ELISA use excess antibodies so that all hormone molecules are captured in antibodyhormone complexes. Hence the amount of hormone present in the sample or in the standard is proportional to the amount of product formed. The ELISA method has become widely used in clinical and research laboratories because (1) It does not use radioactive isotopes, (2) Much of the assay can be automated using 96well plates, and (3) It has proved to be a costeffective and accurate method for assessing hormone levels.