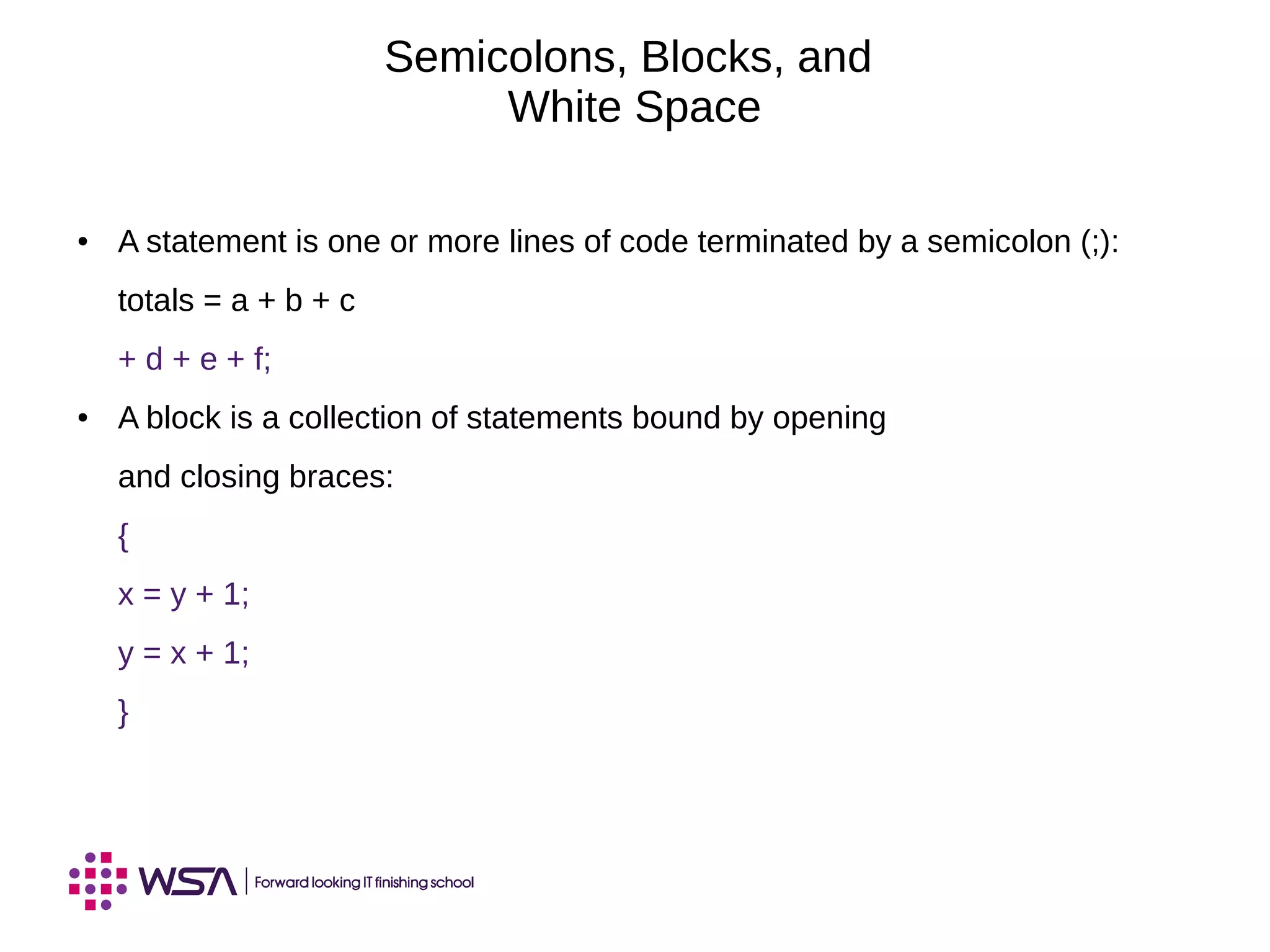
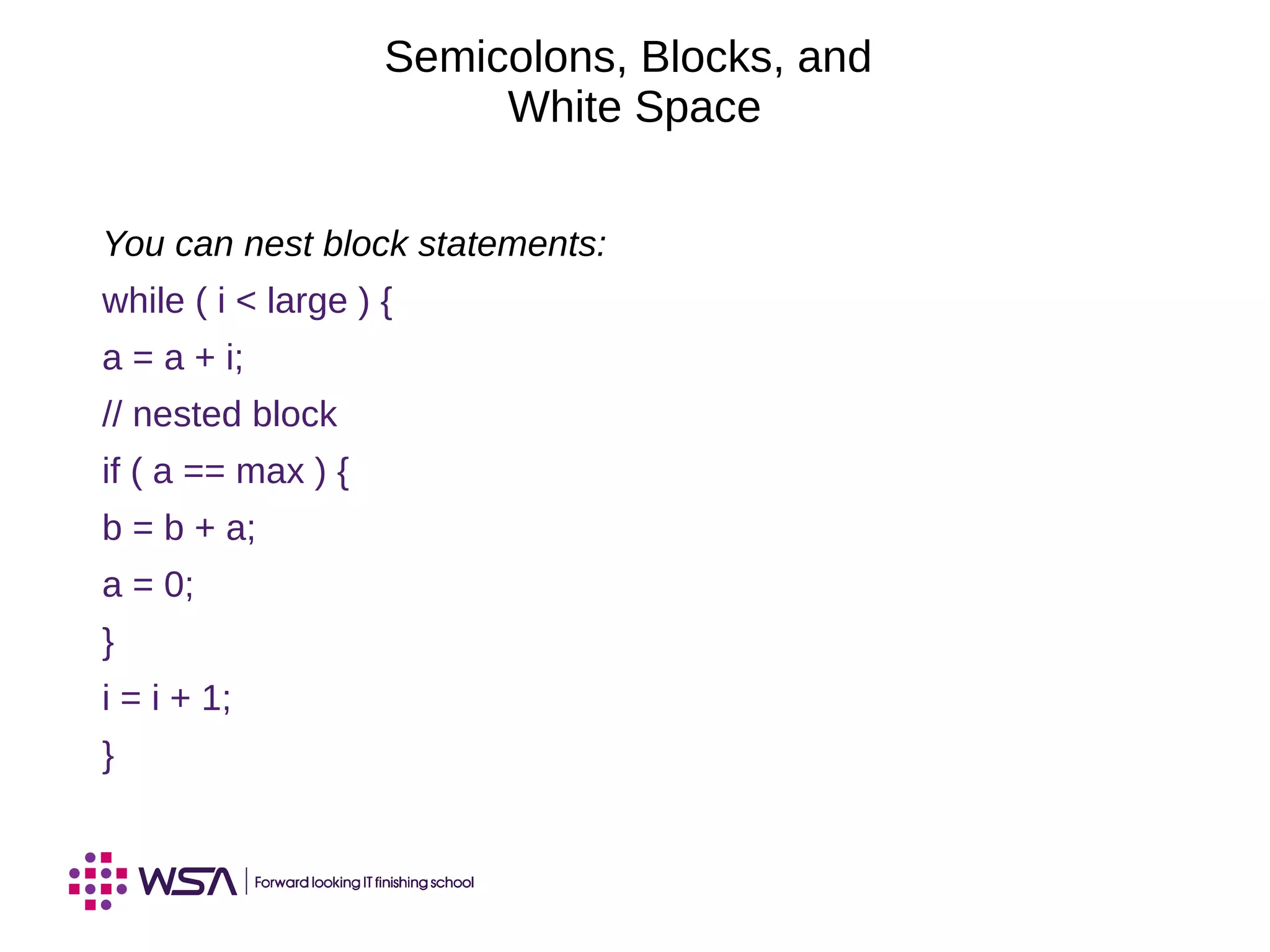
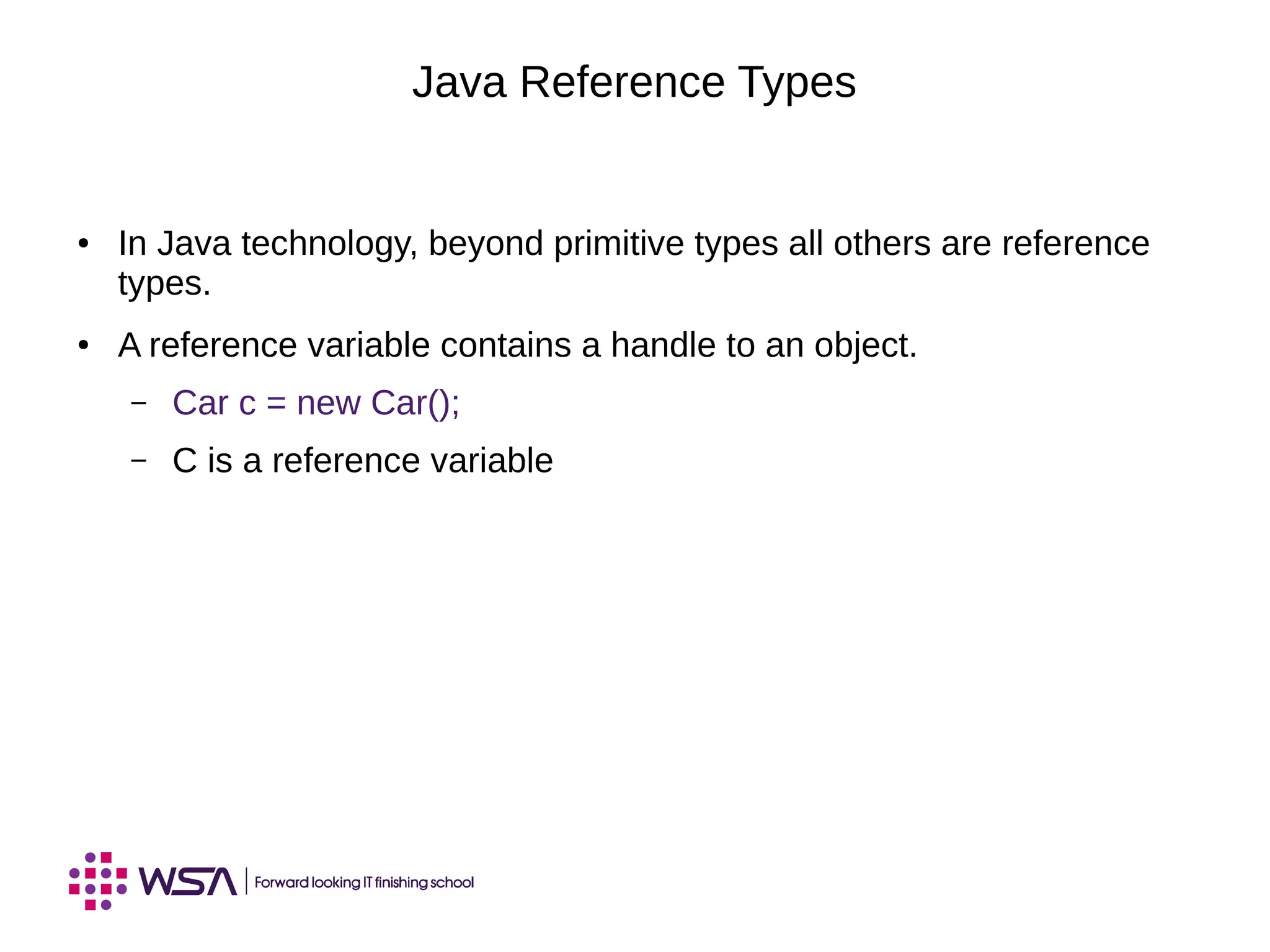
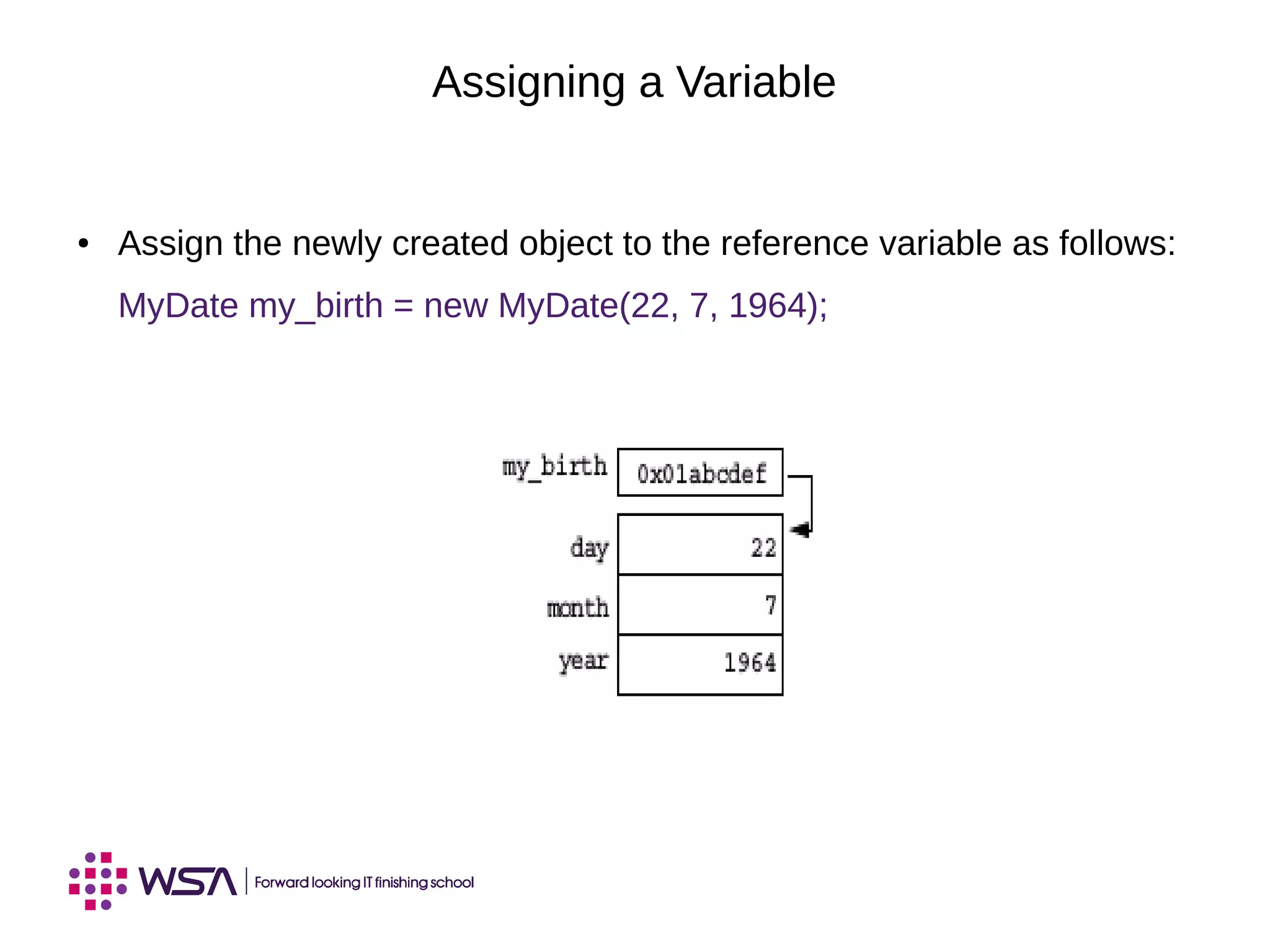
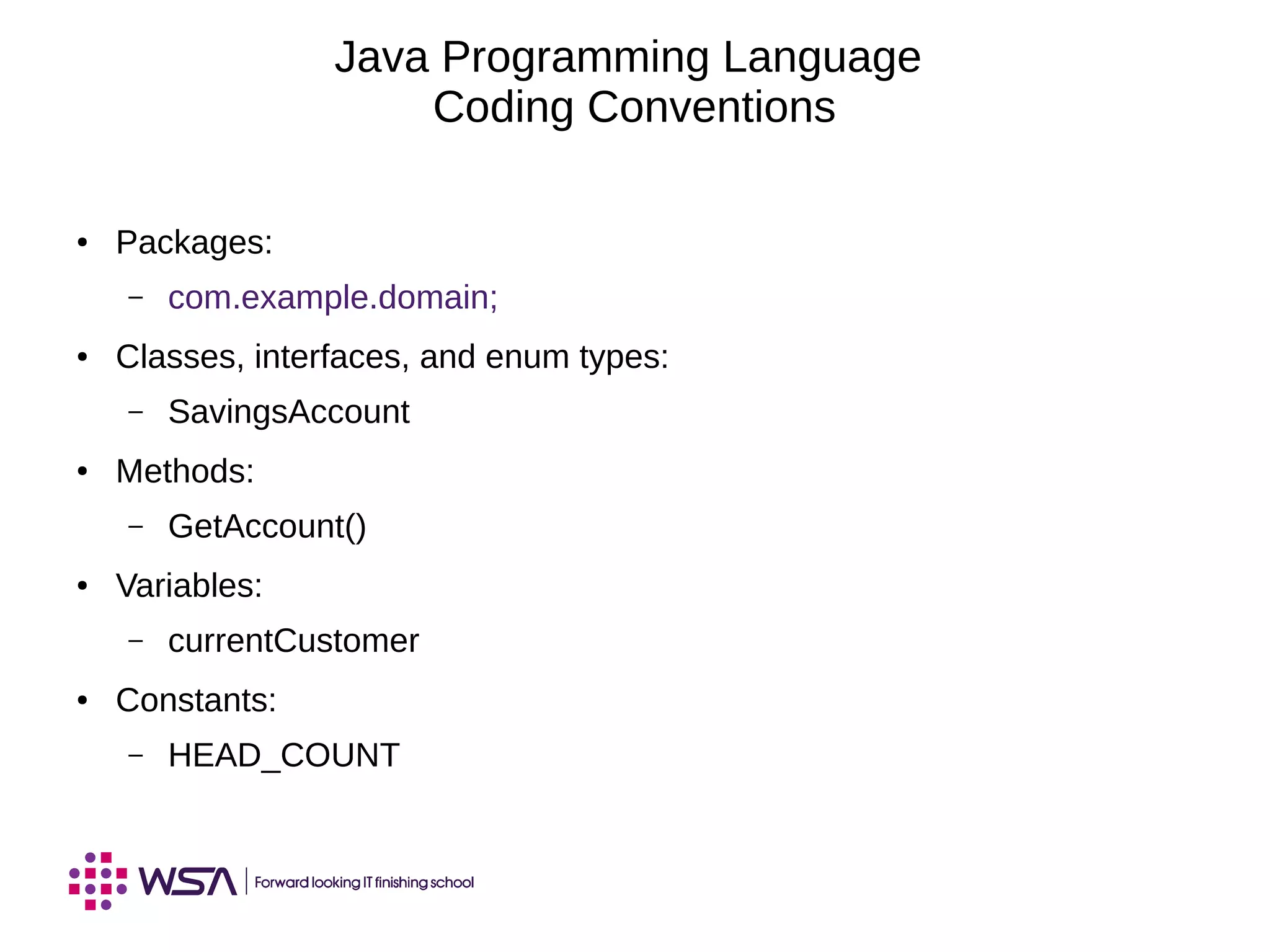
The document covers key concepts in Java programming, including identifiers, keywords, primitive types, and the significance of reference variables. It explains coding conventions and how to construct objects using the 'new' operator, along with memory allocation and assignments. Additionally, it discusses the use of the 'this' keyword and principles of pass-by-value in method arguments.