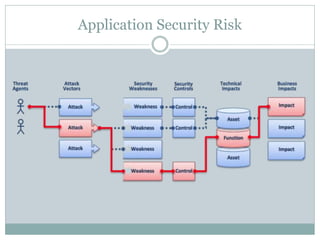
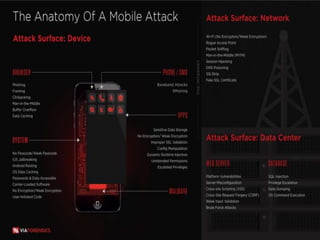
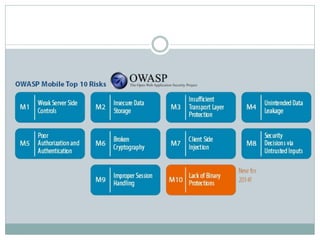
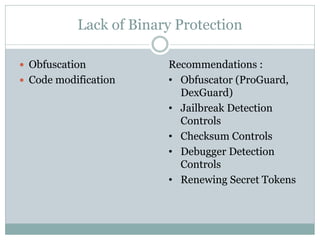
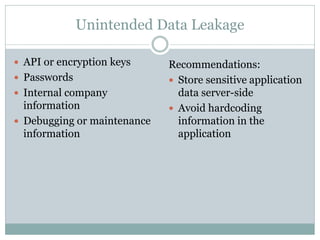
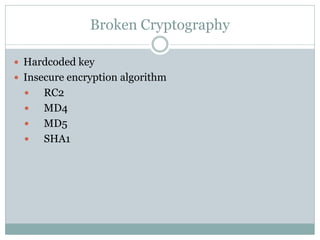
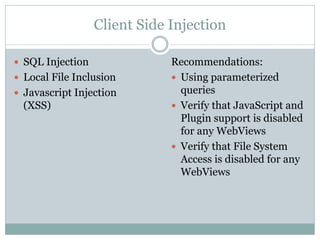
The document discusses several common mobile application security risks including lack of binary protection, weak server-side controls, insecure data storage, insufficient transport layer protection, unintended data leakage, poor authorization and authentication, broken cryptography, client-side injection, and improper session handling. It provides recommendations to address each of these risks such as using obfuscation, secure data storage techniques, TLS, strong authentication, secure cryptography, input validation, and secure session management.