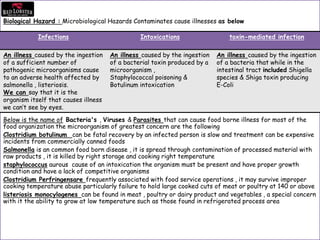
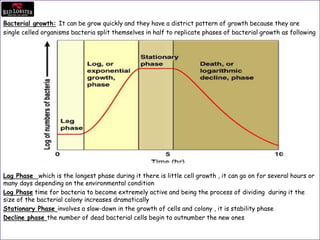
This document provides an overview of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) training. It begins with definitions of food safety terms and an introduction to food hazards like biological, chemical and physical hazards. It then discusses why HACCP was developed, how it works, and its history. Key aspects of HACCP covered include identifying critical control points and limits, monitoring procedures, and record keeping. The document emphasizes controlling food hazards before they occur to ensure food safety.