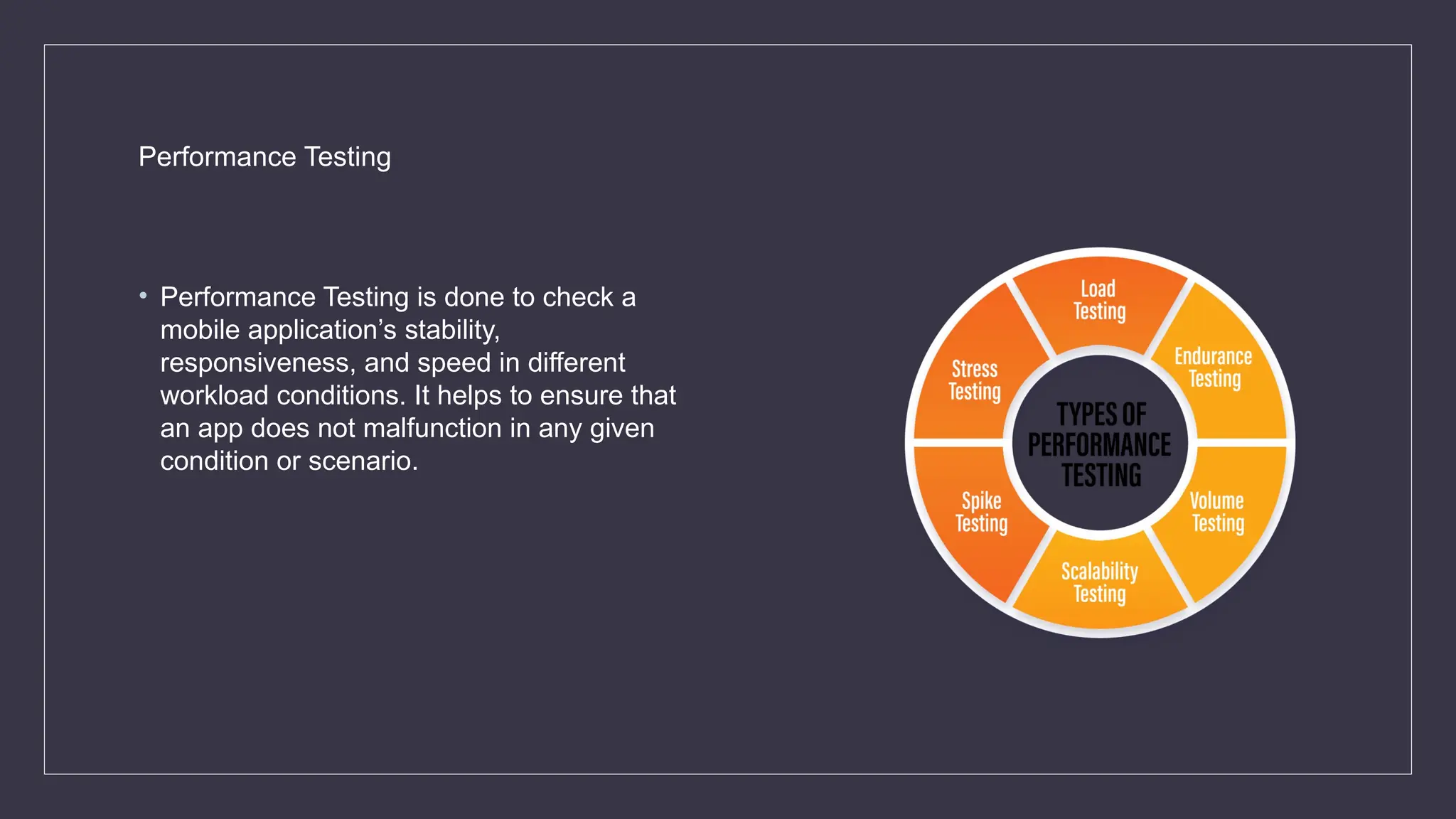
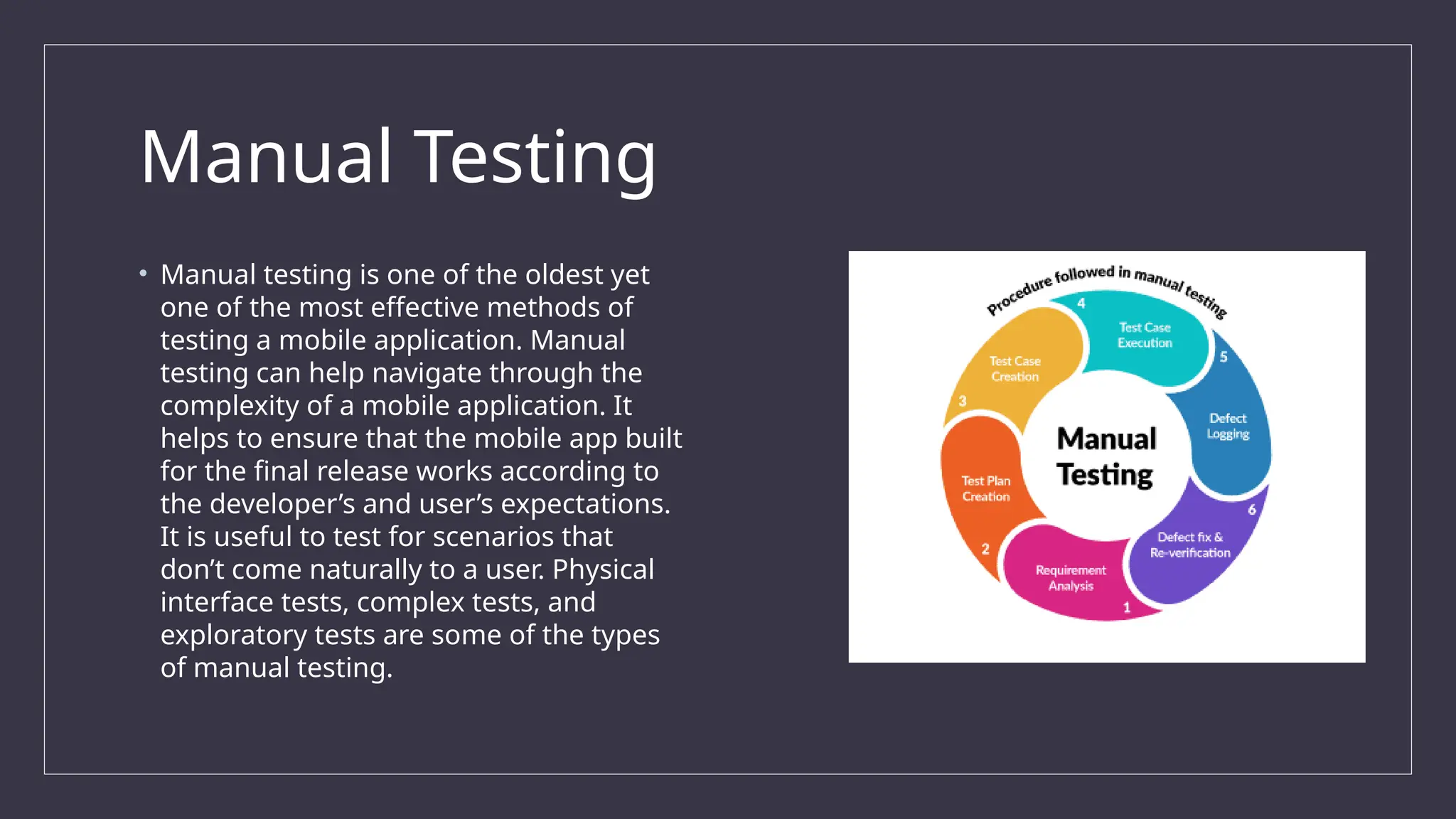
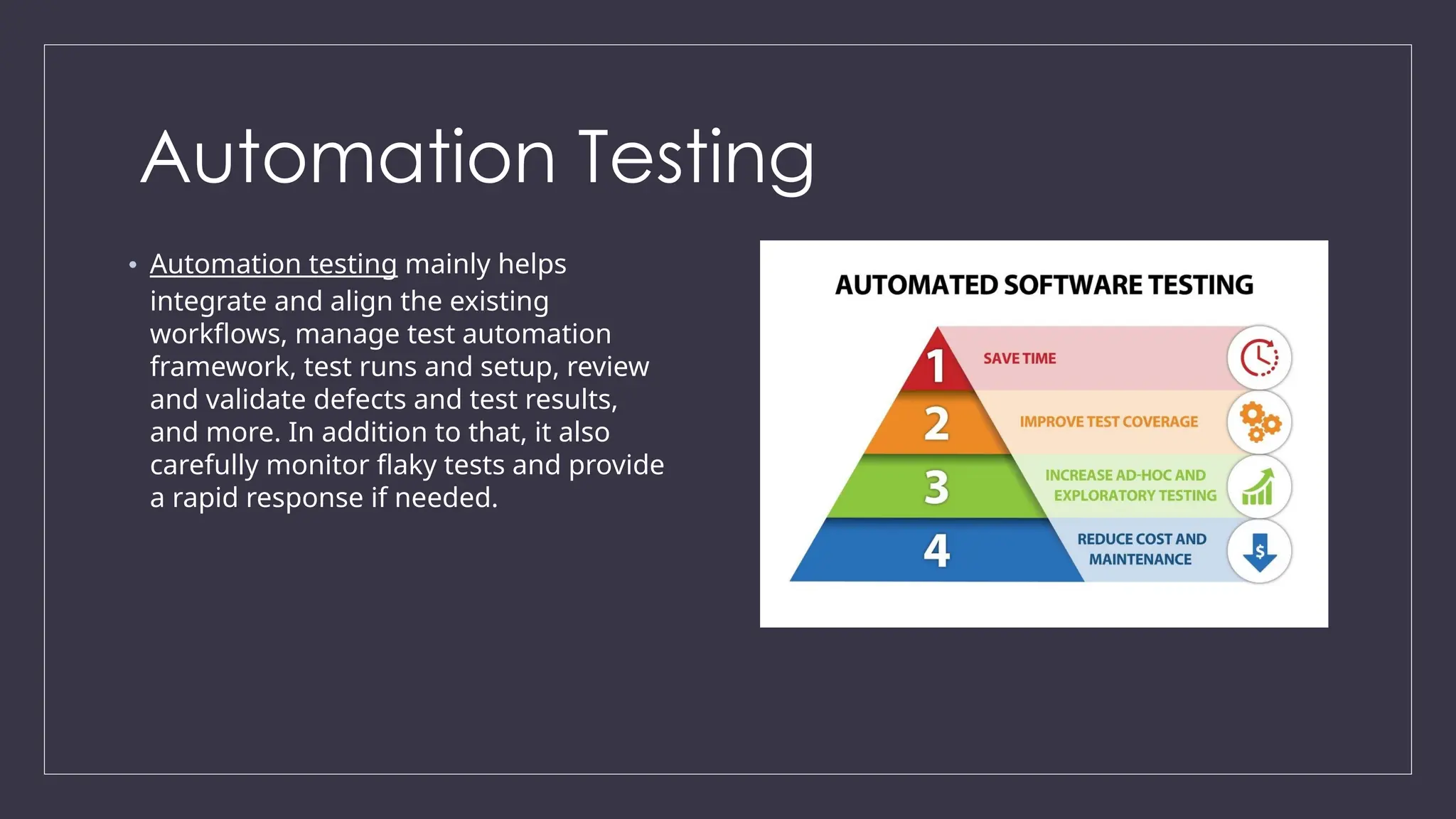
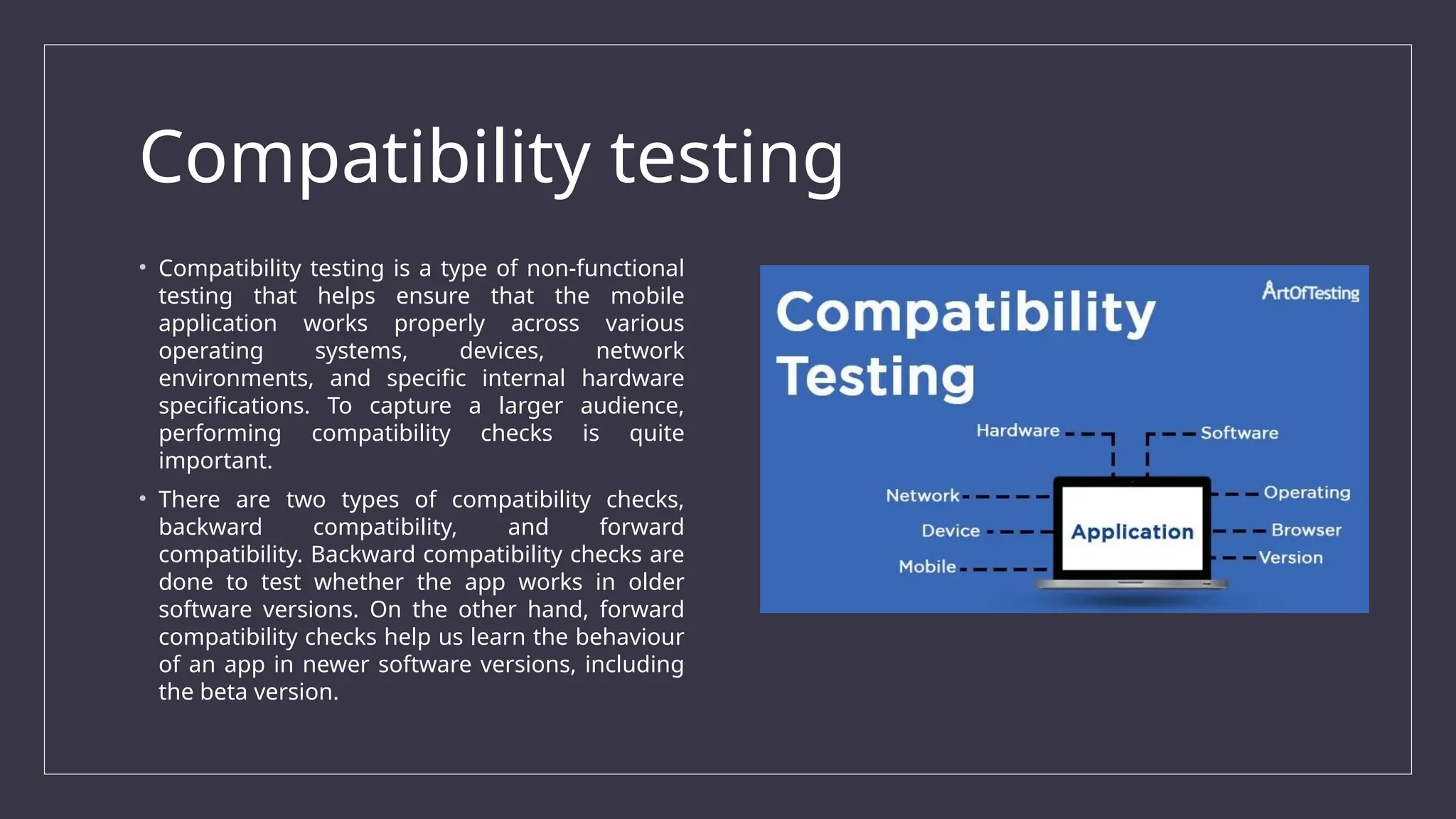
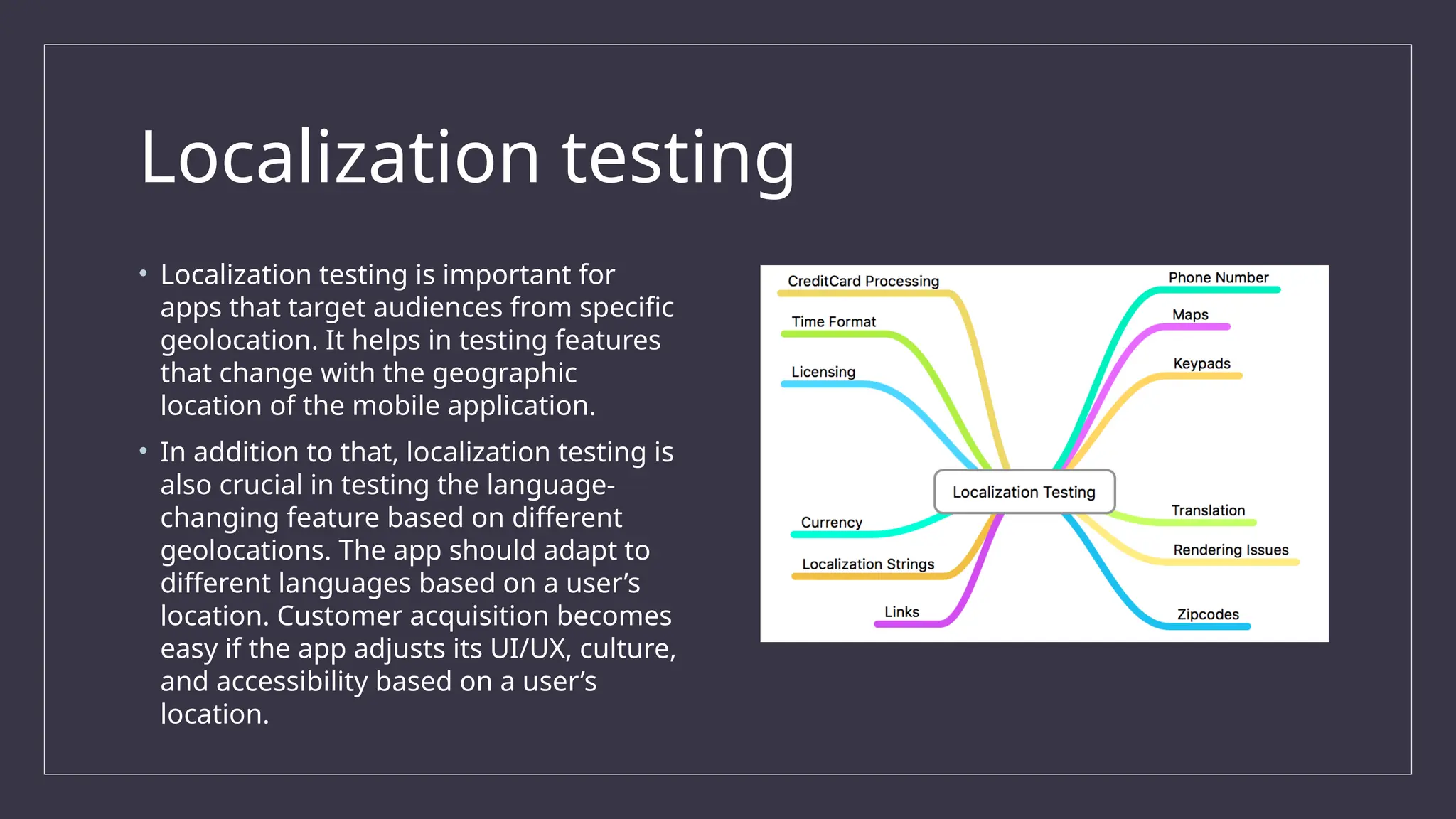
The document outlines the importance and challenges of mobile app testing, which verifies an app's functionality, usability, and performance across various devices and operating systems. It details different types of mobile applications (native, web, hybrid) and testing methods (functional, usability, performance, and more) essential for ensuring a high-quality user experience. The significance of mobile testing is emphasized, given the vast number of smartphone users and the critical need for apps to function correctly to meet user expectations.