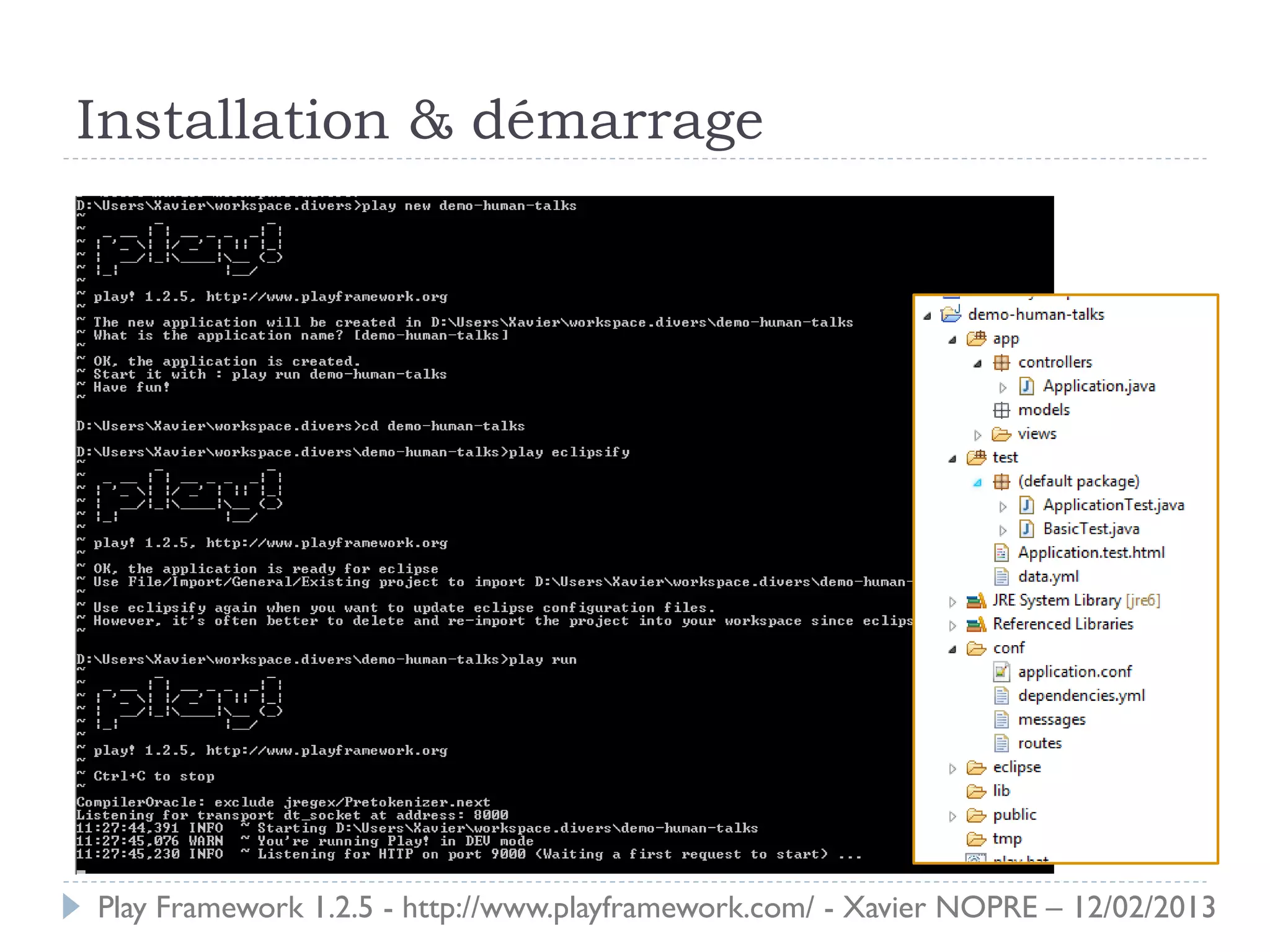
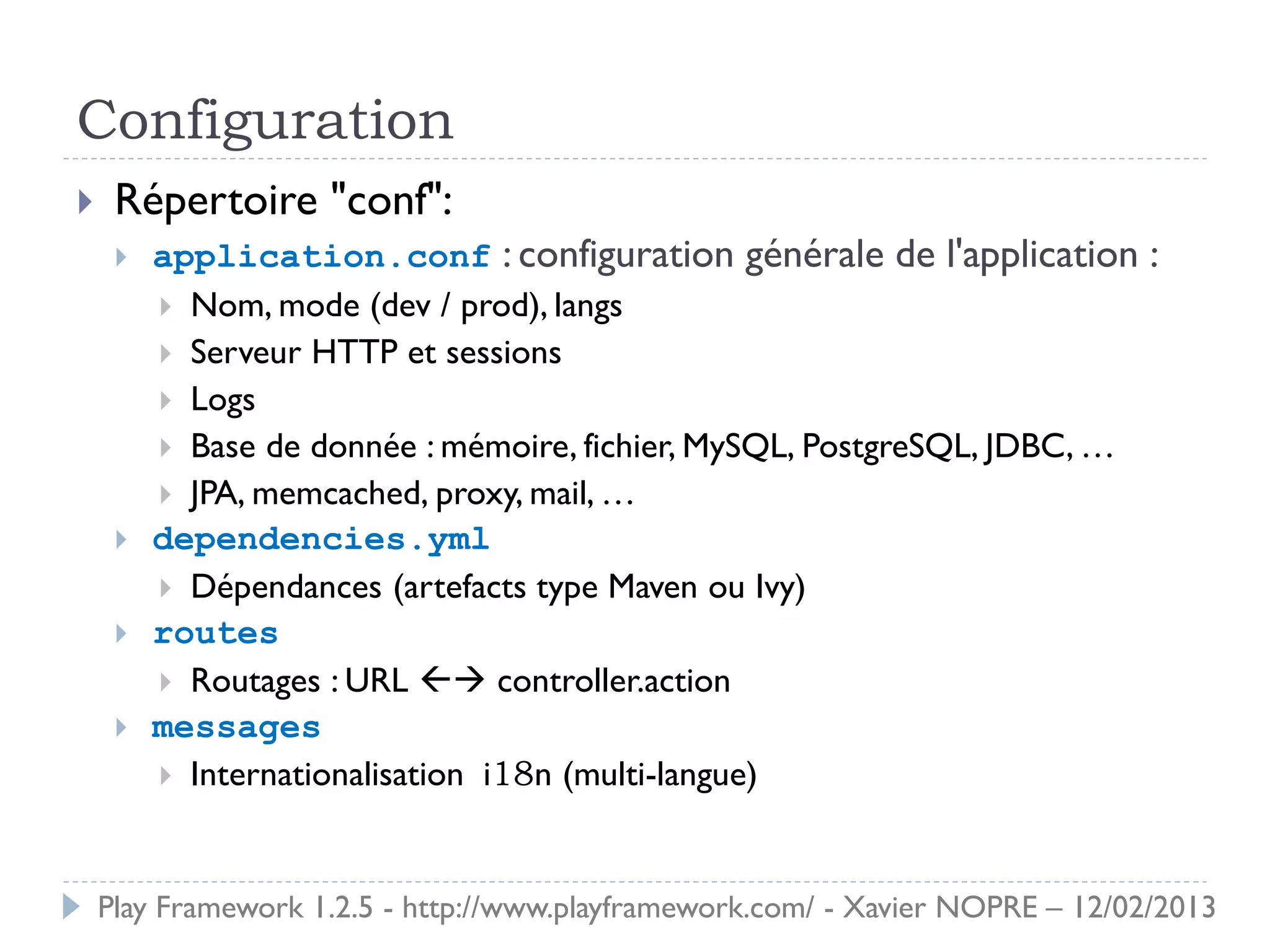
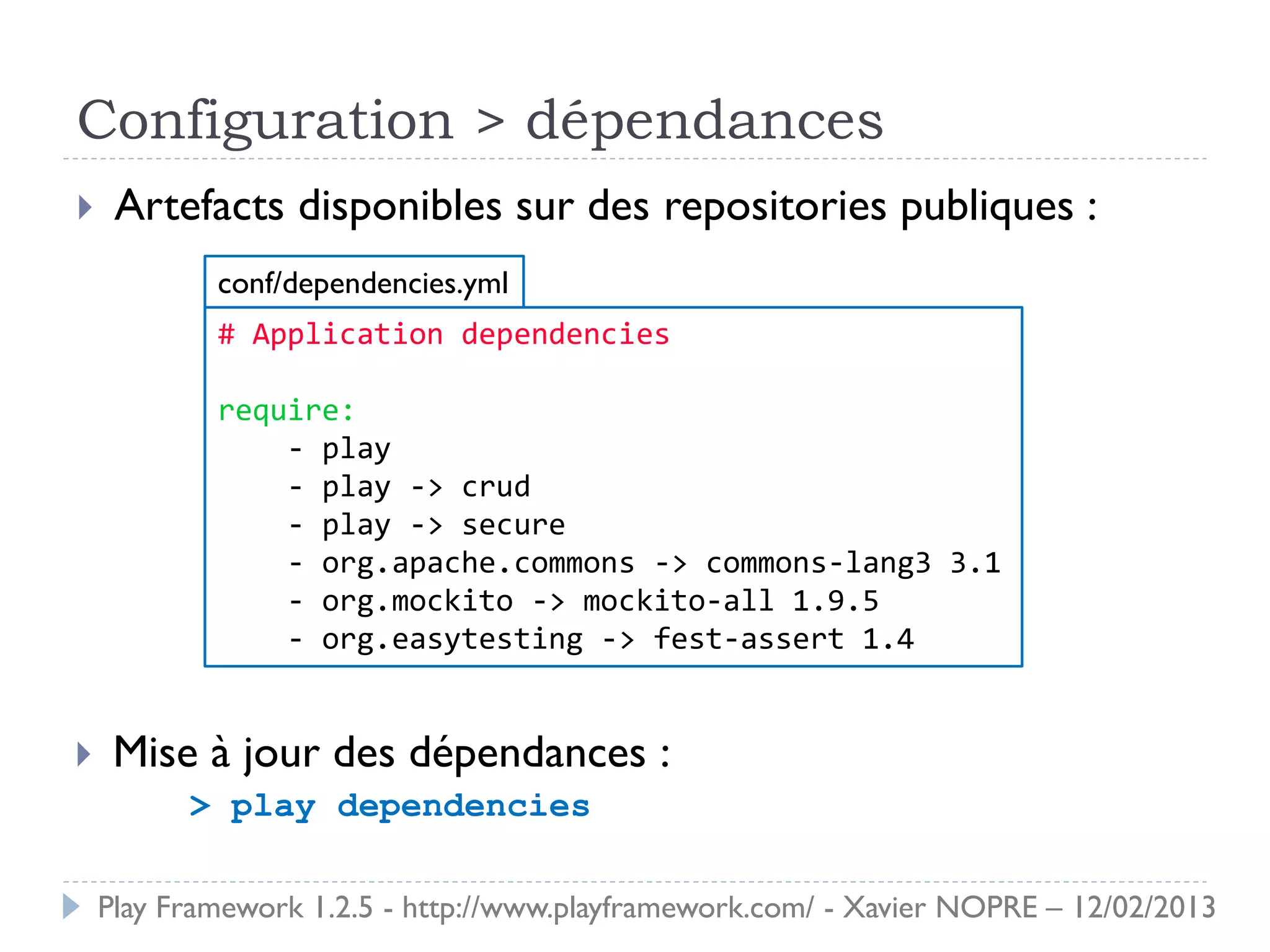
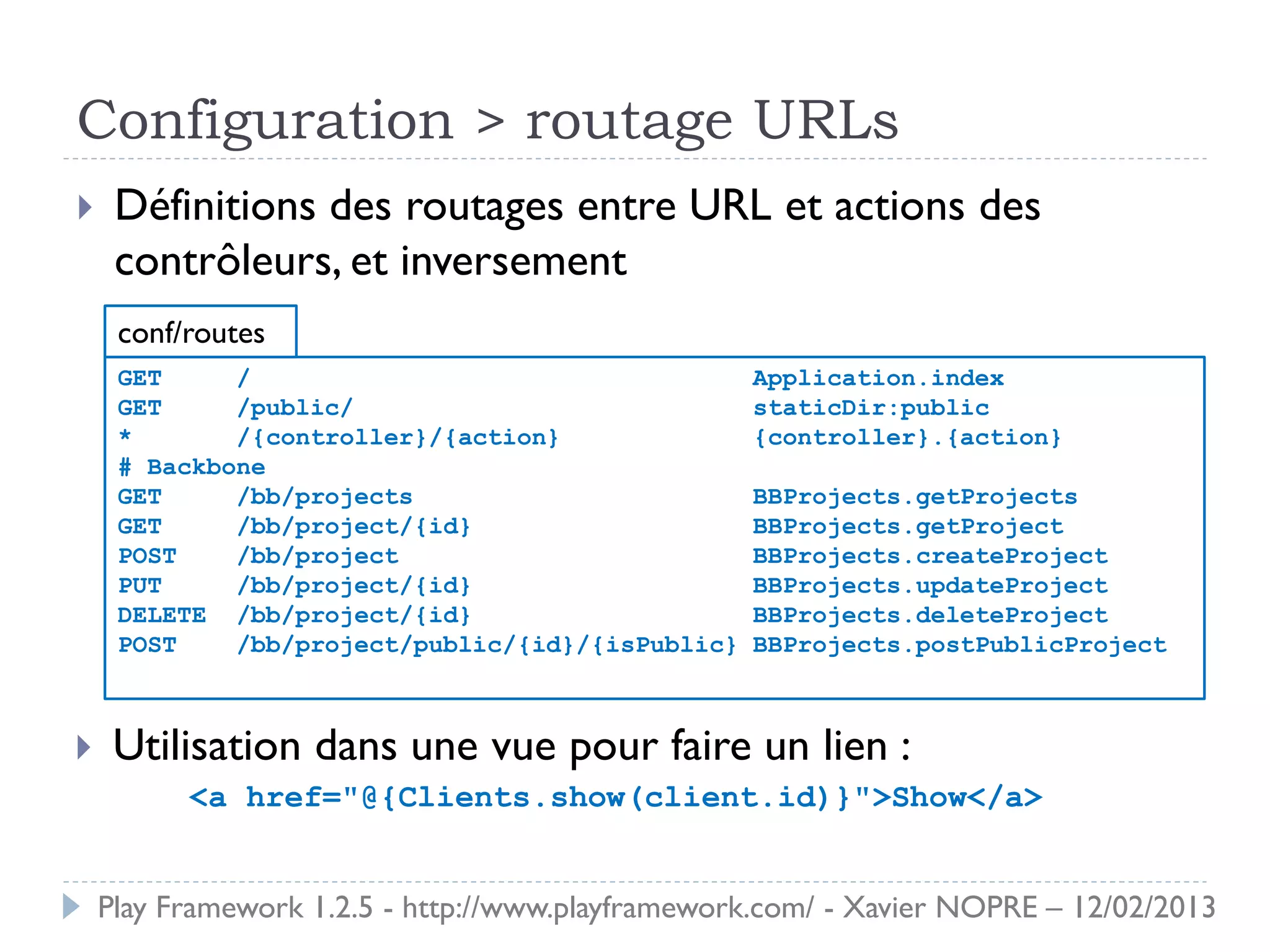
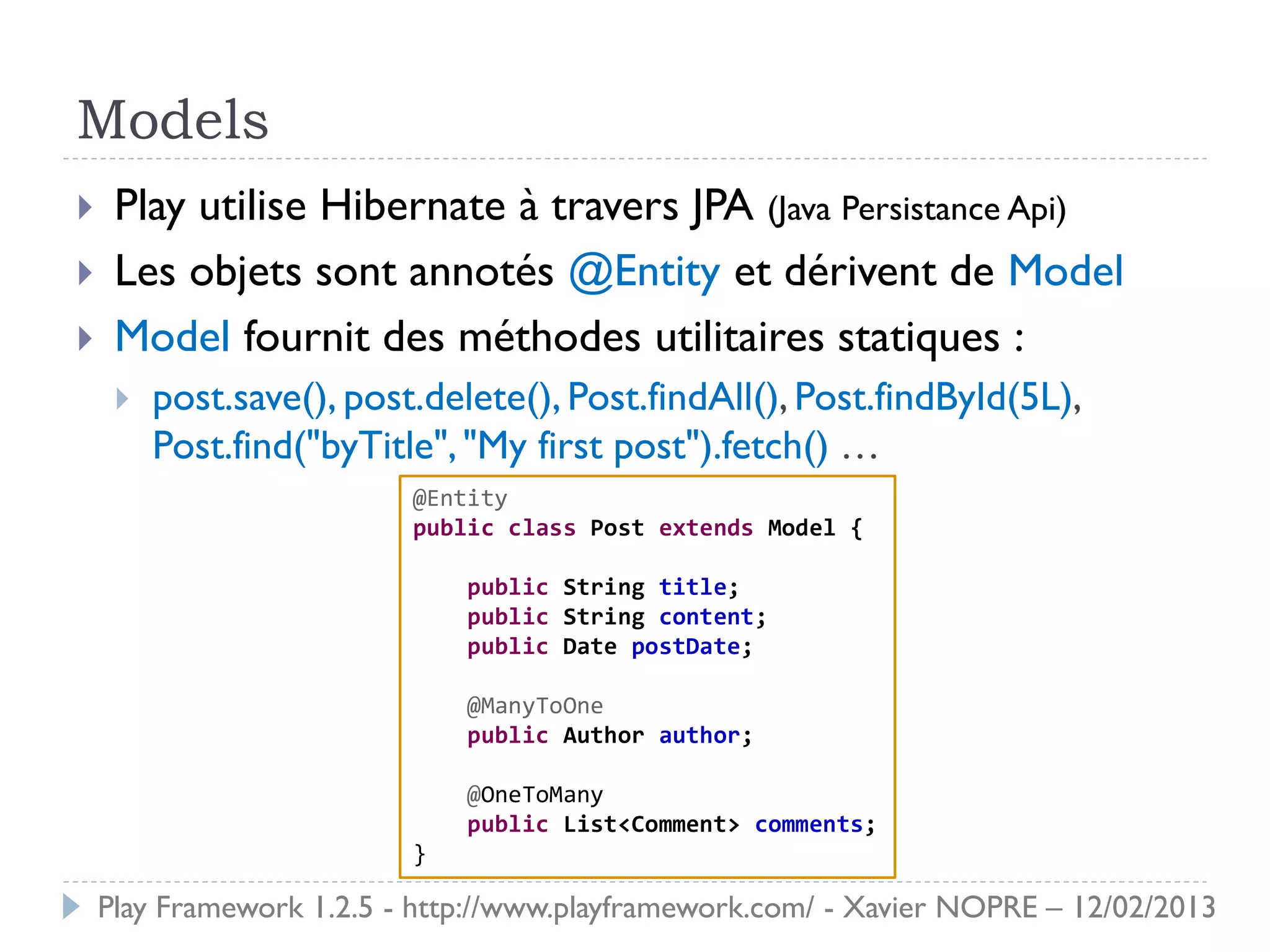
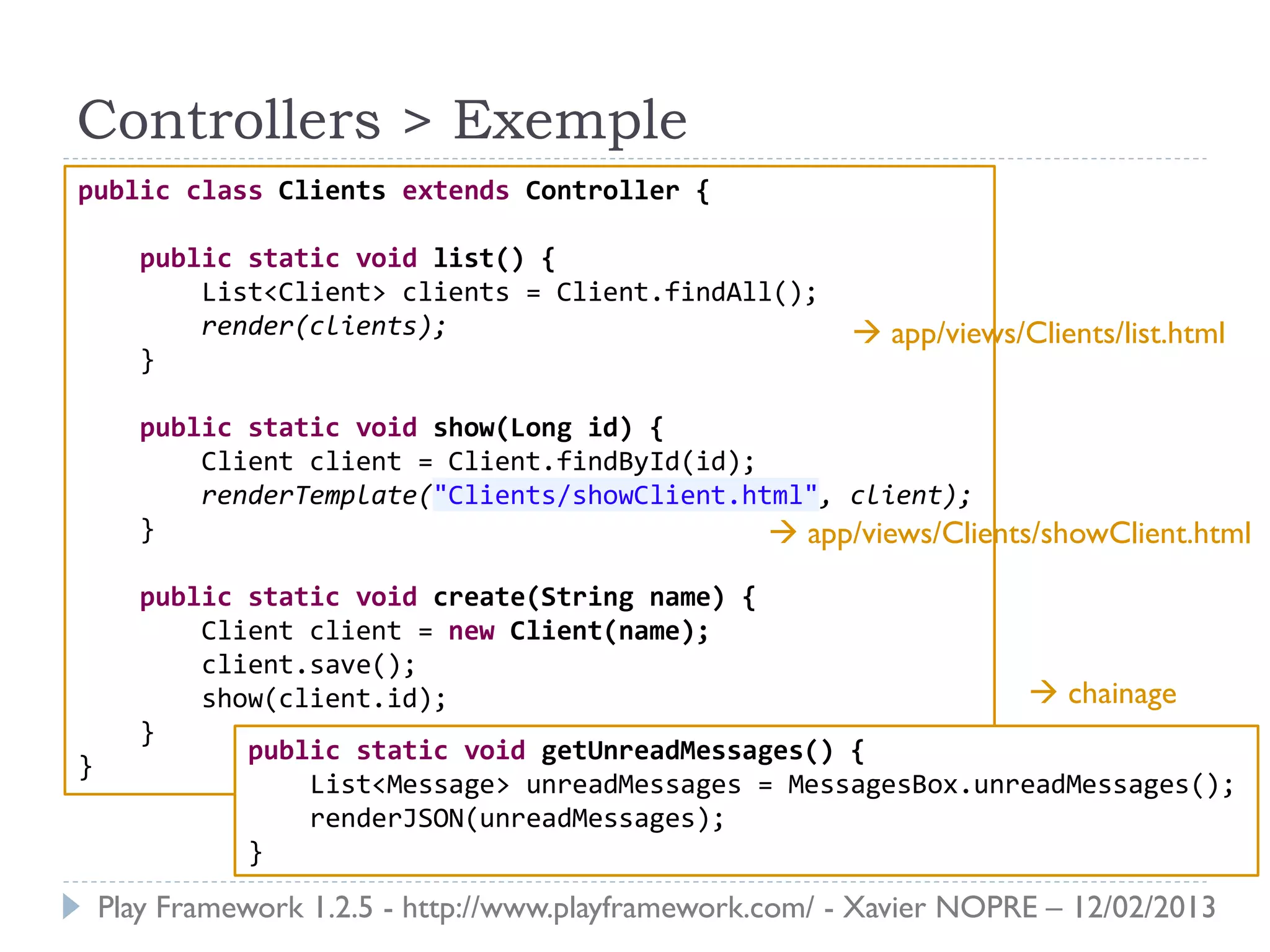
Le document présente le Play Framework v1.2.5, un framework web pour le développement Java qui favorise la simplicité et la productivité grâce à une architecture MVC et des fonctionnalités comme le rechargement à chaud. Il décrit l'installation, la structure des répertoires, la configuration des dépendances et des routages, ainsi que le modèle, les contrôleurs et les vues. En outre, il aborde les tests unitaires, le déploiement et des modules spécifiques pour améliorer le développement web.