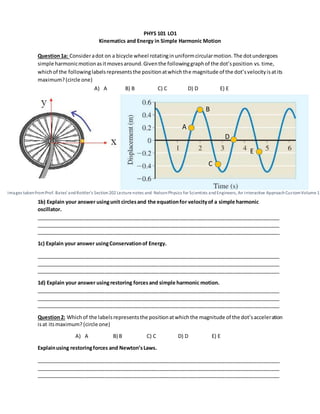
Phys 101 lo1
- 1. Images takenfromProf. Bates’ andRottler’s Section202 Lecture notes and NelsonPhysics for Scientists andEngineers, An Interactive ApproachCustomVolume 1 PHYS 101 LO1 Kinematics and Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion Question1a: Consideradot on a bicycle wheel rotatinginuniformcircularmotion.The dotundergoes simple harmonicmotionasitmovesaround.Giventhe followinggraphof the dot’sposition vs.time, whichof the followinglabelsrepresentsthe positionatwhichthe magnitude of the dot’svelocityisatits maximum?(circle one) A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 1b) Explain your answer usingunit circlesand the equationfor velocityof a simple harmonic oscillator. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 1c) Explain your answer usingConservationof Energy. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 1d) Explain your answer usingrestoring forcesand simple harmonic motion. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Question2: Whichof the labelsrepresentsthe positionatwhichthe magnitude of the dot’sacceleration isat itsmaximum? (circle one) A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E Explainusing restoringforces and Newton’sLaws. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ A B C D E
- 2. Images takenfromProf. Bates’ and Rottler’s Section202 Lecture notes and NelsonPhysics for Scientists andEngineers, An Interactive ApproachCustomVolume 1 PHYS 101 LO1 Kinematics and Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion Question1a: Consideradot on a bicycle wheel rotatinginuniformcircularmotion. Whenviewedon fromabove,the dot can be seen undergoingsimple harmonicmotionasitmovesaround.Giventhe followinggraphof the dot’spositionvs.time,whichof the followinglabelsrepresentsthe positionat whichthe magnitude of the dot’svelocityisatitsmaximum? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E 1b) Explainyour answerusing unit circlesand the equationfor velocityofa simple harmonicoscillator. The velocityof a simple harmonicoscillatorisknowntobe . Asit isa sine function, using the unit circle, we know that the largest value of a sine functionoccurs at 𝜋/2 and 3𝜋/2. Imagining the bike wheel as a unit circle then, its largest velocity is when the dot is at the top or the bottom of the wheel, in other words, when it is at the equilibrium position x=0. 1c) Explain your answer using Conservation of Energy. When the dot is at its maximum displacement (x= +/- 0.5m), it’s in a sense momentarily “not moving”,andall of itsenergyiscontainedaspotential energy.Whenitstartsmovingbackto equilibrium due to the restoring forces on it, its velocity increases and it loses its potential energy as displacement decreases. Once at equilibrium, all its potential energy has been converted into kinetic energy (KE = 1/2mv2 ), so velocity is at its maximum. 1d) Explain your answer using restoring forces and simple harmonic motion. Similarly to the previous explanation, when the dots is at its maximum displacement, it’s like a springthat hasbeenpulledandistemporarilyatrest.The restoringforce onthe dot (F= -kx) pullsitback towards the equilibrium position (the top/bottom of the circle). At equilibrium, its velocity will be at its maximumbefore itgoespastequilibrium againandvelocitydecreasesasthe restoringforce acts against it, tyring to pull it back to equilibrium. Question2: Whichof the labelsrepresentsthe positionatwhichthe magnitude of the dot’sacceleration is at its maximum? A) A B) B C) C D) D E) E A B C D E
- 3. Explain using restoring forces and Newton’s Laws. According to Newton’s Laws, if an object has a net force acting on it, it must be accelerating. In thiscase,we knowthatthere isanetrestoringforce onthe dotinthe formof Hooke’sLaw (F= -kx) sowe knowthat it accelerates andmustfollow the equationF=ma.The restoringforce islargestwhenthe dot has moved its maximum displacement, therefore the acceleration is largest when the dot is at its maximum displacement, or endpoints of its motion.