Indian paper industry-1990-2002-
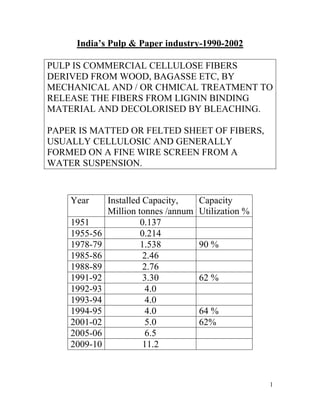
- 1. India’s Pulp & Paper industry-1990-2002 PULP IS COMMERCIAL CELLULOSE FIBERS DERIVED FROM WOOD, BAGASSE ETC, BY MECHANICAL AND / OR CHMICAL TREATMENT TO RELEASE THE FIBERS FROM LIGNIN BINDING MATERIAL AND DECOLORISED BY BLEACHING. PAPER IS MATTED OR FELTED SHEET OF FIBERS, USUALLY CELLULOSIC AND GENERALLY FORMED ON A FINE WIRE SCREEN FROM A WATER SUSPENSION. Year Installed Capacity, Capacity Million tonnes /annum Utilization % 1951 0.137 1955-56 0.214 1978-79 1.538 90 % 1985-86 2.46 1988-89 2.76 1991-92 3.30 62 % 1992-93 4.0 1993-94 4.0 1994-95 4.0 64 % 2001-02 5.0 62% 2005-06 6.5 2009-10 11.2 1
- 2. Pulp and Paper Process The pulp and paper industry converts fibrous raw materials into pulp, paper and paperboard. In a first step, raw materials are processed into pulp and in a second step, paper and paper products are produced out of this pulp. Different plant categories exist depending on whether they only produce pulp (pulp mills) for further processing or only paper out of purchased pulp and /or recycled waste paper (paper mills). The third category, the integrated pulp and paper mills, combines the two processes and is most common in the paper industry. The five principal steps in pulp and paper production are 1) wood preparation, 2) pulping, 3) bleaching, 4) chemical recovery, and 5) papermaking In 1995: Total Number of paper mills in India= 380 Large/medium size mills (>20000 TPA capacity) =21 Small mills = 359 2
- 3. KAGAZ.OM is a vertical portal providing complete information on the paper and allied industries. It intends to be a neutral, online business encyclopedia for the paper industry in India. KAGAZ.COM’s strength lies in its immense data bank. This consequently lays the foundation for a market place wherein buying and selling paper and related products is conducted. Besides this, KAGAZ.COM also aims at providing intrinsic information on paper and its allied industries to the end users. KAGAZ.COM is India's leading and most comprehensive pulp and paper industry portal web site. A pioneer in setting new standards in news and analysis, KAGAZ.COM is promoted by EcoMedia InfoSystems Pvt. Ltd, India's leading independent web solution provider. Users of our services have included the who's who of business ranging from corporates such as Charak Pharmaceuticals, Kores India, Porecha Global Securities, IMP Power, etc. 3
- 4. 1 Wood Preparation Wood preparation involves breaking wood down into small pieces suitable for subsequent pulping operations. Major wood preparation processes are debarking and chipping. This process requires little energy. 2 Pulping Wood is ground and pulped to separate the fibers from each other and to suspend the fibers in water. Pulping breaks apart the wood fibers and cleans them of unwanted residues. The ratio of wood to other materials used for pulp depends on the resources available. The remaining fiber is provided by recycled materials or by non-wood plant sources. Pulping can be performed using chemical, mechanical, or combined chemical-mechanical techniques. In chemical pulping wood chips are cooked in an aqueous solution at high temperature and pressure. Chemical processes dissolve most of the glue that holds the fibers together (lignin) while leaving the cellulose fibers relatively undamaged. This process results in high quality paper with a yield of only 40%-60% of the weight of the 4
- 5. dry wood. The Kraft process, which is the most common, uses a sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide solution. The sulfite process uses a mixture of sulfurous acid and bisulfite iron (typically from sodium sulfite). The most common mechanical pulping technique involves separating the cellulose fibers by pressing logs against wet grindstones or by passing wood chips between counter revolving grooved metal disks (refiners). Lignins and other residues are not removed. This results in a higher yield, but there is more damage to the fibers. In addition, lignin will degrade in time. The lower quality fiber limits the use of this process to less expensive grades of paper, such as newsprint. Combined chemical and mechanical pulping can produce varying grades of paper depending on the particular process used. These processes include thermo-mechanical, chemical thermo -mechanical, and semi-chemical. Large Indian mills that are predominantly based on forest raw materials use the Kraft process. Agro-based mills use a soda process while newsprint mills use mechanical, 5
- 6. chemical, chemi -mechanical and chemi-thermo- mechanical (CTMP) processes. (Mohanty, 1997) 3 Bleaching Bleaching whitens pulps for the manufacture of writing, printing, and decorative papers. The process alters or removes the lignin attached to the wood fiber. Chemical pulps are bleached through the use of alternating treatments of oxidizing agents and alkali solutions. The Kraft process produces a darker pulp that requires more bleaching. Mechanical pulps are treated with hydrogen peroxide or sodium hydrosulfite to reduce the light absorption of the lignin rather than remove it. 4 Chemical Recovery Chemical recovery regenerates the spent chemicals used in Kraft chemical pulping. Chemical pulping produces a waste stream of inorganic chemicals and wood residues known as black liquor. The black liquor is concentrated in evaporators and then incinerated in recovery furnaces, many of which are connected to steam turbine 6
- 7. cogeneration systems. The wood residues provide the fuel and the chemicals are separated as smelt which is then treated to produce sodium hydroxide. Sodium sulfide is also recovered. 5 Papermaking Papermaking consists of preparation, forming, pressing and drying; preparation and drying are the most energy intensive processes. During preparation, the pulp is made more flexible through beating, a mechanical pounding and squeezing process. Pigments, dyes, filler materials, and sizing materials are added at this stage. Forming involves spreading the pulp on a screen. The water is removed by pressing and the paper is left to dry. In one of the most common papermaking processes, the paper is pressed, drained and dried in a continuous process. In another, a pulp matt is formed in layers with water removal and treating occurring between deposits. 7
- 8. Paper- in years - 2000-02 The production of paper and paper board during the year 2001-02 was 3.162 million tonnes. About 60.8 per cent of the total production was based on non- wood raw material and 39.2 per cent based on wood. India’s per capita consumption of paper in 2002 was around 4.00 kg, which was one of the lowest in the world. With the expected increase in literacy rate and growth of the economy, an increase in the per capita consumption of paper is expected. The demand for upstream market of paper products like tissue paper, tea bags, filter paper, light weight online coated paper, medical grade coated paper, etc. , is growing up. These developments are expected to give fillip to the industry. There were (in 2002), about 515 units engaged in the manufacture of paper and paperboards and newsprint in India. The capacity utilization of the industry is low at 62% as about 194 paper mills, particularly small mills, are sick and/or lying closed. Till 1970, the major raw material was wood, based on forests. Since then, agro-residues and waste paper being recycled were used as raw materials for small mills. Newsprint is paper made at a lower cost than white writing paper, as it is not elaborately bleached and finished as writing paper. In 1990-91, newsprint produced in India was 0.3 MT and imported was 0.25MT 8
- 9. India’s per capita consumption of paper in 2002 was around 4.00 kg, which was one of the lowest in the world. In 1990, per capita consumption of paper in India was 3. 0 kg 1990: China = 12 kg USA = 330 kg Japan = 134 kg Australia = 150 kg The Indian paper and paperboards industry is on the growth path. The Indian paper and paperboards industry grew by nearly 7.8 percent during the period 2000-2006. This is substantially higher than the Asian average of 5.1 percent. India’s paper manufacturing capacity is expected to grow at a Compounded Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 7.4 percent from 8.4 million MT per annum to 11.2 million MT per annum between 2008 and 2010. The Indian per capita paper consumption is among the lowest at 7.0 kg, while Asian and global averages are 11.0 kg and 49.0 kg respectively. But the demand for paper is increasing given the rising disposable incomes particularly of the expanding middle income group. 9
- 10. The literacy level in India which is on the increase is further set to improve the demand for paper in the future. The Government of India’s increased budget allocation for education sector is expected to further improve the literacy rates in both urban and rural areas, resulting in increased demand for writing paper. The Indian Pulp and paper industry is expected to grow at 7.4 % CAGR over the period 2008 – 10. With Indian economy in one of its best ever growth mode, the Indian paper industry continues to be a major beneficiary. 10
- 11. Paper Industry Policy - in years – 1991-2002 International Paper Prices Recently, the international prices of pulp have increased from around US$443 per tonne in May 1999 to US$550 per tonne in November 1999. The up trend is expected to continue for another two years and the cycle is currently expected to peak by the end of 2001/ early 2002. The domestic prices of PWP have shown improvement since June 1999 and they are expected to remain firm with demand growth of 6- 7% in next two years without commensurate increase in supply. Growth In Industrial Production / Usage Industries The demand for paperboards is dependent upon growth in usage industries like FMCG, pharmaceuticals, cigarettes etc. Therefore the demand for the fastest growing segment, paperboards can be traced by tracking the growth in these industries. Changes In Import Duty Of Paper With the opening of the economy in 1991, the basic import duty paper and paperboards has come down from a peak of 140% in 1991 to 30% in 1999. This has exposed Indian paper mills to the threat of imports. Any increase in import duty on paper will help the industry in countering the threat from imports 11
- 12. along with increases in price realizations and capacity utilization. Power Tariff Paper manufacturing is an energy intensive process. 10 million kilo calorie of energy are required to produce one ton of paper. The power tariffs, which differ from state to state, have a major impact on the cost of production of paper. Also, the power supply situation in a particular state may become a cause of concern as it will have bearing on production activity of a company, unless the mill has sufficient captive power generation facility. Changes In Import Duty On Wood Pulp And Waste Paper The increase in import duty on wood pulp and waste paper has increased the input cost for many large players as they depend on imports. This has a negative impact on the profitability of the Indian companies as their raw material cost goes up. Any changes in import duty on raw material inputs in the future are bound to have a pronounced impact on operating margins of Indian paper manufacturers. Forest Policy The request by industry to allow use of degraded land for commercial plantation is long pending before the government. Similar schemes in countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil have been carried out 12
- 13. successively and have helped the paper industry to grow to global levels. Therefore, proper policy on this front by GOI will help in boosting the growth of paper industry in the country. Run-up to the Budget 2000-01 Status of the Indian Paper Industry The Indian Paper industry has been passing through a difficult period in recent times. The period from FY 1995 till mid 1999 was particularly tough as imports increased, input costs rose, and the price realization declined. The import duty on paper and paperboard was reduced from 140 per cent in 1990-91 to 20 per cent in 1995-96 leading to sharp increase in imports. The newsprint was put under Open General License in 1994 and since then a large number of independent retailers have been importing newsprint and supplying it to end-users. Currently, the customs duty on Newsprint is 5.5%, and paper manufacturers complain large-scale imports of Light Weight Coated and Kraft paper under the guise of Newsprint. The average capacity utilization of the paper and paperboard industry during 1995-1999 declined to around 67%. But, since mid 1999 some signs of recovery in both the domestic and international markets of paper industry are apparent. The international prices of pulp have increased from around US$443 per tonne in May 1999 to US$550 per 13
- 14. tonne in November 1999. The up trend is expected to continue for another two years and the cycle is currently expected to peak by the end of 2001/ early 2002. The printing and writing paper (PWP) and paperboard prices have been lagging pulp prices but they are expected to move up backed by improvement in fundamentals of Asian region. Asian region accounts for 30 per cent of the global pulp, paper and paperboard consumption. The domestic prices of PWP have shown improvement since June 1999 and they are expected to remain firm with demand growth of 6-7% in next two years without commensurate increase in supply. The demand of industrial paper has also picked but the prices of kraft paper and paperboards have been unable to move up significantly due to increase in supply. Proposals in Union Budget, 1999-2000, affecting the Indian Paper Industry Basic import duty on Paper and Paperboard increased from 30% to 35%. Basic Customs Duty on newsprint rationalized at uniform level of 5%. Basic Customs Duty with ash content exceeding 8% increased from NIL to 5%. No change in concessional Basic Customs Duty of 5% on Light weight coated paper upto 70 gsm imported for printing of magazines by actual users. 14
- 15. Excise duty on Paper and Paperboards reduced from 18% to 16%. Excise duty on cartons and boxes (but not of Corrugated Paper and Paperboards) raised from 13% to 16%. Additional specific duty of Rs. 1/litre on HSD. Restoration of 100 per cent MODVAT credit. Expectations from Union Budget, 2000-01 Increase in total budgetary allocation to education sector. Clarity in definition of newsprint, glazed newsprint and Light weight coated paper to check the clandestine imports of paper. Maintenance of the status quo of customs and excise duty on paper and paperboard and increase in customs duty on newsprint. PAPER INDUSTRY_2000-01: Improved prices augur well for paper units - HBL MUMBAI, JUNE 2. 2001. The paper industry recovered last year[2000-01] after a poor run of about four years and is now back on track. The recovery came more than 18 months ago with improved demand from the government as also for industrial paper from other consumers. 15
- 16. Paper companies had earlier been hit by poor capacity utilisation and poor prices. Prices had reacted significantly while administered input prices had increased leading to pressure on margins. However, with improved realisations and cost cutting measures in place the overall health of the industry improved. There has been some softening of prices by around 20 per cent in the last few months, but still the industry is in good financial shape. As the demand for paper is related to gross domestic product (GDP) growth the industry's growth was hampered by recessionary conditions over the last few years. Consequently, additional capacity created over the last couple of years could not be utilised effectively. Now, it is expected that the increase in demand will lead to a healthy growth in revenues and the rising prices will have a salutary effect on margins. Last year, the mills had done well with prices moving up by 15-16 per cent. At present, prices range from Rs. 35,000 to Rs. 60,000 a tonne with writing paper and map litho occupying the lower end of the spectrum and coated art paper the top end. Packaging paper prices - duplex board and kraft - have not gone up and are hovering around Rs. 15,000-20,000 a tonne. Last year was also good for newsprint and internationally, the U.S. saw a jump in demand. Even in newsprint, there are varieties, ordinary and glazed, the latter being imported. ``In India too, newsprint 16
- 17. prices shot up from around Rs. 16,000 to Rs. 30,000 a tonne before receding to rule around Rs. 27,000 a tonne,'' said Mr. Chandak, executive director, West Coast Paper. Mr. Chandak felt that prices would stay high for the next two years, first because of the cyclical nature of the industry and second, ``there is no import threat and there is no consolidation either.'' As such, consolidation in the industry is unlikely to take place unlike in the global industry where mergers and acquisitions have been common. This is largely due to the fragmented nature of capacity with only a handful of manufacturers having capacity exceeding six lakh tonnes a year. The problems afflicting the industry are mostly price related. Raw material sourcing is one problem and non-pulp inputs are covered by administered pricing. There are entry barriers in the industry - large investments are required and as such no new greenfield projects are planned. Whatever investment is coming in is for upgradation or expansion of existing paper mills. Though there is still some overcapacity it has come down due to rising production and stagnant capacity. The industry size is five million tonnes annually. Of this, 50 per cent constitutes mills using conventional raw materials such as wood and bamboo and the other half use non-conventional raw materials such as 17
- 18. waste paper and agricultural residues. These constitute around 300 mills and they manufacture paper and board. While adequate pulp is not produced in India, international rates had shot up last year from $500 to $850 a tonne. However, they have dropped to around $550 now. The import duty on newsprint and pulp is 5 per cent against the WTO bound rate of 25 per cent. Imports rose steadily from 80,000 tonnes in 1995-96 to 2.70 lakh tonnes in 1998-99 and have remained steady in recent years. Import tariff for various grades of paper is at present 35 per cent against the WTO- bound rate of 40 per cent. Some leading players in the industry: 1. Ballarpur Industries' acquisition of Sinar Mas India for Rs. 530 crores is the latest and a major development in the industry. Sinar Mas is an Indonesian company and entered India about five years ago. The Indian unit has a capacity of 1.15 lakh tonnes and market share in the paper and paper-board segment. After the buyout, the combined capacity will go up to five lakh tonnes and Sinar Mas India has been renamed BILT Graphic Papers. However, the question of sourcing pulp could come up for the company. Earlier, Sinar Mas India could source from its parent in Indonesia. 2. ITC Bhadrachalam Paperboards had expanded capacity from 62,500 tpa to 1.82 lakh tpa. Following 18
- 19. the infusion of around Rs. 150 crores from ITC, the company has carved a niche for itself in the export market for coated paperboards and specialty paper. 3. Tamil Nadu Newsprint (TNPL) boasts of being among the most efficient players in the newsprint industry. In 2000-01, the company reported sales of Rs. 596.40 crores and a net profit of Rs. 76.40 crores. Promoted jointly by the Tamil Nadu Government and IDBI, TNPL manufactures newsprint and printing/writing paper with a capacity of 1.8 lakh tonnes annually. TNPL uses bagasse as the main input. It is now going in for de-bottlenecking to enable capacity increase by around 25 per cent. 4. West Coast Paper Mills (WCPM) has recorded a 88 per cent rise in its net profit at Rs. 28.52 crores in 2000-01 (Rs. 15.20 crores). Sales and income from operations rose 7 per cent to Rs. 351.33 crores (Rs. 328.68 crores). Profits jumped on better realisations coupled with an increase in demand for paper and paper board. ``The industry has emerged from difficult times,'' according to Mr. Chandak ``and there are no foreseeable problems. For the established players, the next two years promise to be good.'' 2010: In the present scenario, apart from capacity augmentation, there is an immense need to improve the Energy Efficiency of the individual units. Many of the Indian Paper mills are also working actively in the 19
- 20. areas of water and environmental management not only to better the statutory norms but also in a proactively move closer to cleaner production. With the liberalization of the Indian economy leading to global competition as well as the growing emphasis on the environment, it is imperative for the Indian Pulp and Paper industry to become World class in operations, energy consumption and environmental impact. 20